Chinesization of Emergency Medical Services Resilience Scale Questionnaire and tests of its reliability and validity
-
+ English摘要:目的 对急救医疗服务心理弹性量表(emergency medical services resilience scale,EMSRS)进行汉化并检验中文版量表的适用性。方法 获得原作者授权同意后,对EMSRS量表进行翻译修订、跨文化调试,形成中文版EMSRS。采用便利抽样法选取太原市某急救中心252名急救人员进行量表调查并进行条目分析和信度、效度检验。条目区分度采用独立样本t检验分析,信度采用Cronbach’s α系数、折半信度、重测信度来评价;采用专家咨询法测量其内容效度,运用探索性因子分析来验证其结构效度。结果 预测试结果显示仅有6.6%的人认为量表的长度和内容不合适或者不清晰,表明原量表接受度较好。项目分析显示31个条目在两组间差异均有统计学意义(P < 0.05),故均予以保留。经专家咨询对量表两个条目内容做了调整。最终得到的中文版急救医疗服务心理弹性量表有6个维度、31个条目,探索性因子分析共提取6个公因子,根据条目内容将6个公因子分别命名为工作动机、工作积极性、压力的影响、自我管理、沟通挑战、社会支持,累计方差贡献率为75.717%。量表各条目的CVI(I-CVI)值为0.833~1.000,量表全部条目的平均CVI(S-CVI)值为0.965。量表的Cronbach’s α系数为0.936,各维度Cronbach’s α系数为0.801~0.940,总量表折半信度为0.848,各维度的折半信度为0.750~0.904,总量表重测信度为0.872,各维度重测信度为0.742~0.879。结论 汉化后的EMSRS量表具有良好的信度、效度,可作为紧急医疗服务人员心理弹性的调查工具。
-
作者声明 本文无实际或潜在的利益冲突
-
表 1 初始修订、尚未汉化的EMSRS量表
条目名称 条目名称 维度1:工作动机 维度3:保持冷静 1. 我提供急救医疗服务时没有动力(拟改为我提供急救医疗服务时有动力) 19. 在事故现场,我希望每个人都能保持冷静 2. 我对自己的职业认识不足(拟改为我对自己的职业有充分的了解) 20. 我以对上帝的信仰进入事故现场 3. 我留在单位中是因为我别无选择(拟改为我留在单位中是因为我喜欢这份职业) 21. 面对事故,我会祈祷 4. 我设法将受伤的人迅速送往医疗中心 22. 在到达现场之前,我将对事故现场进行心理准备 5. 我一直在尽我最大努力抢救伤员 23. 在进入现场之前,我将评估现场的安全性 6. 在任何情况下,我都会自愿去拯救生命 维度4:沟通挑战 7. 在离事故现场很近的情况下,我会立即通知部署单位 24. 在事故现场,我能理解救助者及其同伴的行为 8. 在紧急情况下,我会主动提供医疗救助 25. 在事故现场,我将与我的同事、消防人员和警察进行专业合作 9. 救死扶伤是我的动力 26. 运送伤员时,我尽量控制紧张和慌乱的情绪 10. 救助者的认可激励着我 维度5:社会支持 11. 参与决策能激发我的动力 27. 我的同事们支持我 12. 我能用幽默的方式解决问题 28. 我在解决因任务而引发的问题时,同事们能积极地给予我建议 13. 我跟我的同事有共鸣 维度6:压力的影响 维度2:自我管理 29. 因为任务,我会做噩梦 14. 我相信我对事故现场的判断和决定 30. 我很难入睡 15. 我能应付伤者接下来发生的状况 31. 我使用药物控制压力 16. 我能控制现场的情况 17. 我可以妥善完成分配给我的任务 18. 工作的经验使我能够应对事故现场 表 2 30名医护人员预测试时对EMSRS量表的接受性评价情况
[人数(占比/%)] 评价项目 非常合适或非常清晰 合适或清晰 不合适或不清晰 条目长度 5(16.7) 25(83.3) 0(0) 量表长度 4(13.3) 25(83.3) 1(3.3) 条目内容 10(33.3) 19(63.3) 1(3.3) 量表内容 10(33.3) 20(66.7) 0(0) 表 3 量表的项目分析结果
条目 高分组(n=68) 低分组(n=68) t值 P值 A1 4.49±0.64 3.97±0.73 4.38 <0.01 A2 4.78±0.48 3.57±0.80 10.66 <0.01 A3 4.50±0.61 4.13±0.73 3.18 <0.01 A4 4.94±0.24 4.12±1.20 5.54 <0.01 A5 5.00±0.00 4.21±0.97 6.75 <0.01 A6 5.00±0.00 4.41±0.95 5.11 <0.01 A7 4.99±0.12 3.90±0.90 9.88 <0.01 A8 5.00±0.00 3.84±0.92 10.37 <0.01 A9 4.99±0.12 3.66±1.07 10.10 <0.01 A10 4.87±0.42 3.10±0.98 13.66 <0.01 A11 4.99±0.12 3.10±1.10 14.09 <0.01 A12 4.96±0.21 3.07±0.98 15.47 <0.01 A13 4.96±0.12 3.34±1.00 13.46 <0.01 A14 4.94±0.24 3.47±0.84 13.94 <0.01 A15 4.82±0.38 3.35±0.71 15.07 <0.01 A16 4.81±0.40 3.12±0.80 15.60 <0.01 A17 5.00±0.00 3.82±0.79 12.27 <0.01 A18 4.94±0.24 3.60±0.93 11.47 <0.01 A19 5.00±0.00 3.75±0.98 10.49 <0.01 A20 4.97±0.17 3.79±0.97 9.85 <0.01 A21 4.97±0.17 3.68±0.97 11.39 <0.01 A22 5.00±0.00 3.60±0.79 14.50 <0.01 A23 4.99±0.12 3.74±0.99 10.37 <0.01 A24 4.78±0.83 3.82±0.99 3.11 <0.01 A25 4.96±0.21 3.51±0.87 13.26 <0.01 A26 4.96±0.21 3.68±0.89 11.57 <0.01 A27 4.76±0.55 3.37±1.04 9.83 <0.01 A28 5.00±0.00 3.54±0.92 13.03 <0.01 A29 2.93±1.46 2.47±0.99 2.14 <0.05 A30 3.28±1.58 2.79±1.13 2.06 <0.05 A31 2.35±1.66 1.79±0.94 2.41 <0.05 表 4 量表的各公因子特征值及方差贡献率
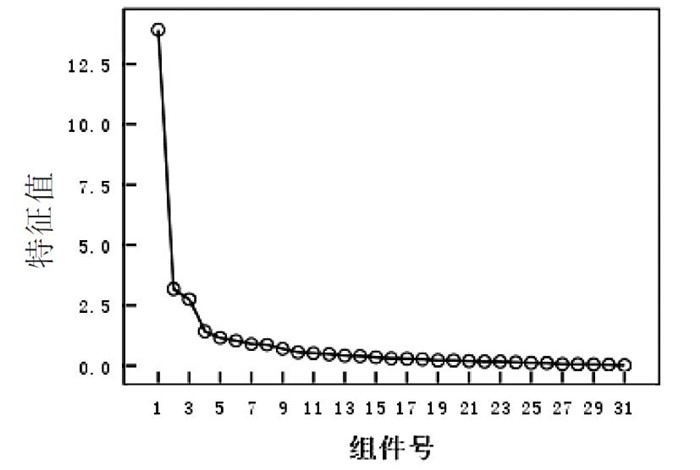
因子 特征值 方差贡献率/% 累计贡献率/% 因子1 10.571 34.100 34.100 因子2 4.113 13.269 47.370 因子3 2.763 8.914 56.283 因子4 2.654 8.562 64.845 因子5 2.025 6.533 71.378 因子6 1.345 4.338 75.717 表 5 量表各条目的因子载荷矩阵
条目 因子1 因子2 因子3 因子4 因子5 因子6 A17 0.828 A22 0.816 A26 0.816 A18 0.815 A14 0.770 A16 0.770 A21 0.765 A23 0.755 A15 0.752 A19 0.747 A25 0.745 A20 0.731 A27 0.720 A28 0.704 A10 0.607 A24 0.528 A4 0.943 A6 0.933 A8 0.862 A9 0.742 A2 0.723 A29 0.962 A30 0.959 A31 0.908 A11 0.781 A12 0.777 A13 0.701 A5 0.830 A7 0.711 A3 0.774 A1 0.679 -
[1] 王冬叶, 张万里, 项少梅, 等. 温州市社区护士突发公共卫生事件应急能力调查分析[J]. 护理学杂志, 2016, 31(4): 82-84. doi: 10.3870/j.issn.1001-4152.2016.04.082 [2] 袁颖, 耿力. 院前急救调度员培训现状及启示[J]. 护理学杂志, 2017, 32(10): 96-99. doi: 10.3870/j.issn.1001-4152.2017.10.096 [3] SHAKESPEARE-FINCH J, DALEY E. Workplace belongingness, distress, and resilience in emergency service workers[J]. Psychol Trauma, 2017, 9(1): 32-35. doi: 10.1037/tra0000108
[4] 于肖楠, 张建新. 韧性(resilience)在压力下复原和成长的心理机制[J]. 心理科学进展, 2005, 13(5): 658-665. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XLXD200505015.htm [5] American Psychology Association. The Road to Resilience: what is resilience?[EB/OL]. (2011-10-18)[2020-08-26]. http://www.apa.org/helpcenter/roadresilience.aspx.2011.
[6] MCDONALD G, JACKSON D, VICKERS M H, et al. Surviving workplace adversity: a qualitative study of nurses and midwives and their strategies to increase personal resilience[J]. J Nurs Manag, 2016, 24(1): 123-131. doi: 10.1111/jonm.12293
[7] MOTIE M R, KALANI M R, SAMADI A, et al. Prevalence of job stressors in male pre-hospital emergency technicians[J]. J Fundam Ment Health, 2010, 12(45): 420-429. http://www.researchgate.net/publication/215445233_Prevalence_of_job_stressors_in_male_pre-hospital_emergency_technicians/download
[8] 郭金玉, 李峥. 量表引进的过程及评价标准[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2012, 47(3): 283-285. doi: 10.3761/j.issn.0254-1769.2012.03.039 [9] 李小妹, 刘彦君. 护士工作压力源及工作疲溃感的调查研究[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2000, 35(11): 645-649. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0254-1769.2000.11.001 [10] DOLAN N. The relationship between burnout and job satisfaction in nurses[J]. J Adv Nurs, 1987, 12(1): 3-12. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2648.1987.tb01297.x
[11] GRAY-TOFT P, ANDERSON J G. Stress among hospital nursing staff: its causes and effects[J]. Soc Sci Med A, 1981, 15(5): 639-647. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/0271712381900870
[12] WHEELER H, RIDING R. Occupational stress in general nurses and midwives[J]. Br J Nurs, 1994, 3(10): 527-534. doi: 10.12968/bjon.1994.3.10.527
[13] 庞晓华, 张丽芳. Connor-Davidson心理弹性量表中文版在煤矿工人中应用的信效度分析[J]. 中华行为医学与脑科学杂志, 2019, 28(7): 655-659. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1674-6554.2019.07.016 [14] YU X N, ZHANG J X. Factor analysis and psychometric evaluation of the Connor-Davison resilience scale(CD-RISC) with Chinese people[J]. SBP J, 2007, 35(1): 19-30.
[15] EBADI A, FROUTAN R, MALEKZADEH J. The design and psychometric evaluation of the emergency medical services resilience scale (EMSRS)[J]. Int Emerg Nurs, 2019, 42: 12-18. doi: 10.1016/j.ienj.2018.09.002
[16] GUILLEMIN F, BOMBARDIER C, BEATON D. Cross-cultural adaptation of health-related quality of life measures: literature review and proposed guidelines[J]. J Clin Epidemiol, 1993, 46(12): 1417-1432. doi: 10.1016/0895-4356(93)90142-N
[17] International Council of Nurses. Translation guidelines for international classification for nursing practice(ICNP)[M]. Geneva: Lmprimerie Fornara, 2008: 16.
[18] PHILLIPS L R, LUNA DE HERNANDEZ I, TORRES DE ARDON E. Strategies for achieving cultural equivalence[J]. Res Nurs Health, 1994, 17(2): 149-154. doi: 10.1002/nur.4770170210
[19] TOPF M. Three estimates of interrater reliability for nominal data[J]. Nurs Res, 1986, 35(4): 253-255. doi: 10.1097/00006199-198607000-00020
[20] 段雪, 张静萍. ICU护士对常用监护仪报警应答疲劳知信行问卷的编制与信效度检验[J]. 护理研究, 2019, 33(7): 1125-1129. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SXHZ201907009.htm [21] HASSON F, KEENEY S, MCKENNA H. Research guidelines for the Delphi survey technique[J]. J Adv Nurs, 2000, 32(4): 1008-1015. http://europepmc.org/abstract/MED/11095242
[22] 阚庭. 医护人员传染病突发事件应对能力培训项目的开发与评价[D]. 上海: 中国人民解放军海军军医大学, 2018. [23] 良平, 关雪. 护理科研设计与统计分析[M]. 北京: 军事医学科学出版社, 2013: 142-145. [24] HABIBIPOUR B, VANAKI Z, HADJIZADEH E. The effect of implementing "Goal Setting Theory" by nurse managers on staff nurses' job motivation[J]. Iran J Nurs, 2009, 22(57): 67-76. http://www.sid.ir/en/viewpaper.asp?id=162531&varstr=1;habibipour%20b.%20,%20vanaki%20z.%20,%20hajizadeh%20ebrahim;iran%20journal%20of%20nursing%20(ijn);may%202009;22;57;67;76
[25] 史静琤, 莫显昆, 孙振球. 量表编制中内容效度指数的应用[J]. 中南大学学报: 医学版, 2012, 37(2): 152-155. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-7347.2012.02.007 [26] LARIJANI T T, YEKTA Z P, KAZEMNEJAD A, et al. Outcomes of the performance appraisal and its relation with nurses job motivation[J]. Hayat, 2007, 12(4): 39-45. http://www.oalib.com/paper/2213710
[27] SOBHANI Z, AHADI H, KHOSRAVI S, et al. Psychometric indices of post bariatric surgery self-management behaviors questionnaire[J]. Arak Med Univ J, 2017, 20(1): 84-95.
[28] DOSS S, DEPASCAL P, HADLEY K. Patient-nurse partnerships[J]. Nephrol Nurs J, 2011, 38(2): 115-124.
[29] CASTELEIN S, BRUGGEMAN R, VAN BUSSCHBACH J T, et al. The effectiveness of peer support groups in psychosis: a randomized controlled trial[J]. Acta Psychiatr Scand, 2008, 118(1): 64-72. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0447.2008.01216.x
[30] NIR M S, EBADI A, KHOSHKNAB M F, TAVALLAIE A, et al. Consequences of living with posttraumatic stress disorder: a qualitative study[J]. J Qual Res Health Sci, 2012, 1(2): 92-101. http://www.researchgate.net/publication/234833697_Consequences_of_living_with_Post_traumatic_Stress_DisorderA_Qualitative_Study
[31] 孙振球, 徐勇勇. 医学统计学[M]. 4版. 北京: 人民卫生出版社, 2014. [32] 郑日昌, 孙大强. 心理测量与测验[M]. 北京: 中国人民大学出版社, 2013: 125-148. [33] 靳荣秀, 田俊, 何鹏飞, 等. 中文版气管切开术后患者生活质量量表的信效度检验[J]. 护理学杂志, 2017, 32(8): 22-24. doi: 10.3870/j.issn.1001-4152.2017.08.022 [34] 沈秋苹, 王娟, 张彩迪. 医护人员工作压力, 心理弹性和工作满意度的关系[J]. 中国健康心理学杂志, 2018, 26(11): 1706-1710. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JKXL201811028.htm





 下载:
下载:
