Effect of Rad51 gene silencing on repair of lead-induced DNA double-strand breaks in TK6 cells
-
+ English摘要:目的 研究Rad51基因沉默后对醋酸铅染毒致人淋巴母细胞(TK6细胞)DNA双链断裂损伤的修复作用的影响。方法 构建Rad51沉默慢病毒载体及阴性对照,感染对数期TK6细胞,荧光定量PCR和Western blot验证感染效果。运用480 μmol/L的醋酸铅染毒TK6细胞24 h(Control组、shRNA-NC组和shRNA-Rad51组),采用免疫荧光法检测TK6细胞的磷酸化组蛋白H2AX(γ-H2AX)的表达,Western Blot检测TK6细胞的Rad51、BRCA1、53BP1蛋白的表达。结果 shRNA-Rad51组的Rad51 mRNA表达水平和Rad51蛋白表达水平均低于Control组及shRNA-NC组(P<0.01);shRNA-Rad51组的γ-H2AX阳性率为(27.48 ± 1.66)%,与Control组的(14.77 ± 1.21)%及shRNA-NC组的(14.04 ± 1.31)%比较,差异均有统计学意义(P<0.01);shRNA-Rad51组的BRCA1蛋白表达水平为(0.25 ± 0.03),与Control组的(0.55 ± 0.04)及shRNA-NC组的(0.51 ± 0.04)比较,差异均有统计学意义(P<0.01);shRNA-Rad51组的53BP1蛋白表达水平为(3.24 ± 0.27),与Control组的(2.01 ± 0.19)及shRNA-NC组的(2.11 ± 0.17)比较,差异均有统计学意义(P<0.01)。结论 Rad51基因沉默后,TK6细胞HR修复通路受抑制和NHEJ修复通路激活,TK6细胞对铅遗传毒性的敏感性增强。
-
铅是一种自然界广泛存在的有毒重金属,主要通过呼吸道、消化道的途径进入人体,会对人体全身多个系统产生毒性作用,是最常见的环境污染物和职业病危害因素[1]。近年来,铅及其化合物对细胞的遗传损伤广受关注,铅会引起细胞DNA双链断裂损伤,但关于铅对细胞DNA双链断裂损伤后的修复机制的研究有限,且存在争议[2-3]。有研究发现铅遗传毒性的发生与DNA损伤修复基因的表达异常有密切联系,但其具体机制目前还不完全清楚[4]。Rad51基因作为一种DNA修复基因,其编码的蛋白是参与同源重组(homologous recombination,HR)的关键酶,对维持DNA的遗传稳定和多样性起着至关重要的作用[5]。为研究Rad51基因对铅遗传毒性的影响,本研究选取TK6细胞进行传代培养,利用短发夹RNA(shRNA)抑制TK6细胞Rad51基因表达,采用免疫荧光法、荧光定量PCR、Western Blot等分子生物学技术从不同的层面研究Rad51基因沉默后铅致TK6细胞遗传损伤的影响,以期为铅遗传损伤的防控提供实验基础。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 实验试剂和仪器
醋酸铅粉剂(美国Sigma公司)、RPMI 1640培养基(美国Gibco公司)、马血清(美国Gibco公司)、γ-H2AX(英国Abcam公司)、Rad51抗体(中国万类生物公司)、BRCA1抗体(中国万类生物公司)、53BP1抗体(中国abclonal公司)、Super M-MLV反转录酶(北京BioTeke公司)、RNase inhibitor(北京BioTeke公司)、2 × Power Taq PCR MasterMix(北京BioTeke公司)、全蛋白提取试剂盒(中国万类生物公司)、内参抗体β-actin(中国万类生物公司)、羊抗兔IgG-HRP(中国万类生物公司);NW10LVF超纯水系统(香港Heal Force公司)、H-2050R超速冷冻离心机(湖南湘仪公司)、DYCZ-24DN双垂直蛋白电泳仪(北京六一公司)、Exicycler 96荧光定量PCR仪(韩国BIONEER公司)、NANO 2000紫外分光光度计(美国Thermo公司)、WD-9413B型凝胶成像系统(北京六一公司)、ELX-800酶标仪(美国BIOTEK公司)。
1.2 方法
1.2.1 Rad51 shRNA干扰慢病毒载体构建
Rad51 shRNA干扰慢病毒载体(pLKO.1-EGFP-puro)由万类生物科技有限公司构建。干扰序列sh-Rad51:ccgCGATGTGAAGAAATTGGAAGAttcaagagaTCTTCCAATTTCTTCACATCGttttt,对照序列sh-NC:ccgTTCTCCGAACGTGTCACGTttcaagagaACGTGACACGTTCGGAGAAttttt。
1.2.2 细胞培养和实验分组
TK6细胞由福建省疾病预防控制中心郑奎成教授提供。TK6细胞培养条件为37 ℃下添加10%热灭活马血清的RPMI1640培养基,置于体积分数5%的二氧化碳培养箱中。TK6细胞分4组:Normal组(未经感染的TK6细胞,醋酸铅未染毒)、Control组(未经感染的TK6细胞,480 μmol/L的醋酸铅避光染毒24 h)、shRNA-NC组(经空载慢病毒感染的TK6细胞,480 μmol/L的醋酸铅避光染毒24 h)、shRNA-Rad51组(经干扰慢病毒感染的TK6细胞,480 μmol/L的醋酸铅避光染毒24 h)。
1.2.3 实时荧光定量聚合酶链反应(qPCR)
提取样本总RNA,使用紫外分光光度计NANO 2000测定各样本中RNA的浓度。将得到的RNA样本进行反转录以得到对应的cDNA(引物序列见表 1),用韩国BIONEER公司生产的ExicyclerTM 96荧光定量仪通过2-△△CT方法进行荧光定量分析,反应条件为94 ℃ 5 min,1个循环;94 ℃ 10 s,60 ℃ 20 s,72 ℃ 30 s,40个循环。
表 1 Rad51基因qPCR的引物序列名称 序列(5′-3′) 引物长度/bp 解链温度(tm)/℃ 产物长度/bp Rad51 F AAATGCCAACGATGTGA 17 49.4 220 Rad51 R GGAGCCAGTAGTAATCTGTATG 22 51.5 β-actin F GGCACCCAGCACAATGAA 18 57.7 168 β-actin R TAGAAGCATTTGCGGTGG 18 55.1 1.2.4 Western blot检测
抽提样本蛋白质,使用酶标仪测定各样本中蛋白质的浓度。依次进行SDS-PAGE、转印至PVDF膜、封闭、孵育一抗、孵育二抗、ECL底物发光、图像保存、用凝胶图像处理系统(Gel-Pro-Analyzer软件)分析目标条带的光密度值。
1.2.5 免疫荧光染色检测γ-H2AX表达
收集细胞并固定在载玻片上,将载玻片与体积分数0.1% tritonX-100在室温下孵育30 min。用磷酸缓冲盐溶液(PBS)清洗,并在室温下与山羊血清孵育15 min。此后,添加多克隆抗H2AX抗体4 ℃过夜孵育。然后,用PBS清洗,并在室温下与Cy3标记山羊抗兔IgG孵育1 h。用PBS清洗,使用荧光染料DAPI进行核复染。用PBS清洗,将细胞均匀地涂在干净的载玻片上,滴加抗荧光淬灭剂封片,于荧光显微镜下放大400倍观察染色效果。
1.2.6 统计学分析
采用SPSS 19.0软件进行统计分析,连续性数据的描述采用均数±标准差(x ± s)表示,多组间均数的比较采用单因素方差分析,进一步两两比较采用LSD-t检验。检验水准α = 0.05。
2. 结果
2.1 Rad51基因沉默对TK6细胞Rad51基因表达的影响
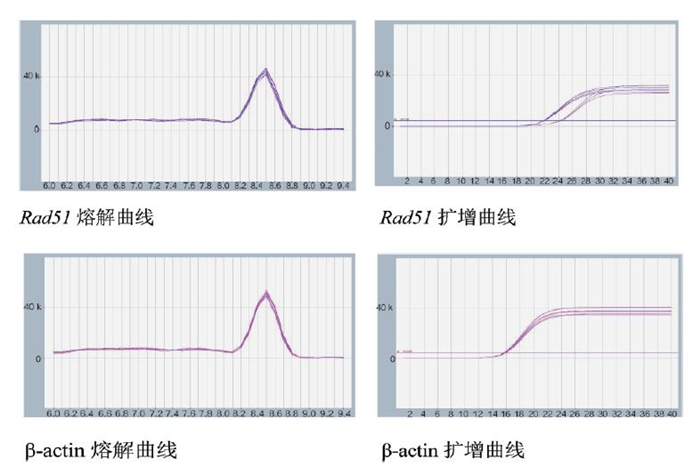
应用荧光定量PCR和Western Blot技术检测Rad51基因沉默后TK6细胞的mRNA和蛋白的表达水平。荧光定量PCR扩增体系稳定,熔解曲线峰值高,无引物二聚体及非特异性产物产生,扩增产物特异(见图 1)。各组间mRNA、Rad51蛋白表达水平差异均有统计学意义(P<0.01)。进一步两两比较,与Control组和shRNA-NC组相比,shRNA-Rad51组细胞中Rad51蛋白mRNA表达量均明显下降,差异有统计学意义(P<0.01),而Control组和shRNA-NC组之间差异无统计学意义(P>0.05)。见表 2。
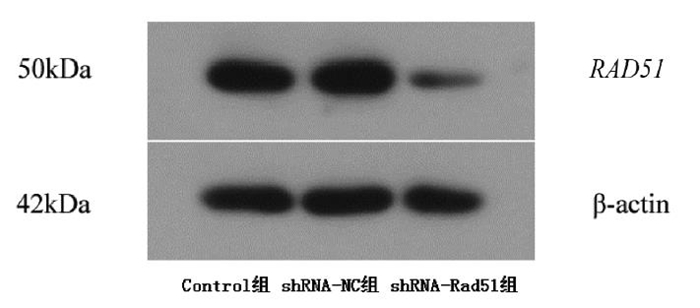
表 2 K6细胞Rad51基因的表达(n = 3)组别 mRNA表达水平 Rad51蛋白表达水平 Control组 1.00 ± 0.02 1.00 ± 0.08 shRNA-NC组 0.99 ± 0.06 0.96 ± 0.06 shRNA-Rad51组 0.24 ± 0.01 0.20 ± 0.03 F值 259.84 167.78 P值 <0.01 <0.01 Western Blot结果显示,相比于Control组和shRNA-NC组,shRNA-Rad51组中Rad51蛋白的表达量呈现明显下降趋势,下降约80%,差异具有统计学意义(P<0.01),而Control组和shRNA-NC组之间差异无统计学意义(P>0.05)。见图 2、表 2。
2.2 Rad51基因沉默对TK6细胞DNA双链断裂损伤生物标志物γ-H2AX表达的影响
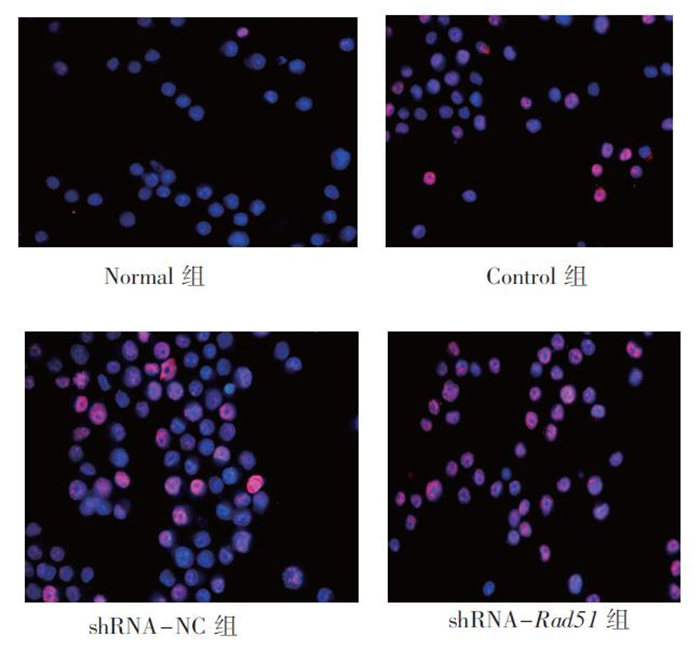
γ-H2AX蛋白是反映DNA双链断裂损伤的生物标志物。采用免疫荧光技术观察Rad51基因沉默后醋酸铅诱导细胞DNA双链断裂的情况,如图 3所示,DAPI荧光染色的细胞核呈现蓝色,而Cy3荧光标记的γ-H2AX蛋白呈现红色。Normal组、Control组、shRNA-NC组、shRNA-Rad51组γ-H2AX阳性率分别为(1.81 ± 0.58)%、(14.77 ± 1.21)%、(14.04 ± 1.31)%、(27.48 ± 1.66)%,4组比较差异有统计学意义(F = 210.32,P<0.01);进一步比较显示,shRNA-Rad51组γ-H2AX阳性率高于Control组和shRNA-NC组,差异均有统计学意义(P>0.01),而Control组细胞γ-H2AX阳性率和shRNA-NC组细胞γ-H2AX阳性率差异无统计学意义(P<0.05)。见图 3、表 3。
表 3 TK6细胞γ-H2AX阳性率和BRCA1、53BP1蛋白表达的影响(n = 3) 组别 细胞γ-H2AX阳性率/% BRCA1蛋白表达水平 53BP1蛋白表达水平 Normal组 1.81 ± 0.58① 1.00 ± 0.06① 1.00 ± 0.11① Control组 14.77 ± 1.21① 0.55 ± 0.04① 2.01 ± 0.19① shRNA-NC组 14.04 ± 1.31① 0.51 ± 0.04① 2.11 ± 0.17① shRNA-Rad51组 27.48 ± 1.66 0.25 ± 0.03 3.24 ± 0.27 F值 210.32 151.21 67.13 P值 <0.01 <0.01 <0.01 注:①与shRNA-Rad51组比较,P<0.01。 2.3 Rad51基因沉默对DNA双链断裂损伤修复蛋白BRCA1表达的影响
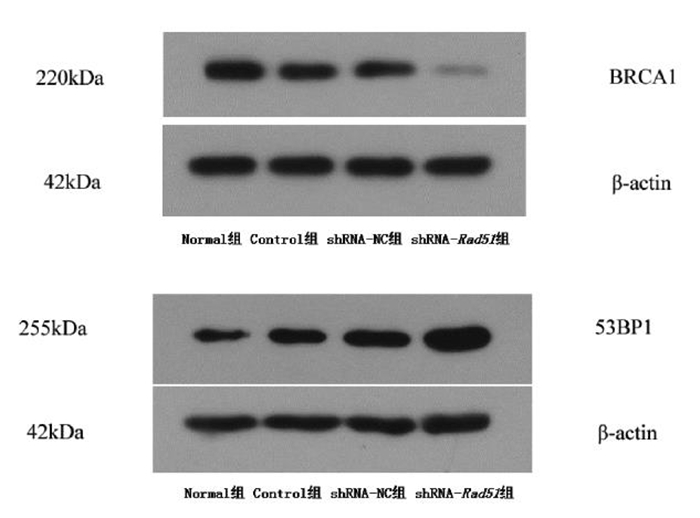
醋酸铅染毒24 h后,Normal组、Control组、shRNA-NC组、shRNA-Rad51组的BRCA1蛋白表达水平分别为(1.00 ± 0.06)、(0.55 ± 0.04)、(0.51 ± 0.04)、(0.25 ± 0.03),4组比较差异具有统计学意义(F = 151.21,P<0.01);进一步比较显示,shRNA-Rad51组BRCA1蛋白表达水平低于Control组和shRNA-NC组,差异均有统计学意义(P<0.01),而Control组细胞BRCA1蛋白表达水平和shRNA-NC组细胞BRCA1蛋白表达水平比较,差异无统计学意义(P>0.05)。见图 4、表 3。
2.4 Rad51基因沉默对DNA双链断裂损伤修复蛋白53BP1表达的影响
醋酸铅染毒24 h后,Normal组、Control组、shRNA-NC组、shRNA-Rad51组的53BP1蛋白表达水平分别为(1.00 ± 0.11)、(2.01 ± 0.19)、(2.11 ± 0.17)、(3.24 ± 0.27),4组比较差异具有统计学意义(F = 67.13,P<0.01);进一步比较显示,shRNA-Rad51组53BP1蛋白表达水平高于Control组和shRNA-NC组,差异均有统计学意义(P<0.01),而Control组细胞53BP1蛋白表达水平和shRNA-NC组细胞53BP1蛋白表达水平比较差异无统计学意义(P>0.05)。见图 4、表 3。
3. 讨论
真核细胞DNA双链断裂主要通过同源重组(homologous recombination,HR)和非同源末端连接(non-homologous end joining,NHEJ)两种方式进行修复,若修复机制产生缺陷将导致遗传物质改变[6]。Rad51蛋白是HR修复通路中的一个生物活性标志物,是调控HR修复DNA双链断裂的核心蛋白,是催化断裂的DNA双链与完整的同源DNA姐妹链进行链间转移置换的关键酶,Rad51蛋白所介导的同源重组修复有利于维持基因组的稳定,抵抗各种细胞毒性因子对DNA的损害,在HR修复通路中扮演主要角色[5, 7]。
TK6细胞为人源细胞,分化能力高,拥有稳定的基因组,与常用的小鼠细胞相比,p53基因表达正常,可以更加真实地反映毒物对人体细胞的毒性作用,可避免动物实验结果外推至人的种属差异等。本研究应用Rad51 shRNA干扰慢病毒载体(pLKO.1-EGFP-puro)感染TK6细胞,应用实时荧光定量PCR和Western Blot技术检测Control组、shRNA-NC组和shRNA-Rad51组中Rad51基因mRNA和蛋白的表达水平,显示shRNA-Rad51组的mRNA和蛋白的表达明显下降,说明Rad51 shRNA能够有效抑制TK6细胞Rad51的表达。γ-H2AX是DNA双链断裂的标志物,本研究使用免疫荧光法检测3组TK6细胞在醋酸铅染毒后细胞γ-H2AX焦点形成情况,发现铅诱导shRNA-Rad51组TK6细胞γ-H2AX的表达显著增高,研究结果提示,Rad51表达下调会明显降低TK6细胞维持基因完整性的能力。Rad51在HR中扮演着不可缺少的角色,Rad51表达的下调与细胞执行HR能力的下降存在着极大的关联[5]。近年来,有实验用siRNA抑制Rad51基因表达后,发现细胞对DNA损伤更敏感[8],这与本研究的结果相似。
DNA双链断裂是最严重的细胞遗传损伤,细胞发生遗传损伤后会引发DNA损伤修复。细胞DNA双链断裂损伤的修复机制主要有HR修复和NHEJ修复两种。BRCA1蛋白是调控HR修复DNA双链断裂的关键蛋白,在HR修复通路的多个环节发挥作用,53BP1蛋白是参与DNA双链断裂后NHEJ修复通路的重要蛋白[9]。本研究中检测了BRCA1与53BP1蛋白的表达,醋酸铅作用TK6细胞后24 h,shRNA-Rad51组TK6细胞BRCA1的表达出现了显著降低,53BP1的表达出现显著升高,提示Rad51基因沉默可能导致TK6细胞HR修复通路的抑制和NHEJ修复通路的激活,促进TK6细胞的NHEJ修复效率。
HR修复和NHEJ修复两种修复通路共同维持基因组的完整性,但也存在着竞争抑制,HR通路的抑制和/或NHEJ通路的激活将使DNA双链断裂倾向于易错修复途径,导致染色体异常等遗传损伤生成[10-12]。本研究显示,Rad51基因沉默后,TK6细胞容易被铅诱导DNA双链断裂,其机制可能存在HR修复通路抑制和NHEJ修复通路异常活化,修复过程有NHEJ的倾向性。
作者声明 本文无实际或潜在的利益冲突 -
表 1 Rad51基因qPCR的引物序列
名称 序列(5′-3′) 引物长度/bp 解链温度(tm)/℃ 产物长度/bp Rad51 F AAATGCCAACGATGTGA 17 49.4 220 Rad51 R GGAGCCAGTAGTAATCTGTATG 22 51.5 β-actin F GGCACCCAGCACAATGAA 18 57.7 168 β-actin R TAGAAGCATTTGCGGTGG 18 55.1 表 2 K6细胞Rad51基因的表达(n = 3)
组别 mRNA表达水平 Rad51蛋白表达水平 Control组 1.00 ± 0.02 1.00 ± 0.08 shRNA-NC组 0.99 ± 0.06 0.96 ± 0.06 shRNA-Rad51组 0.24 ± 0.01 0.20 ± 0.03 F值 259.84 167.78 P值 <0.01 <0.01 表 3 TK6细胞γ-H2AX阳性率和BRCA1、53BP1蛋白表达的影响
(n = 3) 组别 细胞γ-H2AX阳性率/% BRCA1蛋白表达水平 53BP1蛋白表达水平 Normal组 1.81 ± 0.58① 1.00 ± 0.06① 1.00 ± 0.11① Control组 14.77 ± 1.21① 0.55 ± 0.04① 2.01 ± 0.19① shRNA-NC组 14.04 ± 1.31① 0.51 ± 0.04① 2.11 ± 0.17① shRNA-Rad51组 27.48 ± 1.66 0.25 ± 0.03 3.24 ± 0.27 F值 210.32 151.21 67.13 P值 <0.01 <0.01 <0.01 注:①与shRNA-Rad51组比较,P<0.01。 -
[1] 陈林. 职业性铅接触对健康危害的风险评估[D]. 南京: 东南大学, 2018. [2] LIU X, WU J, SHI W, et al. Lead induces genotoxicity via oxidative stress and promoter methylation of DNA repair genes in human lymphoblastoid TK6 Cells[J]. Med Sci Monit, 2018, 24: 4295-4304. doi: 10.12659/MSM.908425
[3] SHAH A J, LAKKAD B C, RAO M V. Genotoxicity in lead treated human lymphocytes evaluated by micronucleus and comet assays[J]. Indian J Exp Biol, 2016, 54(8): 502-508.
[4] SINGH P, MITRA P, GOYAL T, et al. Evaluation of DNA damage and expressions of DNA repair gene in occupationally lead exposed workers (Jodhpur, India)[J]. Biol Trace Elem Res, 2021, 199(5): 1707-1714. doi: 10.1007/s12011-020-02298-2
[5] BONILLA B, HENGEL S R, GRUNDY M K, et al. RAD51 gene family structure and function[J]. Annu Rev Genet, 2020, 54: 25-46. doi: 10.1146/annurev-genet-021920-092410
[6] ENSMINGER M, LÖBRICH M. One end to rule them all: non-homologous end-joining and homologous recombination at DNA double-strand breaks[J]. Br J Radiol, 2020, 93(1115): 20191054. doi: 10.1259/bjr.20191054
[7] GODIN S K, SULLIVAN M R, BERNSTEIN K A. Novel insights into RAD51 activity and regulation during homologous recombination and DNA replication[J]. Biochem Cell Biol, 2016, 94(5): 407-418. doi: 10.1139/bcb-2016-0012
[8] LIAN H, CUI J, WANG Y, et al. Downregulation of Rad51 participates in OTA-induced DNA double-strand breaks in GES-1 cells in vitro[J]. Toxicol Lett, 2014, 226(2): 214-221. doi: 10.1016/j.toxlet.2014.02.002
[9] BELOTSERKOVSKAYA R, RAGA GIL E, LAWRENCE N, et al. PALB2 chromatin recruitment restores homologous recombination in BRCA1-deficient cells depleted of 53BP1[J]. Nat Commun, 2020, 11(1): 819. doi: 10.1038/s41467-020-14563-y
[10] RANJHA L, HOWARD S M, CEJKA P. Main steps in DNA double-strand break repair: an introduction to homologous recombination and related processes[J]. Chromosoma, 2018, 127(2): 187-214.
[11] 李家丽, 刘颖. 非同源末端连接研究进展及其在肿瘤发生和治疗中的意义[J]. 基础医学与临床, 2019, 39(6): 899-903. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JCYL201906026.htm [12] SCULLY R, PANDAY A, ELANGO R, et al. DNA double-strand break repair-pathway choice in somatic mammalian cells[J]. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol, 2019, 20(11): 698-714.
-
期刊类型引用(2)
1. 吴俊,郭丹妮. 低年资护士角色压力与职业认同感的相关性及其职业认同感的影响因素分析. 中国当代医药. 2024(21): 150-154 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 王珍,唐薇敏. 应急预案护理管理在医院面对突发公共卫生事件中的护理管理价值. 中国卫生产业. 2024(20): 83-85+100 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(0)





 下载:
下载: