Application of different risk assessment methods in occupational health risk assessment in sewage treatment industry
-
+ English摘要:目的 比较多种职业健康风险评估方法在污水处理行业重点岗位中的适用性。方法 以3家污水处理企业为研究对象,采用美国国家环境保护署吸入风险评估模型法(简称EPA法)、GBZ/T 229工作场所职业病危害作业分级法、GBZ/T 298-2017综合指数法、国际采矿和金属委员会职业健康风险评估模型法(简称ICMM法)以及澳大利亚职业安全健康风险评估方法(简称澳大利亚法)对接触氨(NH3)和硫化氢(H2S)、粉尘作业岗位的职业健康风险进行评估,比较多种风险评估结果。结果 3家污水处理厂各岗位NH3、H2S和粉尘检测结果均符合国家接触限值要求。经风险比值对各方法的风险评估结果进行标准化后,EPA法的评估结果显示各岗位H2S的职业健康风险均为极高风险(5级),NH3均为中等风险(3级);GBZ/T 229作业分级法和ICMM矩阵法的评估结果显示NH3、H2S和粉尘的职业健康风险均为低风险(2级);ICMM定量法的评估结果显示NH3、H2S及粉尘的职业健康风险均为可忽略风险(1级);GBZ/T 298-2017综合指数法的评估结果显示NH3、H2S的职业健康风险均为中等风险(3级),粉尘为可忽略风险(1级);澳大利亚法的评估结果显示NH3、H2S的职业健康风险为高风险(4级),粉尘为中等风险(3级)。结论 几种风险评估方法对污水处理行业职业健康风险的评估结果不尽一致,GBZ/T 298-2017综合指数法结合澳大利亚法更适用于污水处理行业的职业健康风险评估。
-
作者声明 本文无实际或潜在的利益冲突
-
表 1 3家污水处理厂职业病危害因素检测结果
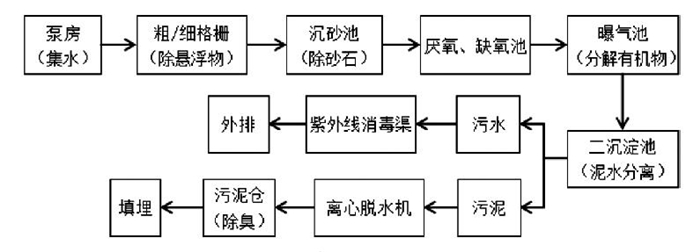
岗位 职业病危害因素 样品数 质量浓度/(mg/m3) 中位数/(mg/m3) E/OEL 粗格栅巡检位 NH3 27 < 0.20 — 0.007 H2S 27 < 0.53 — 0.053 厌氧池采样口 NH3 18 < 0.20 ~ 0.49 0.22 0.016 H2S 18 < 0.53 ~ 2.17 1.17 0.217 缺氧池采样口 NH3 18 < 0.20 ~ 3.49 1.09 0.116 H2S 18 < 0.53 ~ 0.97 0.68 0.097 曝气池巡检位 NH3 27 < 0.20 — 0.007 H2S 27 < 0.53 ~ 2.27 1.46 0.227 沉淀池投料口 NH3 18 < 0.20 — 0.007 H2S 18 < 0.53 — 0.053 聚丙烯酰胺粉尘 18 1.17 ~ 4.58 3.09 0.286 污泥仓 NH3 21 < 0.20 — 0.007 H2S 21 < 0.53 — 0.053 H2S 27 < 0.53 — 0.053 表 2 不同风险评估模型的职业健康风险评估结果比较
岗位 危害因素 EPA法 作业分级法 ICMM定量法 ICMM矩阵法 综合指数法 澳大利亚法 HQ 风险比值 G 风险比值 RR 风险比值 后果 暴露等级 风险比值 HR ER 风险比值 风险等级 风险比值 粗格栅巡检位 NH3 0.03 0.5(3级) 0 0.25(2级) 18 0.2(1级) 1 低 0.25(2级) 5 1.40 0.4(2级) 高 0.8(4级) H2S 18.45 1.0(5级) 0 0.25(2级) 18 0.2(1级) 1 低 0.25(2级) 5 1.40 0.4(2级) 高 0.8(4级) 厌氧池采样口 NH3 0.07 0.5(3级) 0 0.25(2级) 18 0.2(1级) 1 低 0.25(2级) 5 1.40 0.4(2级) 高 0.8(4级) H2S 75.55 1.0(5级) 0 0.25(2级) 18 0.2(1级) 1 低 0.25(2级) 5 1.53 0.6(3级) 高 0.8(4级) 缺氧池采样口 NH3 0.49 0.5(3级) 0 0.25(2级) 18 0.2(1级) 1 低 0.25(2级) 5 1.53 0.6(3级) 高 0.8(4级) H2S 33.77 1.0(5级) 0 0.25(2级) 18 0.2(1级) 1 低 0.25(2级) 5 1.40 0.4(2级) 高 0.8(4级) 曝气池巡检位 NH3 0.03 0.5(3级) 0 0.25(2级) 18 0.2(1级) 1 低 0.25(2级) 5 1.40 0.4(2级) 高 0.8(4级) H2S 79.04 1.0(5级) 0 0.25(2级) 18 0.2(1级) 1 低 0.25(2级) 5 1.53 0.6(3级) 高 0.8(4级) 沉淀池投料口 NH3 0.03 0.5(3级) 0 0.25(2级) 18 0.2(1级) 1 低 0.25(2级) 5 1.40 0.4(2级) 高 0.8(4级) H2S 18.45 1.0(5级) 0 0.25(2级) 18 0.2(1级) 1 低 0.25(2级) 5 1.40 0.4(2级) 高 0.8(4级) 粉尘 — — 0 0.25(2级) 18 0.2(1级) 1 低 0.25(2级) 1 1.76 0.2(1级) 较高 0.6(3级) 污泥仓 NH3 0.03 0.5(3级) 0 0.25(2级) 18 0.2(1级) 1 低 0.25(2级) 5 1.40 0.4(2级) 高 0.8(4级) H2S 18.45 1.0(5级) 0 0.25(2级) 18 0.2(1级) 1 低 0.25(2级) 5 1.40 0.4(2级) 高 0.8(4级) -
[1] 中华人民共和国住房和城乡建设部. 2018年城市建设统计年鉴[R]. 2020-03-27. [2] 冯玉超, 高原, 赵远, 等. 2017-2018年广州市5辖区污水泵站职业病危害调查[J]. 职业卫生与应急救援, 2020, 38(4): 397-400. doi: 10.16369/j.oher.issn.1007-1326.2020.04.019 [3] 梅丽敏, 高建美, 夏佳龙. 一起有限空间急性混合性气体职业中毒事故调查[J]. 职业卫生与应急救援, 2020, 38(1): 83-85. doi: 10.16369/j.oher.issn.1007-1326.2020.01.020 [4] 李海斌, 宋爽, 李添娣, 等. 2种风险评估方法在2-丁氧基乙醇职业健康风险评估中的应用[J]. 中国职业医学, 2019, 46(1): 4649. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XYYX201901012.htm [5] 张蔓, 周振清, 任福琳, 等. 3种风险评估模型在甲苯职业健康风险评估中的应用[J]. 职业与健康, 2018, 34(23): 3180-3185. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZYJK201823004.htm [6] 张金鑫, 陈慧峰, 闫雪华, 等. 应用3种风险评估方法评估某飞机维修企业苯及苯系物职业健康风险[J]. 中国职业医学, 2019, 46(3): 335-339. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XYYX201903019.htm [7] 边洪英, 康宁, 董一文, 等. 三种半定量风险评估方法在矽尘暴露岗位风险等级划分中的比较[J]. 中国工业医学杂志, 2019, 32(3): 167-171. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SOLE201903003.htm [8] 中华人民共和国卫生部. 工作场所空气中有害物质监测的采样规范: GBZ 159-2004[S]. 北京: 人民卫生出版社, 2004. [9] 中华人民共和国卫生部. 工作场所空气有毒物质测定无机含氮化合物: GBZ/T 160.29-2004[S]. 北京: 人民卫生出版社, 2004. [10] 中华人民共和国卫生部. 工作场所空气有毒物质测定无机含硫化合物: GBZ/T 160.33-2004[S]. 北京: 人民卫生出版社, 2004. [11] 中华人民共和国卫生部. 工作场所空气中粉尘测定第1部分: 总粉尘测定: GBZ/T 192.1-2007[S]. 北京: 人民卫生出版社, 2007. [12] 中华人民共和国卫生部. 工作场所有害因素职业接触限值第1部分: 化学有害因素: GBZ 2.1-2007[S]. 北京: 人民卫生出版社, 2007. [13] 中华人民共和国卫生部. 工作场所职业病危害作业分级第1部分: 生产性粉尘: GBZ/T 229.1-2010[S]. 北京: 人民卫生出版社, 2010. [14] 中华人民共和国卫生部. 工作场所职业病危害作业分级第2部分: 化学物: GBZ/T 229.2-2010[S]. 北京: 人民卫生出版社, 2010. [15] 中华人民共和国国家卫生和计划生育委员会. 工作场所化学有害因素职业健康风险评估技术导则: GBZ/T 298-2017[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2017. [16] 张美辨. 国外职业健康风险评估指南[M]. 上海: 复旦大学出版社, 2014: 204-226. [17] 张美辨. 职业健康风险评估方法学实践应用[M]. 北京: 人民军医出版社, 2016: 1-29. [18] 郭少红, 张颖, 詹玉贞. 某污水处理厂职业病危害控制效果评价[J]. 职业卫生与应急救援, 2016, 34(6): 491-493. doi: 10.16369/j.oher.issn.1007-1326.2016.06.019 [19] 周武, 谭剑明. 江门市某生活污水处理厂职业病危害现状调查[J]. 中国卫生工程学, 2017, 16(3): 283-286. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGWX201703007.htm [20] 侯玉兵. 城市生活污水处理厂职业病危害因素的调查分析[J]. 职业卫生与病伤, 2017, 32(2): 117-119. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZYWB201702018.htm [21] 邓冠华, 肖晓琴, 杜伟佳, 等. 一起污水处理站急性硫化氢中毒事故调查分析[J]. 职业卫生与应急救援, 2015, 33(5): 381-382. doi: 10.16369/j.oher.issn.1007-1326.2015.05.027 [22] 王凯彬, 唐侍豪, 孙世宏, 等. 一起职业性急性窒息性气体中毒事件分析[J]. 华南预防医学, 2019, 45(1): 79-81. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GDWF201901020.htm





 下载:
下载:
