Influence of wind speed and leakage rate on the damage space of carbonyl chloride leakage and diffusion
-
+ English摘要:目的 建立某化工厂TDI生产泄漏事故的计算流体动力学(CFD)模型,减少甲苯二异氰酸酯(TDI)生产过程中碳酰氯泄漏造成的危险。方法 研究环境风速和泄漏速率对碳酰氯阈浓度和致死浓度危害三维空间范围的影响,利用结果数据拟合了两种因素共同作用下阈浓度云团危害空间的快速估算式。结果 模拟结果显示风速增大,阈浓度和致死浓度云团危害范围均减小,且风速从1.5 m/s增大到4.5 m/s,阈浓度云团危害范围减半,阈浓度云团危害长度远大于宽度和高度;泄漏速率增大,阈浓度和致死浓度云团危害范围均呈线性增长;最不利条件下,泄漏速率分别为0.018 kg/s、0.031 kg/s、0.045 kg/s时,阈浓度云团危害长度刚好到达下风向1 000 m、1 500 m、2 000 m安全防护距离的位置;对于一般规模的泄漏事故,致死浓度云团不会危害到厂区以外。结论 研究结果可为碳酰氯泄漏事故应急救援提供理论和数据支持。
-
碳酰氯(又称光气,化学式为COCl2)是重要的有机中间体,被广泛地应用于农药、医药和染料的生产,因其毒性剧烈[1],预防碳酰氯泄漏是安全防护重点,因此,研究碳酰氯泄漏扩散规律对于精确预防和减少事故具有重要意义。部分学者利用高斯模型[2]、CALPUFF模型[3]和SLAB模型[4-5]对碳酰氯气相泄漏扩散进行预测和风险评估,但主要是基于特定事故的危害预测研究,针对关键因素对碳酰氯泄漏事故扩散规律影响的研究比较少。因此,本研究采用计算流体动力学(computational fluid dynamics,CFD)模型研究环境风速和泄漏速率对碳酰氯扩散规律的影响,定量计算某参数对碳酰氯泄漏后扩散三维危害空间的影响,为事故的精准风险预测和应急救援方案制定提供理论依据和数据支撑。
1. 碳酰氯泄漏事故扩散的CFD模型
1.1 碳酰氯泄漏事故物理模型构建及网格划分
1.1.1 碳酰氯泄漏事故物理模型
假设某甲苯二异氰酸酯(toluene diisocyanate mixture,TDI)生产化工厂光化反应分离塔内的气相碳酰氯发生泄漏,根据实际情况将光化反应分离塔模型简化为一圆柱体,建立其物理模型,并确定计算域。为了使边界条件对数值模拟结果的影响达到最小,根据LaKehal[6]关于计算域的研究,选择以2 200 m × 500 m × 120 m的空间作为模拟计算域,建立其物理模型如图 1所示(采用ICEM软件建立)。由于此类化工厂区下风向一定安全防护距离内禁止存在人员密集区,因此所选计算域下风向假定无障碍物;而安全防护距离有三个,分别为2 000 m、1 500 m、1 000 m,故主要研究最远的安全防护距离2 000 m以内泄漏事故云团的危害范围。
1.1.2 计算域内网格划分
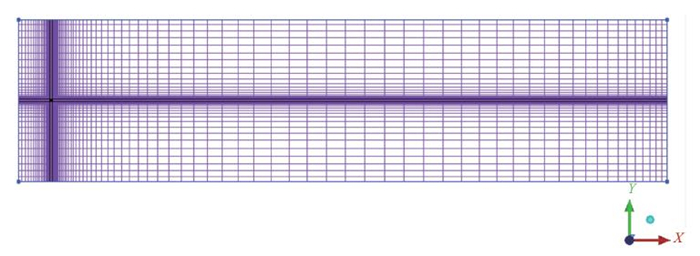
使用结构化体网格的Block划分方法,保证划分的网格数量少、质量好。划分时,对泄漏源、建筑区附近和地面附近的网格进行加密,距离重点研究的危害区域越远的地方网格越稀疏。利用软件ICEM划分计算域网格如图 2所示。划分所得共计556 200个网格(主要的细分网格集中在加密区域),图中左侧中部密集区域交汇点为泄漏源位置。
1.2 碳酰氯泄漏事故扩散的数学模型构建
使用Fluent软件构建数学模型,进行数值模拟研究。采用组分传输模型和湍流k-ε模型描述碳酰氯蒸气的泄漏扩散物理规律,利用质量扩散系数描述碳酰氯蒸气分子在空气中的扩散能力和扩散程度。
1.2.1 组分传输模型
组分传输模型主要用来描述碳酰氯蒸气在空气中的扩散和两者混合组分在空间内输运的物理规律[7]。模型方程如下:
$$ \frac{\partial }{{\partial t}}\left( {\rho {Y_j}} \right) + \nabla \cdot \left( {\rho \vec v{Y_{\rm{j}}}} \right) = - \nabla \cdot {\vec J_{\rm{j}}} $$ (1) 式中:Yj为组分j的质量分数,单位%;$ {\vec J_{j}}$为组分j由于温度、浓度梯度导致的扩散率,单位%;$ \vec v$为速度矢量;t为时间,单位s。
1.2.2 湍流k-ε模型
采用k-ε模型描述近似完全湍流的流动过程[8-9]。模型方程如下:
k方程:
$$ \frac{\partial }{{\partial {\rm{t}}}}(\rho k) + \frac{\partial }{{\partial {x_i}}}\left( {\rho k{u_i}} \right) = \frac{\partial }{{\partial {x_j}}}\left[ {\left( {\mu + \frac{{{\mu _t}}}{{{\sigma _k}}}} \right)\frac{{\partial k}}{{\partial {x_j}}}} \right] + {G_k} + {G_b} - \rho \varepsilon - {Y_M} + {S_k} $$ (2) e方程:
$$ \frac{\partial }{{\partial {\rm{t}}}}(\rho \varepsilon ) + \frac{\partial }{{\partial {x_i}}}\left( {\rho \varepsilon {u_i}} \right) = \frac{\partial }{{\partial {x_i}}}\left[ {\left( {\mu + \frac{{{\mu _t}}}{{{\sigma _\varepsilon }}}} \right)\frac{{\partial \varepsilon }}{{\partial {x_j}}}} \right] + {C_{1\varepsilon }}\frac{\varepsilon }{k}\left( {{G_k} + {C_{3\varepsilon }}{G_b}} \right) - {C_{2\varepsilon }}\rho \frac{{{\varepsilon ^2}}}{k} + {S_\varepsilon } $$ (3) 式中:Gk为由速度梯度产生的湍流动能,单位J;Gb为由浮力引起的湍流动能的产生项,单位J;YM为在可压缩流中的脉动扩张项;σk、σε为k方程和ε方程对应的普朗特数;Sk、Sε为用户自定义源项,可根据不同情况设定;C1ε、C2ε、C3ε为经验常数,C1ε=1.44,C2ε=1.92,C3ε=0.99;k为湍动能,单位J;ε为湍流耗散率;ui为i方向的速度矢量;ui为湍动黏度,单位Pa·s;t为时间,单位s。
1.2.3 扩散系数确定
本文研究碳酰氯蒸气在空气中的扩散,对于二元气体扩散系数的确定,采用Fuller公式[10]进行计算:
$$ D = \frac{{0.101{T^{1.75}}\sqrt {\frac{1}{{{M_A}}} +} \frac{1}{{{M_B}}} }}{{P{{\left[ {{{\left( {\sum {{v_A}} } \right)}^{\frac{1}{3}}} + {{\left( {\sum {{v_B}} } \right)}^{\frac{1}{3}}}} \right]}^2}}} $$ (4) 式中,D为碳酰氯蒸气对空气的扩散系数,单位m2/s;MA、MB为碳酰氯和空气的摩尔质量,单位kg/mol;ΣvA和ΣvB是碳酰氯和空气的分子扩散体积,单位cm3/mol;T为碳酰氯气体的温度,单位K。
计算所得扩散系数D = 9.0×10-6 m2/s,在Fluent软件的组分输运模型中设置其扩散系数。
1.2.4 模型假设
(1)泄漏过程中风向不受高度影响;(2)泄漏物质在扩散过程中不发生任何形式的化学反应;(3)假设气体为不可压缩气体;(4)假设计算域内扩散无障碍物影响;(5)风向和风速均恒定不变;(6)环境温度不发生改变。
2. 泄漏事故场景假设及模拟结果分析
2.1 泄漏事故场景假设
假设该化工厂光化反应分离塔内的气相碳酰氯发生连续泄漏,光化反应分离塔在内的建筑为一直径5 m,高20 m的圆柱体,距离左侧风速入口100 m,泄漏口为一直径100 mm的圆孔,位于分离塔顶部,分离塔内碳酰氯温度为280 k,室外空气温度为283 k。根据HJ 169—2018《建设项目环境风险评价技术导则》设置最不利环境,风速1.5 m/s,空气湿度50%[11]。假设为城市背景,地面粗糙度为0.4。计算域两侧面和顶部为对称边界,地面和壁面为无滑移壁面边界。风速和泄漏速率如此取值的原因分别见2.2和2.3节。
碳酰氯蒸气发生泄漏后形成蒸气云团,会对工作人员及周围居民产生极大的危害,不同浓度云团的危害影响见表 1[12]。因为阈浓度云团是对无防护人员造成伤害的最低浓度,即决定人员疏散撤离的浓度阈值,在致死浓度云团内久留会致人死亡,其内部人员是救援的首要目标,所以本文主要研究的危害空间对象为阈浓度云团和致死浓度云团。
表 1 不同浓度碳酰氯对无防护人员的危害程度危害云团 云团中碳酰氯质量浓度/(mg/m3) 危害程度 阈浓度云团 5 阈浓度,长期(10 min以上)处于该浓度将有害健康 不可耐浓度云团 20 不可耐浓度,该浓度下作用1 min会产生典型中毒症状恶心、咳嗽和呕吐,人体已经能感觉到明显不适 致死浓度云团 500 致死浓度,该浓度下15 min内会使90%以上无防护人员死亡 2.2 风速对阈浓度云团危害范围的影响
为研究风速对碳酰氯泄漏阈浓度云团危害范围的影响,采用控制变量的方法,控制泄漏速率0.031 kg/s和其他条件不变,仅改变风速大小进行展开研究。文献[11]中规定的最不利风速为1.5 m/s,实验发现:发生8级以上大风时,阈浓度云团的危害长度均小于相应泄漏速率下安全防护距离的一半。基于此,从1级风的1.5 m/s到7级风的16.5 m/s,其间等距划分模拟风速,分别取风速为1.5 m/s、4.5 m/s、7.5 m/s、10.5 m/s、13.5 m/s和16.5 m/s。未加入0级风速的原因是:一方面,本次研究针对某一方向风对泄漏扩散危害空间的影响。另一方面,是为提高计算速度,环境风入口距泄漏源较近,若加入0级风,则需要向上风向扩展计算域,会严重增加其他风速下的危害空间计算的计算量。
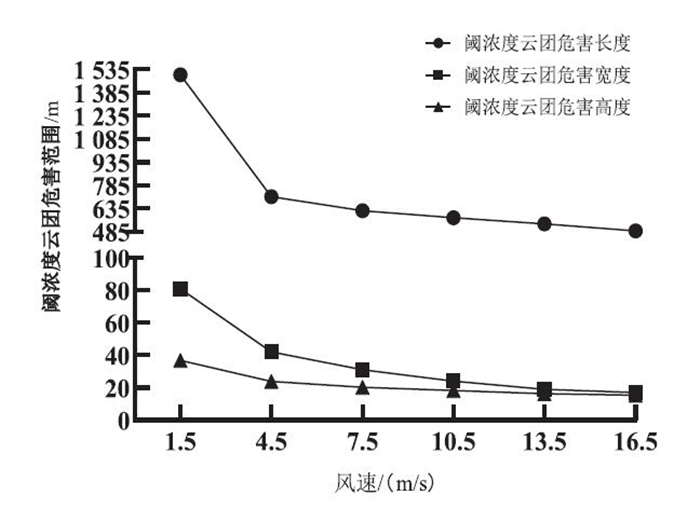
模拟计算碳酰氯连续泄漏的事故场景,整理计算结果得到不同风速下阈浓度云团的最大危害长度、宽度和高度,见图 3。
如图 3所示,随着风速增大,阈浓度云团的危害范围(包括长度、宽度和高度)减小。当风速小于4.5 m/s时,风速增大,阈浓度云团危害范围迅速下降,且风速从1.5 m/s增大到4.5 m/s时,云团的长、宽和高从原来的1 500 m、81 m、36.8 m减小到712 m、42 m、23.9 m,各长度约为原来长度的一半左右;当风速超过4.5 m/s时,阈浓度云团危害范围下降速度明显变缓。这是因为风速加大,风对泄漏物云团的卷吸作用增强,加快了云团的稀释,阈浓度云团危害范围快速减小,但是云团被稀释到一定浓度后和周围空气的浓度梯度越来越小。根据菲克定律[13],云团扩散稀释的速度减小,所以阈浓度云团危害范围下降、速度变缓直至不再变化。另外,发现阈浓度云团危害长度在数值上远大于宽度和高度,这是因为碳酰氯蒸气云团属于典型的重气云团,其在两侧和垂直方向上的自主扩散不明显,而风对它具有明显的输运和卷吸作用,且风速越大,输运和卷吸能力越显著。经过在不同泄漏速率下的模拟计算和分析,证明以上取得的结论不会因泄漏速率不同而改变。
由以上规律可知:风速1.5 m/s(1级风)是在有风情况下,事故危害的最不利条件。结论与HJ 169—2018《建设项目环境风险评价技术导则》中的推荐的最不利气象参数[11]一致。为了研究事故的最大危害范围,继续以1.5 m/s为固定风速进行研究。
2.3 泄漏速率对阈浓度云团危害范围的影响
2.3.1 泄漏速率的设置依据
为贴近应急救援行动实际,选择了泄漏速率为0.018 kg/s、0.031 kg/s、0.045 kg/s实施研究,具体理由如下:
国家标准《光气及光气化产品生产安全规程》[14]中规定:“装置系统光气(折纯)总量 < 3 000 kg,安全防护距离为1 000 m;总量3 000 ~ 5 000 kg,安全防护距离为1 500 m;总量 > 5 000 kg,安全防护距离为2 000 m。安全防护距离是从光气及光气化产品生产装置的边界开始计算,至人员相对密集区域边界之间的最小允许距离。”标准中规定了安全防护距离,但是对于泄漏事故应急救援而言,如果能够根据泄漏孔径确定泄漏速率,从而快速确定阈浓度云团危害范围能否蔓延到安全防护距离以外,明确安全防护距离以外的人员是否需要紧急疏散,这将在很大程度上提高事故处置的反应速度和救援效率。
假设风速固定为1.5 m/s,其他条件按上节设置,上述安全防护距离为危害范围的长度,研究不同安全防护距离对应的泄漏速率。
在实际应用时通过泄漏速率就能确定最不利风速下的阈浓度云团危害范围是否在规定的安全防护距离以内。事故处置人员可以通过测量泄漏孔径和分离塔内压力,利用公式(5)计算出泄漏速率。采用实验设计中的来回调试优选法反复调整泄漏速率,模拟计算使阈浓度云团危害范围长度不断接近1 000 m、1 500 m、2 000 m。最终,得到对应的泄漏速率分别为0.018 kg/s、0.031 kg/s、0.045 kg/s。
$$ Q = Y{C_{\rm{d}}}AP\sqrt {\frac{{M\gamma }}{{RT}}{{\left( {\frac{2}{{\gamma + 1}}} \right)}^{\frac{{\gamma + 1}}{{\gamma - 1}}}}} $$ (5) 式中:Q为碳酰氯泄漏速率,单位kg/s;P为容器压力,单位Pa;Cd为碳酰氯泄漏系数;泄漏口是圆形,取1.00;M为物质的摩尔质量,单位kg/mol;R为气体常数,单位J/(mol·K);T为气体温度,单位K;A为泄漏口面积,单位m2;P0为环境压力,单位Pa;γ为气体的绝热指数,即定压比热容与定容比热容之比;Y为流出系数,若为临界流Y = 1.0;若为次临界流,按式(6)计算:
$$ Y = {\left[ {\frac{{{P_0}}}{P}} \right]^{\frac{1}{\gamma }}} \times {\left\{ {1 - {{\left[ {\frac{{{P_0}}}{P}} \right]}^{\frac{{(\gamma - 1)}}{\gamma }}}} \right\}^{\frac{1}{2}}} \times {\left\{ {\left[ {\frac{2}{{\gamma - 1}}} \right] \times {{\left[ {\frac{{\gamma + 1}}{2}} \right]}^{\frac{{(\gamma + 1)}}{{(\gamma - 1)}}}}} \right\}^{\frac{1}{2}}} $$ (6) 2.3.2 泄漏速率对阈浓度云团危害范围的影响
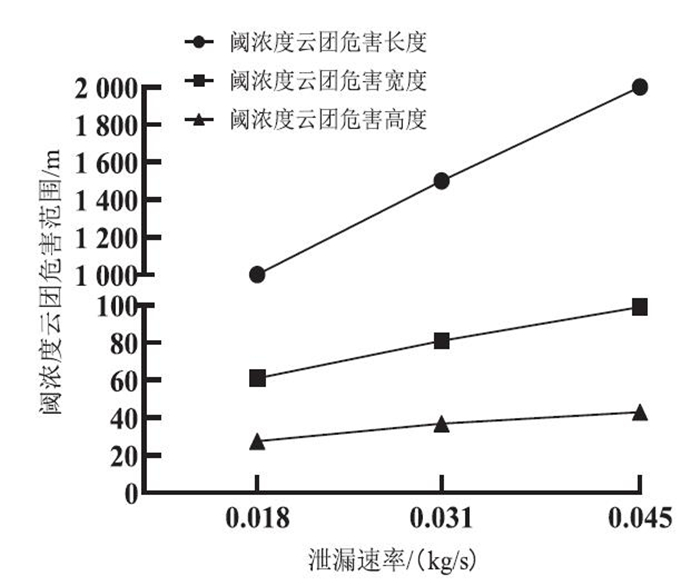
为研究泄漏速率对碳酰氯泄漏阈浓度云团危害范围的影响,固定风速为1.5 m/s且其他条件不变,取不同的泄漏速率0.018 kg/s、0.031 kg/s、0.045 kg/s,模拟计算碳酰氯连续泄漏的事故场景,整理计算结果得到不同泄漏速率下阈浓度云团的最大危害长度、宽度和高度,见图 4。
由图 4可见:随着泄漏速率增大,阈浓度云团的危害范围(包括长度、宽度和高度)呈线性增长;速率为0.018 kg/s时,阈浓度云团危害最大长度为1 000 m,最大宽度为61 m,最大高度为27.4 m;速率为0.031 kg/s时,阈浓度云团危害最大长度为1 500 m,最大宽度为81 m,最大高度为36.8 m;速率为0.045 kg/s时,阈浓度云团危害最大长度为2 000 m,最大宽度为99 m,最大高度为43 m。这是因为泄漏速率增大,单位时间碳酰氯的泄漏量加大,所以阈浓度云团危害范围在各个方向上均呈线性增长。且此线性变化规律同样不会因风速的不同而改变,本次研究分别通过风速4.5 m/s、7.5 m/s、10.5 m/s、13.5 m/s、16.5 m/s的对比实验,已验证以上结论均成立。
2.4 风速和泄漏速率对阈浓度云团危害范围的综合影响
从上述分析可知,已得出的风速对阈浓度云团危害空间范围的影响多是定性结论,此外,CFD数值模拟虽能达到较高精度,但存在计算速度慢的缺点,因此,为将研究成果量化,本文将以上数据进行数据拟合,得到阈浓度云团最大危害范围与环境风速和泄漏速率的关系式,用来快速计算考虑风速和泄漏速率影响下阈浓度云团的最大危害空间范围。拟合关系式如下:
阈浓度云团危害长度拟合关系式:
$$ L = \frac{{ - 5.127 \times {{10}^9} + 5.993 \times {{10}^8}v + 5.87 \times {{10}^{11}}q}}{{1 + 2.914 \times {{10}^6}v + 1.559 \times {{10}^8}q}} $$ (7) 拟合度为0.98。
阈浓度云团危害宽度拟合关系式:
$$ W = \frac{{4.661 \times {{10}^7} + 3.849 \times {{10}^7}v + 3.1 \times {{10}^{10}}q}}{{1 + 5.385 \times {{10}^6}v + 1.611 \times {{10}^8}q}} $$ (8) 拟合度为0.99。
阈浓度云团危害高度拟合关系式:
$$ H = \frac{{ - 6.461 + 40.282v + 1.188 \times {{10}^4}q}}{{1{\rm{ + }}3.652v + 161.429q}} $$ (9) 拟合度为0.99。
以上式中:L、W、H分别为阈浓度云团长度、宽度、高度,单位m;v为风速,单位m/s;q为碳酰氯泄漏速率,单位kg/s。
验证:随机取不同的风速和泄漏速率,代入式(7)、(8)、(9)计算阈浓度云团危害长度、宽度、高度,再将风速和泄漏速率条件输入Fluent软件模拟计算阈浓度云团危害长度、宽度、高度,两者比较结果见表 2(表中括号内数据即为Fluent软件模拟计算所得数据),拟合度均达到0.96以上,证明拟合关系式能够满足快速估算的精度。
表 2 拟合关系式估算精度验证[关系式计算值(CFD实验值)] 验证编号 风速/(m/s) 泄漏速率/(kg/s) 阈长度 阈宽度 阈高度 拟合度 1 1.5 0.030 1 478(1 480) 80(78) 36.2(36.5) >0.97 2 4.0 0.031 935(955) 44(45) 25.4(24.8) >0.97 3 7.0 0.043 896(862) 37(38) 23.5(23.3) >0.96 2.5 风速和泄漏速率对致死浓度云团危害距离的影响
2.5.1 风速对致死浓度云团危害距离的影响
从2.2节中所得计算结果数据中提取致死浓度云团尺寸信息,研究风速对致死浓度云团危害距离的影响,得到结果见图 5。风速为1.5 m/s、4.5 m/s、7.5 m/s、10.5 m/s、13.5 m/s、16.5 m/s时,致死浓度危害距离长度分别为40 m、31 m、23 m、18 m、14 m、12 m,最大危害距离为40 m;风速越大,致死浓度云团危害距离越小,所得规律与2.2所述一致,原因亦相同;但是减小的速度与2.2不同,风速大于7.5 m/s时,致死浓度影响距离减小的趋势才开始变缓,这是因为致死浓度云团浓度比阈浓度云团浓度高两个量级,与周围气体的浓度梯度更大,保持高扩散稀释速率的能力更强,所以在更大风速的输运稀释作用下才会放缓稀释速度。
2.5.2 泄漏速率对致死浓度云团危害距离的影响
为研究泄漏速率(Q)对致死浓度云团危害距离的影响,从2.3节计算结果数据中获取致死浓度云团尺寸信息,并增加泄漏速率0.062 kg/s和0.124 kg/s两种工况,其他条件不变,计算整理结果得到图 6。由图 6可见:速率为0.018 kg/s、0.031 kg/s、0.045 kg/s、0.062 kg/s、0.124 kg/s时,致死浓度云团危害距离分别为30 m、40 m、48 m、55 m、100 m,最大危害距离为100 m;泄漏速率增大,致死浓度云团危害长度随之线性增长,与2.3节中所得规律和原因均一致。
另外,对比分析模拟结果和相关规定发现:在一般规模泄漏事故下,致死浓度云团不会危及厂区以外的人员。假定2.3节中2 000 m安全防护距离对应的泄漏速率0.045 kg/s为“一般规模泄漏”速率。在本节假定条件下,泄漏速率达到0.124 kg/s时,约为“一般规模”的2.75倍,致死浓度云团从泄漏口泄漏并因重力作用逐渐沉降至地面,危害长度达到100 m,危害高度刚好降至0 m,如图 7所示。模拟计算结果与国家标准中的相关规定相符合:《光气及光气化产品生产安全规程》中规定“光气及光气化生产装置与厂围墙的距离不应小于100 m”[14]。若按标准建设厂区,发生泄漏速率小于2.75倍“一般规模”的泄漏时,致死浓度云团到达围墙处前高度已经降至0 m,不会对人员产生致死危害;若不按标准建厂,致死浓度云团可能会危害至厂区以外。
3. 研究结果对事故应急救援的意义及应用
3.1 风速对阈浓度云团危害长、宽、高的影响对应急救援的意义
(1)阈浓度云团危害长度、宽度和高度在风速从1.5 m/s增加到4.5 m/s之间迅速减半,所以,若实测时发现风速在1.5 ~ 4.5 m/s,建议增加测量次数取平均值以提高预测危害范围的准确度。(2)阈浓度云团危害长度远大于宽度,发生事故时可根据情况采取向泄漏源两侧远处疏散的方案。
3.2 泄漏速率对阈浓度云团危害长、宽、高的影响对应急救援的意义
利用本文的研究结果,事故发生后,可通过测量泄漏孔径的大小计算泄漏速率,与0.018 kg/s、0.031 kg/s、0.045 kg/s做比较,快速确定阈浓度云团危害长度是否到达1 000 m,1 500 m,2 000 m三个安全防护距离,安全防护距离之外的人员是否需要疏散撤离。
3.3 阈浓度云团危害范围的快速估算公式对应急救援的意义
拟合定量关系公式可以用来快速估算风速和泄漏速率影响的阈浓度云团最大危害长度、宽度和高度,为应急救援提供快速数据支持。特别地,若最大危害高度远低于建筑高度,可采取向高处疏散的方案。
3.4 致死浓度影响长度和高度对应急救援的意义
(1)依据研究得出的致死浓度云团最大危害长度,在其附近布设氨水或者其他稀碱液喷淋设备,以便在事故发生时快速精准地处理泄漏物,减小危害范围和时间。(2)本文研究表明:若按规定建厂,发生一般规模的泄漏时,致死浓度云团到达下风向100 m处危害高度降至0,不会影响到厂区外。因此,厂区必须严格按照标准建设,光气及光气化装置到下风向围墙的距离不得小于100 m。
本研究是在一定的假设条件下完成的,为了救援人员能够准确应用,需要根据现实情况调整应用策略。(1)实际风速可能是随时变化的,应用时可采用实测风速的最大值或平均值进行危害范围估算。(2)现实环境中温度和风向可能变化,可能存在建筑物等障碍物,本文假设温度和风向恒定,安全防护距离内无障碍物遮挡,因此,环境发生变化时可根据本文的研究方法重新计算,得到准确可靠的结果。本文的研究方法可为此类事故的危害空间研究提供思路。
4. 结论
使用ICEM建立物理模型并划分网格,利用CFD软件Fluent构建了某化工厂碳酰氯气相泄漏扩散的数值模拟模型,研究复杂三维空间环境下,风速和泄漏速率对事故阈浓度云团危害空间范围和对致死浓度云团危害长度的影响规律,得到如下结论:
(1)风速变大,阈浓度云团在空间中的最大危害长度、宽度和高度都变小,具体为:①风速从1.5 m/s升高到4.5 m/s,阈浓度云团的最大危害长度、宽度和高度迅速减半,而升高到4.5 m/s以上,减小的速度放缓;②阈浓度云团的最大危害长度远大于其宽度和高度。以上规律在不同泄漏速率下依然适用。
(2)泄漏速率越大,阈浓度云团在空间中的最大危害长度、宽度和高度都随之线性增大,此规律在不同风速下依然适用;在本文假设最不利条件下,阈浓度云团恰好到达下风向1 000 m、1 500 m、2 000 m防护距离时的泄漏速率分别为0.018 kg/s、0.031 kg/s、0.045 kg/s;风速增大,泄漏速率减小,致死浓度云团最大危害距离长度变短。
(3)本文主要运用CFD模型研究了碳酰氯泄漏事故的危害云团扩散规律,精准计算了危害云团在三维环境中的危害空间,为解决运算速度慢的问题,采用数据拟合的方法,能够又快又准地计算出危害云团的危害空间。此方法在碳酰氯泄漏事故的应急救援工作中具有实际应用价值,在其他类似事故的研究中也同样适用。
作者声明 本文无实际或潜在的利益冲突 -
表 1 不同浓度碳酰氯对无防护人员的危害程度
危害云团 云团中碳酰氯质量浓度/(mg/m3) 危害程度 阈浓度云团 5 阈浓度,长期(10 min以上)处于该浓度将有害健康 不可耐浓度云团 20 不可耐浓度,该浓度下作用1 min会产生典型中毒症状恶心、咳嗽和呕吐,人体已经能感觉到明显不适 致死浓度云团 500 致死浓度,该浓度下15 min内会使90%以上无防护人员死亡 表 2 拟合关系式估算精度验证
[关系式计算值(CFD实验值)] 验证编号 风速/(m/s) 泄漏速率/(kg/s) 阈长度 阈宽度 阈高度 拟合度 1 1.5 0.030 1 478(1 480) 80(78) 36.2(36.5) >0.97 2 4.0 0.031 935(955) 44(45) 25.4(24.8) >0.97 3 7.0 0.043 896(862) 37(38) 23.5(23.3) >0.96 -
[1] 张素雅, 张健健. 光气检测用小分子荧光探针的研究进展[J]. 精细化工, 2020, 37(11): 2229-2237. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JXHG202011009.htm [2] 顾建栋, 刘桂玲, 夏昕, 等. 光气生产装置事故后果分析及提高装置安全性的对策措施[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2006, 16(12): 117-122. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZAQK200612021.htm [3] 李沁怡, 蔡旭晖, 王雪, 等. 太原煤化工区有毒气体泄漏环境风险分析[J]. 环境科学学报, 2012, 32(3): 537-544. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJXX201203005.htm [4] 李文博. 某TDI生产项目光气泄漏事故气相环境风险防范与应急措施研究[J]. 福建轻纺, 2020(12): 45-49. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-550X.2020.12.010 [5] 邓云峰, 李群, 盖文妹. 有毒气体泄漏场景模拟与区域疏散分析[J]. 中国安全生产科学技术, 2014, 10(6): 12-19. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LDBK201406002.htm [6] LAKEHAL D. Computation of turbulent shear flows over rough-walled circular cylinders[J]. J Wind Eng Ind Aerod, 1999, 80(1): 47-68.
[7] 江攀, 杨俊佳, 张琼, 等. CFD瞬态模拟楼宇布局对城镇燃气管道泄漏的影响[J]. 油气储运, 2019, 38(12): 1383-1390. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YQCY201912011.htm [8] 秦雅琦, 李玉星, 韩辉, 等. 障碍物对大型LNG储罐泄漏蒸气扩散影响的模拟研究[J]. 石油与天然气化工, 2019, 48(2): 103-110. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-STQG201902022.htm [9] 郦胜, 张小会. FLUENT仿真计算在丝网印刷作业环己酮弥散分析中的应用[J]. 职业卫生与应急救援, 2019, 37(1): 5-10. doi: 10.16369/j.oher.issn.1007-1326.2019.01.002 [10] EDWARD N FULLER, PAUL D SCHETTLER, J CALVIN GIDDINGS. A new method for prediction of binary gas-phase diffusion coefficients[J]. Ind Eng Chem, 1966, 58(5): 18-27. doi: 10.1021/ie50677a007
[11] 国家环保总局环境工程评估中心. 建设项目环境风险评价技术导则: HJ 169-2018[S]. 北京: 中国环境出版社, 2018. [12] 陈金周, 陈海平, 王玄玉, 等. 化学武器效应及销毁[M]. 北京: 兵器工业出版社, 2003: 11-14. [13] 周云飞, 冯文奂, 王洪胜, 等. 煤矿自然环境下瓦斯气体预混燃烧污染物的扩散规律数值模拟研究[J]. 环境科学与管理, 2020, 45(4): 58-61. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-BFHJ202004013.htm [14] 化学工业第二设计院. 光气及光气化产品生产安全规程: GB 19041-2003[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2003. -
期刊类型引用(1)
1. 李显,侯晓,张麟征,晏飞,常淑凡,王卓文,陈洋,王威. 发电企业职业病危害因素与防护策略探讨. 中国职业医学. 2023(02): 235-241 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(0)






 下载:
下载: