Comparison between two methods for assessment of occupational health risk caused by coal dust
-
+ English摘要:目的
通过大样本比较国际采矿与金属委员会定量评估法和职业危害风险指数法在煤矿煤尘职业健康风险评估中的应用效果。
方法选取11座煤矿6个生产系统的煤尘作业岗位作为评估对象,通过两种风险评估方法分别对196个岗位进行评估,分析两种方法评估结果的差异与相关性。
结果两种方法的评估结果呈较好的正相关性(r = 0.611,P < 0.05),最高风险级别的作业岗位主要聚集在煤炭开采企业的采煤、掘进生产系统。两种方法评估结果相近岗位多为风险等级较低的岗位,在风险等级较高岗位的评估结果中存在较大分歧。
结论国际采矿与金属委员会定量评估法可较好地反映工作环境中煤尘的暴露风险水平,职业危害风险指数法更能反映出劳动者在得到防护设施保护后实际接触的风险水平。
-
职业健康风险评估是一种评估因暴露于各种职业病危害因素而导致的健康风险的方法,该方法能依据风险等级,提出行动策略,决定控制和管理的优先顺序[1-2]。目前,美国、新加坡等发达国家已建立较为完善的职业健康风险评估方法与体系,我国卫生部门也将职业健康风险评估作为重要的职业卫生工作之一[3-4]。研究表明,职业危害风险指数法、国际采矿与金属委员会职业健康风险评估法、定量分级法等多种方法适用于煤尘的职业健康风险评估,但在大样本的基础上比较各方法评估结果异同的研究[4-5]较少。煤矿是煤尘职业危害最严重的企业,本次研究拟使用国际采矿与金属委员会定量评估法和职业危害风险指数法分别对多个煤矿主要煤尘作业岗位的职业健康风险进行评估,通过大样本探索两种评估方法结果的差异,探讨其评估煤矿煤尘职业健康风险的适用性。
1. 对象与方法
1.1 对象
选取11座煤矿作为调查对象,其中9座为山西省同一煤矿集团的9个大型煤矿,其余2座分别为陕西省的大、中型煤矿。
1.2 方法
1.2.1 职业卫生调查
于2015年3月至2016年1月,对调查对象的生产制度、生产工艺、煤尘作业岗位、工作场所煤尘游离二氧化硅含量和煤尘浓度、工程防护措施(防尘设施)情况、个体防护措施(个人使用的职业病防护用品)情况和职业卫生管理等情况进行调查。
1.2.2 煤尘风险评估方法
选择国际采矿与金属委员会(International Council on Mining and Metals,ICMM)职业健康风险评估方法中的定量评估法(简称ICMM法)和职业危害风险指数法(简称指数法)分别对调查对象的同一岗位进行煤尘风险评估。
(1)ICMM法[6-7]:结合煤尘职业病危害特点,通过健康危害后果、暴露概率、暴露时间、不确定性等四个因素进行定量评估。评估公式为:RR = C × PrE × PeE × U,式中RR为风险等级;C为健康危害后果,煤尘可导致上呼吸道炎症、煤尘相关弥散性纤维化及煤工尘肺等健康结局[8-9],本次研究将壹期煤工尘肺确定为煤尘健康风险评估的健康危害后果,赋值为15[10];PrE为暴露概率,即超过煤尘呼吸性粉尘职业接触限值的可能性,根据煤尘场所暴露浓度和各岗位的工作内容赋值,可能性非常小赋值为0.5,可能性很小(在工作场所某一处有较小概率发生)赋值为1,不经常但可能会发生赋值为3,会间断地发生赋值为6,暴露浓度持续超过煤尘呼吸性粉尘职业接触限值赋值为10;PeE为暴露时间,根据接触频次与时间赋值,每年1次赋值为0.5,每年几次赋值为1,每月几次赋值为2,每个班次连续暴露1 ~ 2 h赋值为3,每个班次连续暴露2 ~ 6 h赋值为6,每个班次连续暴露7 ~ 8 h赋值为10;U为不确定性,根据危害风险和暴露评估的不确定性赋值,确定赋值1,不确定赋值2,非常不确定赋值3。ICMM法风险评估结果共有5个等级,依次为可容忍的风险(1级)、潜在的风险(2级)、高风险(3级)、非常高的风险(4级)、不可容忍的风险(5级)。
(2)指数法[11]:依据安全风险评估原理,综合考虑工作场所中煤尘对健康影响的严重性、危害的可能性以及工作场所中的作业环境条件进行评估。评估公式为:职业危害风险指数= 2 健康效应等级 × 2 暴露比值 ×作业条件等级,其中健康效应等级根据煤尘中游离SiO2质量分数(0 ~ < 10%、10% ~ 50%、> 50% ~ 80%、> 80%)依次分为0至3级[12];暴露比值=粉尘浓度平均实测值/职业接触限值;作业条件等级=(暴露时间等级×暴露人数等级×工程防护措施等级×个体防护措施等级)1/4,具体见表 1。指数法风险评估结果共有5个等级,无危害、轻度危害、中度危害、重度危害、极度危害。
表 1 作业条件各项等级划分标准等级 暴露人数 暴露时间(h/工作班) 工程控制措施等级 个体防护措施等级(即使用率/%) 5 > 50 > 12 无 0 ~ 20 4 26 ~ 50 > 8 ~ 12 整体控制(整体防护、消噪或防尘) > 20 ~ 50 3 16 ~ 25 > 5 ~ 8 局部控制,有运转,但效果不确定 > 50 ~ 80 2 6 ~ 15 > 2 ~ 5 局部控制,效果明显 > 80 ~ 90 1 0 ~ 5 0 ~ 2 密闭设施 > 90 注:个体防护措施(PPE)的使用率=现场使用个体防护用品的人数/现场应该使用个体防护用品的总人数× 100%。 1.2.3 统计学分析
采用R(3.5.2)软件进行统计学分析。通过有序分组资料的线性趋势χ2检验和Spearman等级相关分析对两种风险评估方法评估结果进行相关性分析,根据煤矿生产系统进行分层,使用马赛克图与Spearman等级相关分析对不同生产系统两种评估结果进行比较研究。以P < 0.05为差异有统计学意义。
2. 结果
2.1 职业卫生调查情况
经焦磷酸法[13]检测,本研究所采集的煤尘样本中游离二氧化硅质量分数为3.6% ~ 7.6%,均小于10%。11座煤矿不同系统工人煤尘暴露时间和工作人数根据岗位的不同而有所差异,其中综采系统和掘进系统的煤尘暴露水平最高,其次为井下运输系统和井上辅助生产系统。各系统煤尘暴露情况及个体防护情况见表 2。
表 2 煤矿各系统煤尘呼吸性粉尘暴露及个体防护情况生产系统 呼吸性粉尘CTWA/(mg/m3) 暴露时间/h 暴露人数 个体防护装备使用率/% 工程控制措施等级 平均值 最小值 最大值 井上辅助生产系统(n = 29) 2.24 0.10 7.00 1 ~ 8 1 ~ 10 20 ~ 50 2 ~ 3 井下辅助生产系统(n = 25) 0.29 0.10 0.90 1 ~ 8 1 ~ 3 20 ~ 50 2 井下运输系统(n = 17) 2.78 1.00 4.20 6 ~ 8 2 ~ 12 50 2 ~ 3 掘进系统(n = 53) 4.11 0.60 14.00 2 ~ 8 1 ~ 8 50 2 ~ 3 选煤系统(n = 7) 1.44 0.20 4.40 1 ~ 8 3 50 2 ~ 3 综采系统(n = 65) 4.33 0.50 13.60 2 ~ 8 1 ~ 6 50 2 ~ 3 注:CTWA为时间加权平均浓度;n为岗位个数。 2.2 两种评估方法结果对比
2.2.1 岗位风险评估结果的对比
本次研究共对11个煤矿中的196个煤尘作业岗位进行煤尘职业健康风险评估,两种评估方法结果对应关系见表 3。指数法评估结果中5种等级的岗位个数分别为无危害118个(占60.2%)、轻度危害48个(占24.5%)、中度危害16个(占8.2%)、重度危害10个(占5.1%)、极度危害4个(占2.0%),主要集中于无危害和轻度危害两个等级;ICMM法评估结果中5种等级的岗位个数分别为可容忍的风险0个、潜在的风险44个(占22.4%)、高风险22个(占11.2%)、非常高的风险14个(占7.1%)、不可容忍的风险116个(占59.2%)个,主要集中于潜在的风险和不可容忍的风险两个等级。两种方法评估结果较为接近的岗位主要分布在风险较低的岗位,评估结果均为同一等级的岗位分布于中度风险等级(1个)和最高等级(4个),共有5个,占评估岗位总数的2.6%。经有序分组资料的趋势χ2检验(χ2 = 46.92,P < 0.05)和Spearman等级相关分析,两种方法评估结果存在正相关关系且为线性关系(r = 0.611,P < 0.05)。
表 3 ICMM法和指数法各岗位煤尘风险评估结果对应的岗位数ICMM法 指数法 总计 无危害 轻度危害 中度危害 重度危害 极度危害 可容忍的风险 0 0 0 0 0 0 潜在的风险 44 0 0 0 0 44 高风险 21 0 1 0 0 22 非常高的风险 14 0 0 0 0 14 不可容忍的风险 39 48 15 10 4 116 合计 118 48 16 10 4 196 2.2.2 生产系统风险评估结果的对比
煤矿各生产系统具有不同的煤尘暴露特点、工作内容、工作环境和防护措施,因此煤尘暴露风险等级也不尽相同[4]。本次研究覆盖了煤矿的6个生产系统(见表 4),按生产系统分层后,各层内两种方法评估结果之间的Spearman等级相关分析显示,在煤尘暴露浓度较低的井上辅助系统中,两种方法评估结果的相关性较分层前高,相关系数r为0.725(P < 0.05);选煤系统、综采系统、掘进系统、井下运输系统两种方法评估结果的相关性较分层前低,相关系数r分别为0.569(P = 0.18)、0.547(P < 0.05)、0.476(P < 0.05)、0.386(P = 0.13);井下辅助生产系统的指数法评估结果均为无危害等级,故未计算相关系数。
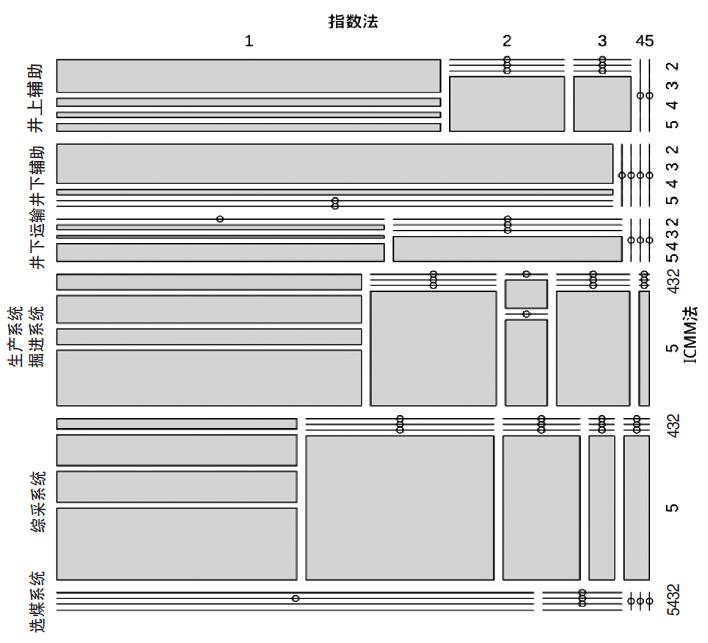
表 4 ICMM法和指数法煤矿生产系统煤尘风险评估结果比较生产系统 评估方法 评估结果岗位数 1级 2级 3级 4级 5级 合计 井上辅助生产系统(n = 29) ICMM法 0 12 3 2 12 29 指数法 20 6 3 0 0 井下辅助生产系统(n = 25) ICMM法 0 22 3 0 0 25 指数法 25 0 0 0 0 井下运输系统(n = 17) ICMM法 0 0 2 1 14 17 指数法 10 7 0 0 0 掘进系统(n = 53) ICMM法 0 4 8 4 37 53 指数法 29 12 4 7 1 选煤系统(n = 7) ICMM法 0 4 0 1 2 7 指数法 6 1 0 0 0 综采系统(n = 65) ICMM法 0 2 6 6 51 65 指数法 28 22 9 3 3 注:1级=可容忍的风险或无危害;2级=潜在的风险或轻度危害;3级=高风险或中度危害;4级=非常高风险或重度危害;5级=不可容忍的风险或重度危害;n为岗位数。 按生产系统分层后,指数法和ICMM法评估结果在层内的对比见图 1。ICMM法中面积较大的方块多集中于2级和5级处,而指数法中较大的方块多位于其较低的评估等级处,反映两种方法在较低风险等级结果相近的较多。在煤尘暴露水平较低的井下辅助系统中,大面积方块均分布在两种方法较低的风险等级处。井上辅助系统和井下运输系统中,大面积方块位于指数法风险等级较低处,但其中有一半左右的岗位ICMM法评估结果为最高级。在煤尘暴露水平较高的掘进系统和综采系统中,大面积方块主要分布于指数法的低风险等级处和ICMM法的最高等级处,反映两种方法评估结果差异较大。
3. 讨论
本研究采用职业健康风险评估较为常用的两种方法对多个煤矿的煤尘接触岗位进行煤尘风险评估,两种方法的评估结果呈较好的正相关性,在两种评估方法的结果中,ICMM法共有116个5级(极度危害风险级别或不可容忍的风险)评估结果,其中有88个来自于掘进系统和综采系统,占总数的75.9%;指数法共有4个5级评估结果,均来自于掘进系统和综采系统,占总数的100%。即两种评估方法的5级评估结果大多都来自于综采和掘进系统,同时体现出掘进系统和综采系统的风险较高,故两者评估方法在此方面的结果较为统一。本次煤尘健康风险分级中,极度危害风险级别(不可容忍的风险)聚集的煤矿生产系统,正是我国煤工尘肺病例高发工种所在的工作场所,说明两种评估方法适用性良好。
但是,两种方法评估结果相近的绝大多数岗位分布在风险较低等级的岗位,所以显示两种方法评估结果的相关性较高。而在对煤矿生产系统分层后,煤尘浓度较高生产系统的两种评估结果的相关性明显降低。相比指数法,ICMM法对煤尘职业健康风险评估的结果更为严重,这种现象也见于其他职业病危害因素风险评估的研究[14]。分析原因主要是在煤尘的风险评估中,ICMM法更侧重于煤尘的暴露水平,而指数法会考虑到工作场所作业条件的工程控制和个体防护等降低风险因素,因此,在高浓度的煤尘作业环境中的评估结果相对较低。
职业健康风险评估涉及关键因素包括危害识别、潜在健康影响调查、暴露测量、风险特征描述[10],本次研究所采用的两种方法的评估内容均包含有上述因素,但两种方法部分评估标准主观性较强,如健康效应和后果,评估结果会因方法应用者不同的关注点而得出不同结果,因此,两种方法是否考虑使用客观指标仍需进行深入研究。
综上所述,在煤尘的职业健康风险评估中,ICMM法可较好地反映工作环境中煤尘的暴露风险水平,在工程防护措施和个体防护措施未能有效实施的场所可进行预测性评估,指数法更能反映出劳动者在得到防护设施的保护后实际的风险水平,在煤尘暴露浓度较低的环境中,两种方法评估效果较为一致。
作者声明 本文无实际或潜在的利益冲突 -
表 1 作业条件各项等级划分标准
等级 暴露人数 暴露时间(h/工作班) 工程控制措施等级 个体防护措施等级(即使用率/%) 5 > 50 > 12 无 0 ~ 20 4 26 ~ 50 > 8 ~ 12 整体控制(整体防护、消噪或防尘) > 20 ~ 50 3 16 ~ 25 > 5 ~ 8 局部控制,有运转,但效果不确定 > 50 ~ 80 2 6 ~ 15 > 2 ~ 5 局部控制,效果明显 > 80 ~ 90 1 0 ~ 5 0 ~ 2 密闭设施 > 90 注:个体防护措施(PPE)的使用率=现场使用个体防护用品的人数/现场应该使用个体防护用品的总人数× 100%。 表 2 煤矿各系统煤尘呼吸性粉尘暴露及个体防护情况
生产系统 呼吸性粉尘CTWA/(mg/m3) 暴露时间/h 暴露人数 个体防护装备使用率/% 工程控制措施等级 平均值 最小值 最大值 井上辅助生产系统(n = 29) 2.24 0.10 7.00 1 ~ 8 1 ~ 10 20 ~ 50 2 ~ 3 井下辅助生产系统(n = 25) 0.29 0.10 0.90 1 ~ 8 1 ~ 3 20 ~ 50 2 井下运输系统(n = 17) 2.78 1.00 4.20 6 ~ 8 2 ~ 12 50 2 ~ 3 掘进系统(n = 53) 4.11 0.60 14.00 2 ~ 8 1 ~ 8 50 2 ~ 3 选煤系统(n = 7) 1.44 0.20 4.40 1 ~ 8 3 50 2 ~ 3 综采系统(n = 65) 4.33 0.50 13.60 2 ~ 8 1 ~ 6 50 2 ~ 3 注:CTWA为时间加权平均浓度;n为岗位个数。 表 3 ICMM法和指数法各岗位煤尘风险评估结果对应的岗位数
ICMM法 指数法 总计 无危害 轻度危害 中度危害 重度危害 极度危害 可容忍的风险 0 0 0 0 0 0 潜在的风险 44 0 0 0 0 44 高风险 21 0 1 0 0 22 非常高的风险 14 0 0 0 0 14 不可容忍的风险 39 48 15 10 4 116 合计 118 48 16 10 4 196 表 4 ICMM法和指数法煤矿生产系统煤尘风险评估结果比较
生产系统 评估方法 评估结果岗位数 1级 2级 3级 4级 5级 合计 井上辅助生产系统(n = 29) ICMM法 0 12 3 2 12 29 指数法 20 6 3 0 0 井下辅助生产系统(n = 25) ICMM法 0 22 3 0 0 25 指数法 25 0 0 0 0 井下运输系统(n = 17) ICMM法 0 0 2 1 14 17 指数法 10 7 0 0 0 掘进系统(n = 53) ICMM法 0 4 8 4 37 53 指数法 29 12 4 7 1 选煤系统(n = 7) ICMM法 0 4 0 1 2 7 指数法 6 1 0 0 0 综采系统(n = 65) ICMM法 0 2 6 6 51 65 指数法 28 22 9 3 3 注:1级=可容忍的风险或无危害;2级=潜在的风险或轻度危害;3级=高风险或中度危害;4级=非常高风险或重度危害;5级=不可容忍的风险或重度危害;n为岗位数。 -
[1] 李旭东, 丁俊, 刘明, 等.三种职业健康风险评估方法评估涂料生产企业有机溶剂风险的应用比较[J].预防医学, 2018, 30(8):43-47. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/zjyfyx201808009 [2] 国家质量监督检验检疫总局, 中国国家标准化管理委员会.风险管理术语: GB/T 23694-2013[S].北京: 中国标准出版社, 2014. [3] 丁俊, 苏世标, 靳雅丽, 等.家具生产企业有机溶剂的三种健康风险评估方法比较[J].预防医学, 2019, 31(4):400-404. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/zjyfyx201904019 [4] 吴宾, 张永亮, 陈永青.煤尘职业健康风险评估中两种风险评估方法的应用研究[J].中华劳动卫生职业病杂志, 2017, 35(4):276-279. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/zhldwszyb201704009 [5] 袁树杰, 姜丽, 王晓楠.风险评估模型对煤矿职业危害评价的适用性研究[J].煤矿安全, 2019, 50(4):248-252. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/mkaq201904060 [6] 汉锋, 陈永青, 吴宾, 等.煤炭产业链煤尘接触职业健康风险评估[J].中华劳动卫生职业病杂志, 2018, 36(4):291-294. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/zhldwszyb201804015 [7] International Council on Mining & Metals. Good practice guidance on Occupational Health Risk Assessment.[D/OL].[2020-04-01].https://www.academia.edu/13777478/Good_Practice_Guidance_on_Occupational_Health_Risk_Assessment.
[8] HAN L, GAO Q, YANG J, et al. Survival analysis of coal workers'pneumoconiosis (CWP) patients in a state-owned mine in the east of China from 1963 to 2014[J]. Int J Environ Res Public Health, 2017, 14(5):E489. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/28481235
[9] PERRET J L, PLUSH B, LACHAPELLE P, et al. Coal mine dust lung disease in the modern era[J]. Respirology, 2017, 22(4):662-670. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=c7bd7c1ccf251592da5133c01b9ae857
[10] 丁钢强, 张美辨.国外职业健康风险评估指南[M].上海:复旦大学出版社, 2014. [11] 林嗣豪, 王治明, 唐文娟, 等.职业危害风险指数评估方法的初步研究[J].中华劳动卫生职业病杂志, 2006, 24(12):769-771. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/zhldwszyb200612022 [12] 中华人民共和国卫生部.工作场所职业病危害作业分级第1部分: 生产性粉尘: GBZ/T 229.1-2010[S].北京: 人民卫生出版社, 2010. [13] 中华人民共和国卫生部.工作场所空气中粉尘测定第4部分: 游离二氧化硅含量: GBZ/T 192.4-2007[S].北京: 人民卫生出版社, 2007. [14] 陈琳, 岑子博, 马炜钰, 等.三种风险评估方法在某汽车4S店职业健康风险评估中的应用[J].中华劳动卫生职业病杂志, 2019, 37(11):866-870. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/zhldwszyb201911018 -
期刊类型引用(0)
其他类型引用(1)





 下载:
下载: