Characteristics of regional clustering of pneumoconiosis in Foshan City during 2011 to 2020
-
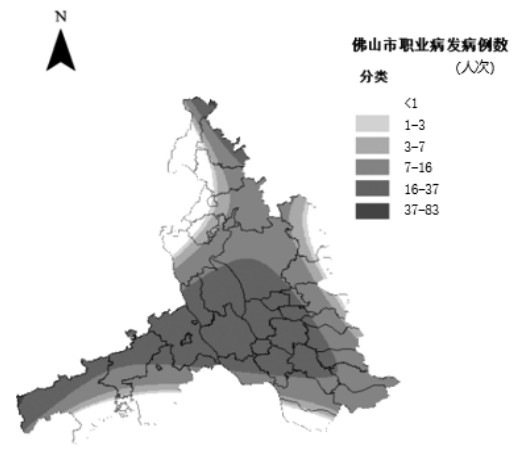
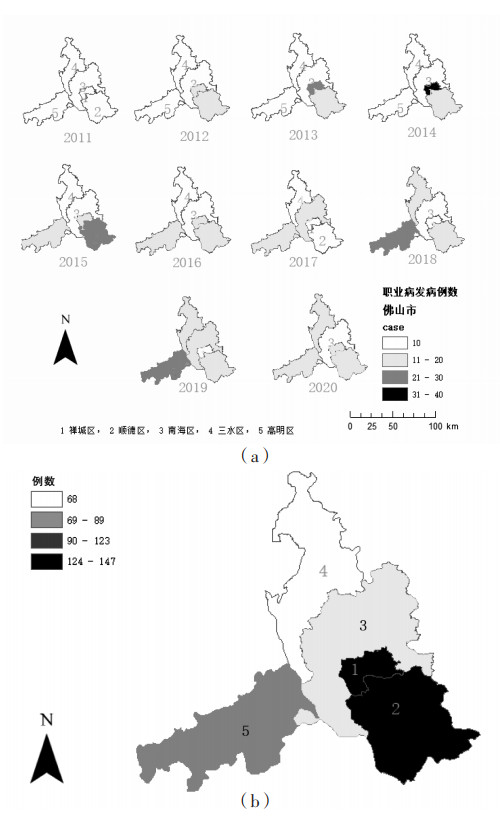
+ English摘要:目的 对佛山市2011—2020年尘肺病发病的空间流行病学特征进行分析,为该市尘肺病防控工作提供科学依据。方法 利用地理信息系统(ArcGIS)对佛山市2011—2020年尘肺病发病情况进行空间流行病学特征分析,呈现该市尘肺病发病的时空聚集性和空间流行特点。结果 佛山市2011—2020年共报告尘肺病新病例573例,全局空间自相关分析显示,尘肺病发病人数在2012—2014年存在空间聚集性;局部空间自相关分析显示,南海区与周围区域尘肺病发病分布呈低-高相邻模式,高明区与周围区域尘肺病发病分布呈高-低相邻模式;趋势面分析显示,聚集区域主要分布在禅城区、顺德区西北侧、南海区西南侧和高明区北侧。结论 佛山市2011—2020年尘肺病发病情况总体呈锯齿状上升趋势,尘肺病发病人数在佛山市各区分布呈离散性。
-
作者声明 本文无实际或潜在的利益冲突
-
表 1 佛山市2011—2020年尘肺病发病情况
(例) 年份 禅城区 南海区 顺德区 三水区 高明区 总计 2011 2 2 4 3 6 17 2012 16 5 13 3 4 41 2013 23 7 18 2 3 53 2014 33 7 18 2 3 63 2015 18 8 26 2 13 67 2016 14 10 13 9 12 58 2017 9 12 9 8 14 52 2018 5 10 17 15 28 75 2019 10 18 18 13 23 82 2020 16 10 11 11 17 65 合计 146 89 147 68 123 573 表 2 佛山市2011—2020年尘肺病发病全局空间自相关分析结果
年份 Moran’s I值 Z值 P值 2011 - 0.286 - 0.162 0.871 2012 0.294 2.184 0.029 2013 0.340 2.379 0.017 2014 0.221 2.131 0.033 2015 0.082 1.441 0.149 2016 - 0.012 0.973 0.330 2017 - 0.306 - 0.234 0.815 2018 - 0.126 0.572 0.567 2019 - 0.290 - 0.172 0.863 2020 - 0.456 - 0.813 0.416 合计 - 0.005 0.996 0.319 表 3 2011—2020年佛山市尘肺病发病全局空间自相关分析结果
年份 Moran’s I值 Z值 P值 聚类模式 禅城区 0.051 368 0.468 0.354 无 南海区 - 0.595 619 - 1.576 0.002 低-高 顺德区 0.144 433 0.544 0.356 无 三水区 0.602 308 1.401 0.180 无 高明区 - 0.654 076 - 1.620 0.002 高-低 -
[1] 孙贵范, 邬堂春, 牛侨. 职业卫生与职业医学[M]. 7版. 北京: 人民卫生出版社, 2013: 16-17; 221-222. [2] 陈婉霞, 陈松根, 谭强, 等. 佛山市2011-2015年职业病防治现状与对策探讨[J]. 中国职业医学, 2017, 44(3): 345-347. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XYYX201703023.htm [3] KENNEDY M. ArcGIS地理信息系统基础与实训[M]. 2版. 蒋波涛, 袁娅娅, 译. 北京: 清华大学出版社, 2011: 3-5. [4] 谭强, 顾春晖, 王茂, 等. 广东省职业病发病的空间分析[J]. 预防医学, 2019, 31(2): 119-123. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZYFX201902003.htm [5] 陈剑, 孔德广, 胡权, 等. 地理信息系统在公共卫生领域的应用[J]. 国际流行病学传染病学杂志, 2014, 41(1): 61-64. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YXQB201211008.htm [6] 刘晓勇, 李旭东, 周珊宇, 等. 广东省职业病新发病例变化趋势拟合模型探讨[J]. 中国职业医学, 2020, 47(4): 410-413. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XYYX202004007.htm -
期刊类型引用(0)
其他类型引用(2)





 下载:
下载: