Epidemiological characteristics of coal workers' pneumoconiosis during 2006-2015 in Jiangsu Province and trend predicted by the grey dynamics model GM
-
+ English摘要:目的
分析江苏省2006-2015年间煤工尘肺的发病特征及规律, 并对发病趋势进行预测, 进一步加强煤工尘肺的防治和管理。
方法查阅江苏省疾病预防控制中心的统计数据, 对2006-2015年间江苏省煤工尘肺进行人口学特征分析, 再根据灰色系统理论建立灰色数列GM (1.1)预测模型, 预测未来三年江苏省煤工尘肺发病趋势。
结果江苏省2006-2015年间煤工尘肺新发病例1 270例, 2010年新发病例数最多(307例, 占24.2%)。主要接尘年代为1970-1980年间, 接尘工龄为20~30年。多分布在5个工种:纯掘进工、主掘进工、纯采煤工、主采煤工和煤矿混合工。主要分布在5个地区:徐州、南京、无锡、盐城和镇江。发病年龄主要分布在51~60岁。根据灰色数列预测模型得出时间响应方程为$\hat Y$(t+1)=-241.629 45 e-0.223 53 t+295.629 45, 预测2016-2018年间江苏省煤工尘肺新发病例数分别为20例、16例、13例。
结论江苏省未来三年内煤工尘肺的发病趋势可能呈现下降态势, 但是发病形势依然严峻, 需进一步加强管理。
-
随着我国城市化、工业化迅速发展,许多职业卫生问题不断出现。职业性有害因素分布广泛,职业危害转嫁问题严重,职业病防治形势严峻。煤工尘肺作为一种常见的由生产性粉尘引起的职业性疾病,已经成为职业卫生领域乃至社会关注的焦点。职业病分析和预测是职业病预防控制的重要基础[1]。为了进一步研究煤工尘肺发病规律以及预测未来若干年内的发病趋势,进一步加强其防治和管理,本文拟利用灰色数列预测模型GM(1.1)对江苏省2006—2015年间报告的1 270例煤工尘肺进行统计分析,并对今后几年间的发病趋势进行模型预测,现将结果报告如下。
1. 资料与方法
1.1 资料来源
2006—2015年江苏省疾病预防控制中心统计的江苏省各地区报告的各期煤工尘肺病共1 270例,其中2011—2015年间确诊的新发病例数为195例,资料完整可靠。
1.2 方法
1.2.1 调查方法
通过查询“中国疾病预防控制中心信息系统”中的“健康危害因素信息监测系统”,获取2006—2015年江苏省煤工尘肺发病数据。对2006—2015年间江苏省煤工尘肺进行病例特征分析,分析其人口学特征,对其发病趋势进行预测。
1.2.2 统计学分析
1)病例特征分析。数据审核后录入Excel 2010软件,采用SPSS 15.0软件对数据进行统计学处理。计数资料以均值±标准差(x ± s)表示,计量资料以率表示[2]。
2)灰色预测法运用。根据2006—2015年江苏省历年的新发病例数,本次研究选择煤工尘肺病例数增减幅度较为平稳的2011—2015年的煤工尘肺病的发病资料作为时间数列数据。
设2011—2015年5年间煤工尘肺病例数灰色数列为:X = [X(t1)]、[X(t2)]、[X(t3)]、[X(t4)]、[X(t5)]。依据赵定义在《灰色数列预测模型在医学中的应用》中的方法[3],利用Excel 2010软件求出一次累加生成数据,又有累加数据的估计值方程(时间响应方程):${\hat Y_{\left( {t + 1} \right)}} = \left( {{X_1} - \frac{\mu }{\alpha }} \right){{\rm{e}}^{{\rm{ - \mathsf{ α} t}}}} + \frac{\mu }{\alpha }$。再利用累加生成数据构造特征矩阵,使用矩阵计算器求解参数μ、α(μ为发展系数、α为灰色作用量)的值。再将μ、α的值代入方程得出${\hat Y_{\left( {t + 1} \right)}}$的预测模型,再依据${\hat Y_{\left( {t + 1} \right)}}$还原$\hat X$方法:${{\hat X}_t} = {{\hat Y}_t} - {{\hat Y}_{(t - 1)}}$得出估计值[4]。最后利用后验差检验方法检验预测精度等级:当检验指标小误差概率P > 0.9、后验差比值C < 0.35时,等级为优;P > 0.8、C < 0.50,等级为良;P > 0.7、C < 0.65,等级为中;P≤0.7、C≥ 0.65,等级为差[5]。
1.2.3 质量控制
本次研究数据均由各市疾病预防控制中心上报所得,数据统计处理时经双人录入核对,确保数据准确。
2. 结果
2.1 焊工尘肺发病基本情况
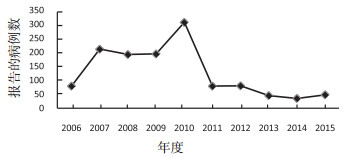
2006—2015年间江苏省煤工尘肺病例数分别为79(占6.2%)、211(占16.6%)、192(占15.1%)、194(占15.3%)、307(占24.2%)、79(占6.2%)、80(占6.3%)、45(占3.5%)、35(占2.8%)、48(占3.8%),共1 270例,其中2010年新发病例数最多。见图 1。由于煤矿工业等接触生产性粉尘的职业都属于重体力工作,女性人数极少,本次研究对象并无女性病例。
2.2 煤工尘肺主要地区分布
2006—2015年江苏省煤工尘肺发病地区主要分布于徐州、南京、无锡、盐城和镇江。徐州地区新发病例数最多,为735例,占57.9%,显著高于江苏省其他地区。其余按发病例数依次为无锡(205例,占16.1%)、南京(106例,占8.3%)、镇江(96例,占7.6%)、盐城(70例,占5.5%)和其他地区(58例,占4.5%)。
2.3 煤工尘肺病发病年龄分布
将病例发病年龄以10年为间隔进行统计,2006—2015年江苏省煤工尘肺主要发病年龄分布在51 ~ 60岁,共428例,占33.70%。其余年龄段分别为:30 ~ 40岁53例(占4.17%),41 ~ 50岁317例(占24.96%),61 ~ 70岁255例(占20.08%),70岁以上217例(占17.09%)。
2.4 煤工尘肺接尘工龄
1 270例病例主要接尘年代为20世纪70—80年代,共有528例,占41.6 %。所有新发病例中接尘工龄多在21 ~ 30年间,共有561例,占44.2%。工龄≤ 10年、11 ~ 20年、21 ~ 30年、30年以上者分别为131例(占10.3 %)、269例(21.2%)、561例(44.2%)、309例(24.3%)。见表 1。
表 1 病例在不同接尘年代及接尘工龄间的分布(例) 开始接尘时间 工龄/年 ≤10 11 ~ 21 ~ 31 ~ 总计 构成比/% 1940—1949年 0 3 7 23 33 2.6 1950—1959年 13 31 92 78 214 16.9 1960—1969年 6 47 77 47 177 13.9 1970—1979年 47 124 202 155 528 41.6 1980—1989年 15 42 179 6 242 19.1 1990—1999年 34 21 4 0 59 4.6 2000—2010年 16 1 0 0 17 1.3 合计 131 269 561 309 1 270 100 2.5 主要工种分布
2006—2015年江苏省煤工尘肺新发病例以煤矿混合工为主(648例,占51.0%),其余依次是主采煤工(194例,占15.3%)、主掘进工(162例,占12.8%)、纯采煤工(52例,占4.1%)、纯掘进工(37例,占2.9%);其他工种177例,占13.9%。
2.6 预测
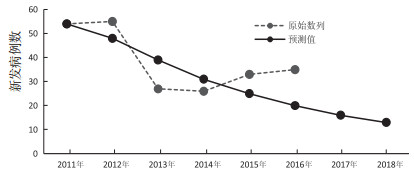
煤工尘肺是一种慢性职业病,从接触生产性粉尘到发病的时间较长,影响的因素很多,想要准确地预测煤工尘肺的发病趋势较为困难[1]。本次研究通过灰色理论的数据处理方法,先整理原始灰色数据,将2011—2015年的发病例数54、55、27、26、33设为原始数列,再分别得出各累加生成数据。见表 2。
表 2 累加生成数据和均值生成数据原始与生成数据 2011年 2012年 2013年 2014年 2015年 Xt(原始数列) 54 55 27 26 33 Y(t)((—次累加数列) 109 136 162 195 Zt(—次累加均值) 81.5 122.5 149.0 178.5 Zt2—次累加均值平方) 6 642.25 15 006.25 22 201.00 31 862.25 Xt×Zt(累加均值与原始数列之积) 4 482.5 3 307.5 3 874.0 5 890.5 通过计算得出α = 0.223 53,μ= 66.082 05。故预测模型(时间响应方程)如下:
$$ \begin{array}{l} \;\;\;{{\hat Y}_{(t + 1)}} = \left( {{X_1} - \frac{\mu }{\alpha }} \right){{\rm{e}}^{ - \alpha t}} + \frac{\mu }{\alpha } = - 241.62945{{\rm{e}}^{ - 02353t}}\\ + {295.62945^{\left[ 6 \right]}} \end{array} $$ 再还原估计值结果见表 3、图 2。用后验差检验法对该预测模型进行精度检验,后验差比值C = 0.30,小误差频率P > 0.95,表明该预测模型的预测精度较好。利用这个模型,对江苏省未来三年煤工尘肺新发病例的预测结果为:2016—2018年间江苏省煤工尘肺病各年的新发病例数为20例、16例、13例。表明江苏省未来三年煤工尘肺病的新发病例数可能呈现下降趋势。
表 3 煤工尘肺发病例数的预测值与实际值比较原始与生成数据 2011年 2012年 2013年 2014年 2015年 2016年 2017年 2018年 ${\hat Y}$(—次累加预测值) 54 102 141 172 197 216 232 245 ${\hat X}$(原始数列预测值) 54 48 39 31 25 20 16 13 Xt(原始数列) 54 55 27 26 33 35 |Xt-${\hat X}$|(两者差绝对值) 0 7 12 5 8 15 3. 讨论
煤工尘肺是尘肺病中最为严重的一种[7]。目前,其无特殊的治疗方法,关键在于预防。本研究希望通过研究2006—2015年江苏省煤工尘肺发病特征及趋势,为江苏省煤工尘肺防治工作提供参考依据。
本次调查发现江苏省煤工尘肺的发病年龄多在51 ~ 60岁之间,占33.7 %,提示防治工作者对于年龄在51 ~ 60岁之间的曾有生产性粉尘接触史的职业工人应该进行重点职业病健康体检工作,尽量做到早发现、早诊断、早治疗。
从发病地区分布来看,江苏省煤工尘肺的重点防治地区应是徐州、南京、无锡、盐城和镇江地区,2006—2015年间徐州地区共新发煤工尘肺735例,位于江苏省首位。这与徐州地区是江苏省重要的重工业区有关。江苏省有关政府部门应重视徐州地区煤工尘肺的防治工作,建立健全并完善煤工尘肺防治体系。
煤矿尘肺的发生受多种因素的影响,不同的作业环境、不同的煤田地质条件下,尘肺病的患病情况不同。本次研究结果显示在工种方面,煤矿混合工的患者最多,其他工种依次为主采煤工、主掘进工、纯掘进工、纯采煤工,显然尘肺病防治工作的重点人群是混合工[2]。
灰色预测法是一种对含有不确定因素的系统进行预测的方法[8]。灰色预测通过鉴别系统因素之间发展趋势的相异程度,即进行关联分析,并对原始数据进行生成处理来寻找系统变动的规律,生成有较强规律性的数据序列,然后建立相应的微分方程模型,从而预测事物未来发展趋势的状况[9]。GM(1,1)模型是常用的灰色模型之一,它是由一个包含单变量的一阶微分方程构成的模型,通过简单的累加生成模块,使上下波动的时间序列转变为单调上升的线性或指数律的序列[10]。当原始数据序列符合或基本符合指数规律变化,且变化速度不是很快时,应用该预测模型有可能得到较好的预测结果。GM(1,1)的建模步骤主要包括:1)由原始数据序列生成一次累加序列;2)建立矩阵;3)计算逆矩阵;4)根据逆矩阵求估计参数;5)根据时间响应方程计算拟合值,再用后减运算还原需要估计的值;6)对精度进行检验和预测。以往研究表明,用灰色数列预测模型对概率分布并不呈典型分布的尘肺发病趋势进行预测是合理的[11]。
此次调查发现,2006—2010年江苏省煤工尘肺的新发病人数呈现上升态势,截至2010年到达峰值。经过灰色数列预测模型得出在2011年后江苏省煤工尘肺的发病呈现下降趋势。该灰色数列预测模型的C = 0.30、P > 0.95,预测精度较好。本次研究表明20世纪70—80年代接尘工人新发病例数最多,此后新发病数呈下降态势,而接尘工龄在21 ~ 30年间最多。以上结果与江苏省煤工尘肺在2006—2010年煤工尘肺发病人数呈上升态势,而在2011年后呈下降态势相吻合。我国在1987年颁布并实施了《中华人民共和国尘肺病防治条例》[12],政府更加重视尘肺病的防治工作,这与在20世纪80年代后发病人数减少相互吻合,符合客观规律。
虽然本次研究预测显示在未来三年间江苏省煤工尘肺发病呈现下降趋势,但是总体形势依然严峻。如何做好工尘肺发病重点地区的防治工作仍是一项艰巨的任务。
-
表 1 病例在不同接尘年代及接尘工龄间的分布
(例) 开始接尘时间 工龄/年 ≤10 11 ~ 21 ~ 31 ~ 总计 构成比/% 1940—1949年 0 3 7 23 33 2.6 1950—1959年 13 31 92 78 214 16.9 1960—1969年 6 47 77 47 177 13.9 1970—1979年 47 124 202 155 528 41.6 1980—1989年 15 42 179 6 242 19.1 1990—1999年 34 21 4 0 59 4.6 2000—2010年 16 1 0 0 17 1.3 合计 131 269 561 309 1 270 100 表 2 累加生成数据和均值生成数据
原始与生成数据 2011年 2012年 2013年 2014年 2015年 Xt(原始数列) 54 55 27 26 33 Y(t)((—次累加数列) 109 136 162 195 Zt(—次累加均值) 81.5 122.5 149.0 178.5 Zt2—次累加均值平方) 6 642.25 15 006.25 22 201.00 31 862.25 Xt×Zt(累加均值与原始数列之积) 4 482.5 3 307.5 3 874.0 5 890.5 表 3 煤工尘肺发病例数的预测值与实际值比较
原始与生成数据 2011年 2012年 2013年 2014年 2015年 2016年 2017年 2018年 ${\hat Y}$(—次累加预测值) 54 102 141 172 197 216 232 245 ${\hat X}$(原始数列预测值) 54 48 39 31 25 20 16 13 Xt(原始数列) 54 55 27 26 33 35 |Xt-${\hat X}$|(两者差绝对值) 0 7 12 5 8 15 -
[1] 杨海兵, 杨磊, 褚启龙, 等.某煤矿企业尘肺发病特征分析与预测[J].卫生研究, 2004, 33(6):722-724. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8020.2004.06.024 [2] 蒋胜兰, 臧永志, 蒋宇.煤矿煤工尘肺发病特征及防控措施的探讨[J].中外医学研究, 2016, 14(12):152-153. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/zglyyx201501056 [3] 赵定义.灰色数列预测模型在医学中的应用[J].中国卫生统计, 1988, 5(1):5. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-ZGWT198801002.htm [4] 孙冬.基于灰色系统模型的城乡建设用地规模预测——以济南市为例[J].国土与自然资源研究, 2014(4):28-29. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-7853.2014.04.010 [5] 徐文娟, 李勇, 李娜, 等.基于灰色预测对我国心血管疾病的研究[J].高师理科学刊, 2017, 37(6):12-16. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-9831.2017.06.004 [6] 马兰, 陈彦龙.应用数列模型对煤矿尘肺发病趋势的预测[J].南通医学院学报, 2003, 23(3):282-283. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-7887.2003.03.020 [7] 程秀英.白山市2010-2012年煤工尘肺哨点监测结果分析[J].中国卫生工程学, 2016, 15(4):394-395, 398. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zgwsgcx201604028 [8] 李亚东, 龚志起, 陈柏昆.基于灰色理论的西宁市建筑垃圾产量预测研究[J].青海大学学报, 2017, 35(3):82-87. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=QKC20172017062800193729 [9] 董鲁祺, 舒麟棹.基于指数平滑法和GM(1, 1)模型的公路客运量预测方法[J].科技展望, 2017, 27(26):314. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-8289.2017.26.275 [10] 施久玉, 胡程鹏.股票投资中一种新的技术分析方法[J].哈尔滨工程大学学报, 2004, 25(5):680-684. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-7043.2004.05.031 [11] 杨永利, 刘宏志, 孙世奎, 等.灰色系统GM(1, 1)模型对大隆矿煤工尘肺发病趋势的预测[J].职业与健康, 2007, 27(18):1581-1583. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-1257.2007.18.001 [12] 中华人民共和国国务院.中华人民共和国尘肺病防治条例[A]. 1987-12-03. -
期刊类型引用(5)
1. 徐世斌,王小皙,张毅,张华东. 2018-2020年重庆市永川区新发尘肺病流行病学分析. 职业卫生与病伤. 2022(06): 328-331 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 张毓媛,张延松,刘博. 3种模型在煤工尘肺病预测中的比较研究. 工业卫生与职业病. 2020(02): 94-97 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 梁伟,聂继盛. 同煤总医院煤工尘肺并发肺癌病例的危险因素、临床表现和CT征象. 职业与健康. 2020(17): 2321-2325 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 徐衍,朱为梅,赵红宇,殷丽娇,徐安彪. 某三甲综合医院2013年-2017年职业性尘肺住院患者分析. 中国病案. 2019(02): 51-53 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 谭聪,田娇. 2007—2017年益阳市职业病发病情况. 职业与健康. 2018(19): 2628-2631 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(4)





 下载:
下载: