Excitatory neurotoxicity of CO-releasing molecules-2 on PC12 cells
-
+ English摘要:目的 探讨一氧化碳释放分子2(CORM-2)对PC12细胞谷氨酸信号通路的影响及作用机理,揭示急性一氧化碳中毒迟发性脑病(delayed encephalopathy after acute carbon monoxide poisoning,DEACMP)发生的可能机制,为CO的中毒及其后遗症的防治提供实验依据。方法 以高分化的PC12细胞为研究对象,经不同浓度的CORM-2暴露后,用MTS法检测细胞活力,确定合适的染毒浓度及染毒时间,收集细胞后用蛋白免疫印迹法检测N-甲基-D-天冬氨酸(NMDA)受体主亚基(NR1)及NMDA受体2B亚基(NR2B)蛋白的表达,检测细胞内钙离子浓度及细胞释放的谷氨酸含量,用流式细胞术检测细胞的凋亡情况。结果 随着CORM-2浓度的增加,PC12细胞的活力呈剂量依赖性降低(P < 0.05);各剂量与对照组相比,NMDA受体的NR1亚基的表达未发生显著的变化(P > 0.05),250 μmol/L和300 μmol/L剂量组NR2B蛋白的相对表达水平以及Ca2+浓度、谷氨酸水平均高于对照组和200 μmol/L剂量组(P < 0.05);随着CORM-2浓度的增加,PC12细胞的凋亡率也呈剂量依赖性增加(P < 0.05)。结论 随着COMR-2浓度的增加,PC12细胞的活力呈剂量依赖性降低。CORM-2可使PC12细胞谷氨酸信号通路激活。CORM-2可能通过激活谷氨酸信号通路引起Ca2+内流,进而导致细胞凋亡。这些结果对认识CO中毒机制具有重要意义。
-
一氧化碳(carbon monoxide,CO)是一种无色、无味、无刺激性的窒息性气体,主要由含碳有机物不完全燃烧产生,是日常生产生活中常见的有毒有害性气体之一[1],生产生活中以急性一氧化碳中毒多见[2-3]。CO入血之后80% ~ 90%与血红蛋白结合,形成碳氧血红蛋白,降低了血液携氧和输氧的能力[4],长期的缺氧将严重损伤中枢神经系统(central nervous system,CNS)的功能[5]。一部分急性一氧化碳中毒的患者在意识障碍恢复后,经过2 ~ 60 d的“假愈期”,可出现急性一氧化碳中毒迟发性脑病(delayed encephalopathy after acute carbon monoxide poisoning,DEACMP)[6-7]。研究表明,急性DEACMP的发生率高达45% [8-9]。目前临床上针对DEACMP尚缺乏有效的治疗手段,主要是高压氧疗辅助药物治疗。目前认为可能导致该病发生的几种机制包括:缺血缺氧损伤和细胞凋亡机制;免疫损伤神经脱髓鞘机制;再灌注损伤和自由基机制;神经递质异常学说;基因易感性和其他[10]。
谷氨酸(glutamate,Glu)是哺乳动物中枢神经系统主要的兴奋性神经递质,对维持大脑皮层的兴奋性具有重要意义。Glu由突触前膜释放,作用于突触后膜上相应的谷氨酸受体而发挥作用。谷氨酸受体分为离子型受体和代谢型受体两种,其中离子型谷氨酸受体又分为N-甲基-D-天冬氨酸(NMDA)受体和非NMDA受体。研究表明,谷氨酸信号通路在学习、记忆、神经生长发育和突触的可塑性方面发挥着重要作用[11]。病理条件下,产生过量的谷氨酸使谷氨酸受体过度激活,对神经系统产生兴奋毒性,引发神经组织细胞的功能障碍甚至死亡[12]。
PC12细胞是源于大鼠肾上腺髓质嗜铬细胞瘤的一种细胞系,被广泛用于神经系统的相关疾病的体外研究。外源性的一氧化碳释放分子2(CORM-2)是一种新型的CO供体,溶解于二甲基亚砜(DMSO)溶剂中时,可稳定和缓慢地释放出CO气体。本实验将以PC12细胞为研究对象,以CORM-2为CO供体,建立CO神经损伤的体外模型,探究外源性CO对PC12细胞谷氨酸系统的影响和可能机制,为一氧化碳中毒迟发性脑病的治疗提供实验依据。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 材料
1.1.1 主要试剂
胎牛血清(以色列Biological Industries公司);CORM-2(美国GLPBIO公司);MTS细胞活性测定试剂盒(上海信裕生物工程有限公司);兔抗NR1多克隆抗体(美国Abcam公司);兔抗NR2A多克隆抗体(美国Abcam公司);兔抗NR2B多克隆抗体(美国Abcam公司);兔抗β-actin多克隆抗体(美国Abcam公司);ECL发光试剂盒(美国Millipore公司);预染蛋白Marker(上海雅酶生物科技有限公司);Fluo-2,AM(北京索莱宝有限公司);二喹啉甲酸(bicinchoninic acid,BCA)蛋白浓度测定试剂盒(北京鼎国昌盛生物技术公司);谷氨酸比色法测试盒(武汉Elabscience公司)等。
1.1.2 主要仪器
二氧化碳培养箱(上海Heal Force公司),蛋白质电泳装置(美国Bio-Rad公司),干式恒温器(杭州奥盛仪器有限公司),全自动酶标仪(美国Labsystems公司),-40 ℃低温冰箱(美国Thermo公司)等。
1.2 方法
1.2.1 细胞分组与处理
PC12细胞于37 ℃,体积分数5%的CO2条件下培养至状态稳定后,经细胞消化,用DMEM培养基调节细胞浓度为4 × 105/mL接种至96孔板中,待细胞铺满80% ~ 90%时,分别以0 ~ 400 μmol/L的CORM-2对其进行染毒。根据MTS法检测细胞活力结果确定合适的染毒浓度,最终实验设置对照组、200 μmol/L CORM-2组、250 μmol/L CORM-2组、300 μmol/L CORM-2组,培养12 h,染毒结束后用蛋白免疫印迹试验分别检测NR1、NR2B蛋白的表达水平,用比色法检测谷氨酸的含量,荧光探针法检测钙离子浓度。
1.2.2 用Western Blotting法检测目的蛋白相对表达水平
CORM-2染毒PC12细胞后,去除培养基,用磷酸缓冲盐溶液(phosphate buffered saline,PBS)洗3遍,加入细胞裂解液,冰上裂解40 min,并用细胞刮将裂解好的细胞刮落,收集细胞至EP管中,4 ℃下12 000 r/min离心20 min,取上清,置- 20 ℃保存。BCA法测定上清液中蛋白浓度,并调整各标本至相同蛋白浓度。蛋白样品经聚丙烯酰胺凝胶电泳,转膜,磷酸盐吐温缓冲液(PBST)浸泡,封闭,PBST洗膜,分别加入相应的一抗NR1(1∶1 000稀释),NR2B(1∶1 000稀释),4 ℃孵育过夜,PBST洗膜,加入相应二抗山羊抗兔(1∶5 000稀释),孵育2 h,PBST洗膜3次,ECL试剂盒显色。
1.2.3 细胞内Ca2+含量测定
按上述方法培养PC12细胞,经不同浓度CORM-2暴露12 h后去除培养基,用预冷的D-hanks溶液洗涤细胞3次后收集细胞,加入1 mL D-hanks溶液,预温37 ℃,加入5 μL的Fura-2/AM工作液,置于37 ℃恒温振荡培养箱中,避光孵育30 ~ 45 min。用D-hanks溶液洗涤细胞3次,置于37 ℃恒温振荡培养箱中避光孵育30 min。荧光酶标仪检测细胞,激发波长380 nm和340 nm,发射波长510 nm。细胞内游离Ca2+浓度采用公式(1)计算:
$$ {\left( {{\rm{C}}{{\rm{a}}^{2 + }}} \right)_{\rm{I}}} = {K_{\rm{d}}} \times \left( {F - {F_{\min }}} \right)/\left( {{F_{\max }} - F} \right) $$ (1) 式中:Kd值为224 nmol/L;Fmax为最大的荧光比值,以10% Triton - X100测得;Fmin为最小的荧光比值,在Fmax基础上加入EGTA后所测得;F为340 nm、380 nm的荧光比值。
1.2.4 统计学分析
所有实验数据均使用统计分析软件SPSS 20.0进行数据处理分析,正态分布资料用均数±标准差(x ± s)表示。组间比较采用单因素方差分析,进一步的两两组间比较采用SNK法,以P < 0.05为差异有统计学意义。
2. 结果
2.1 MTS法检测细胞活力
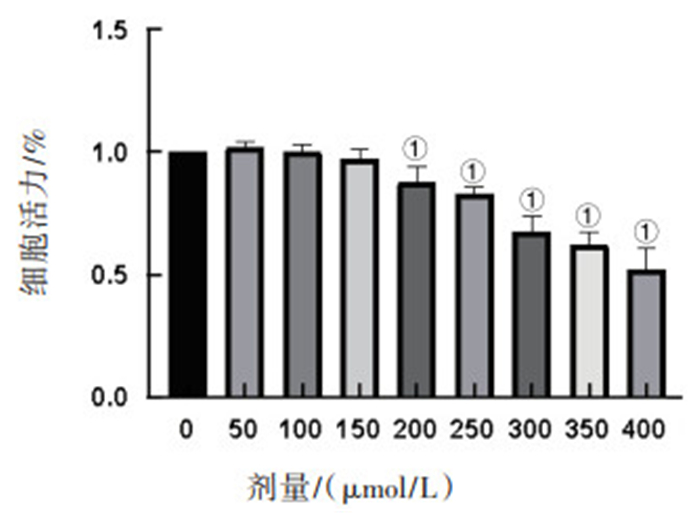
当CORM-2浓度<200 μmol/L时,PC12细胞存活率与对照组相比差异无统计学意义(P>0.05);CORM-2浓度≥ 200 μmol/L时,PC12细胞存活率明显下降,与对照组相比,差异均有统计学意义(P<0.05)。见图 1。
2.2 CORM-2对内谷氨酸受体NR1和NR2B蛋白表达的影响
染毒12 h后,各剂量与对照组相比,NMDA受体的NR1亚基的表达未发生显著变化,说明CORM-2处理对NR1亚基的表达没有显著影响;染毒12 h后,随着染毒剂量的增加,NR2B亚基的表达也随之增加,当CORM-2浓度为250 μmol/L和300 μmol/L时,与对照组相比,细胞内的NR2B亚基含量显著升高,差异具有统计学意义(P < 0.05),且250 μmol/L和300 μmol/L两组间相比,NR2B亚基的表达水平差异也有统计学意义(P < 0.05)。见图 2、表 1。
表 1 各组PC12中NR1和NR2B蛋白相对表达水平比较(x ± s) 组别 重复次数 NR1 NR2B 对照组 4 1.41 ± 0.18 0.99 ± 0.21 200 μmol/L 4 1.37 ± 0.23 1.14 ± 0.18 250 μmol/L 4 1.29 ± 0.20 1.24 ± 0.13① 300 μmol/L 4 1.28 ± 0.13 1.61 ± 0.18①②③ F值 0.46 13.63 P值 > 0.05 < 0.01 注:①与对照组比较,P < 0.05;②与200 μmol/L剂量组比较,P < 0.05;③与250 μmol/L剂量组比较,P < 0.05。 2.3 谷氨酸浓度检测
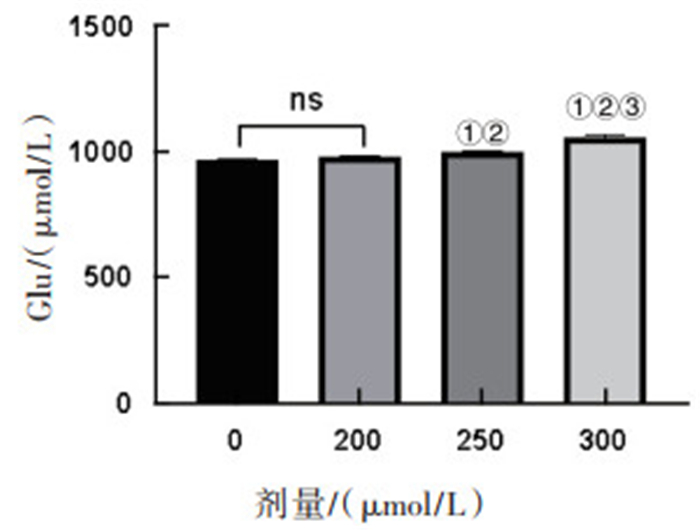
CORM-2处理12 h后,对照组、200 μmol/L、250 μmol/L和300 μmol/L染毒组Glu含量分别为(968.75 ± 11.09)μmol/L、(977.50 ± 4.08)μmol/L、(995.00 ± 9.57)μmol/L和(1047.50 ± 15.81)μmol/L。与对照组和200 μmol/L染毒组相比,250 μmol/L和300 μmol/L染毒组细胞释放的谷氨酸的浓度水平显著上升,并随染毒剂量的增加而增加,差异具有统计学意义(P < 0.05)。见图 3。
2.4 细胞内Ca2+浓度测定
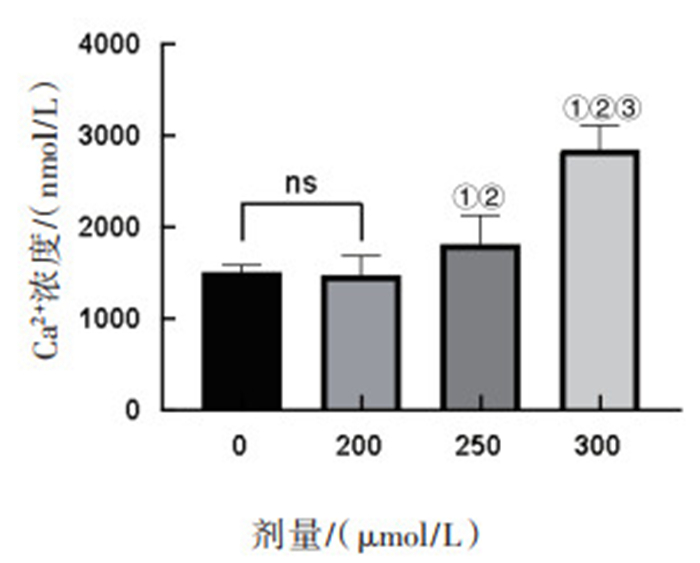
如图 4所示,CORM-2处理12 h后,对照组、200 μmol/L、250 μmol/L和300 μmol/L染毒组Ca2+浓度分别为(1 497.89 ± 91.67)nmol/L、(1 465.23 ± 228.11)nmol/L、(1 945.90 ± 164.84)nmol/L和(2 844.47 ± 262.96)nmol/L。与对照组和200 μmol/L染毒组相比,250 μmol/L和300 μmol/L染毒组细胞内Ca2+浓度水平显著上升,并随染毒剂量的增加而增加,差异有统计学意义(P < 0.05)。
2.5 流式细胞术检测细胞凋亡
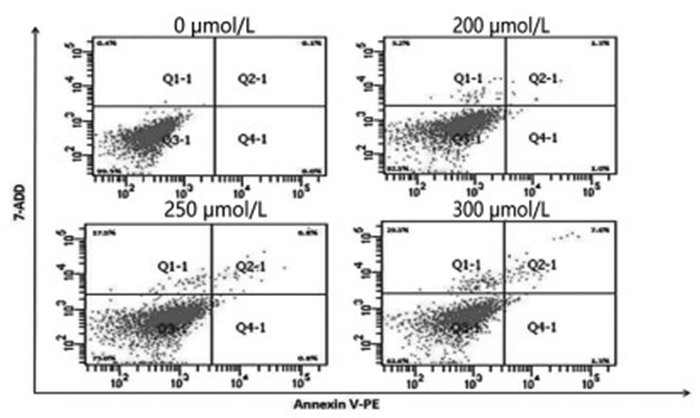
如图 5所示,CORM-2处理12 h后,对照组、200 μmol/L、250 μmol/L和300 μmol/L染毒组细胞凋亡比例分别为(0.13 ± 0.06)、(2.83 ± 1.46)、(7.17 ± 1.10)和(7.37 ± 0.25)。与对照组相比,200 μmol/L、250 μmol/L和300 μmol/L染毒组细胞凋亡水平显著上升,并随染毒剂量的增加而增加,差异具有统计学意义(P < 0.05)。
3. 讨论
目前,一氧化碳对神经系统损伤的发病机制尚未完全阐明,尤其是其特有的迟发性脑病的病因尚不明确。CO是新发现的除一氧化氮(NO)以外,体内又一种重要的气态信号分子。生理条件下,体内也会产生一定量的内源性CO,主要由血红素氧合酶(HO)代谢血红素产生[13]。其分子结构与NO相似,可通过与NO相似的作用机制发挥与之类似的生理调节作用,但在缺血缺氧等应激因素的刺激下,诱导型血红素氧合酶(HO-1)大量表达,致使内源性CO的量超过生理水平而发挥损害作用。
NMDA受体广泛分布于中枢神经系统中,因涉及学习、记忆和神经退行性疾病等各种生理病理过程而备受关注。NMDA受体主要由NR1和NR2两个亚单位构成,NR1是基本功能单位,含有甘氨酸和Ca2+通道的结合位点;而NR2是其调节单位,含有谷氨酸结合位点[14],因此,PC12细胞中NR1和NR2亚单位的表达水平可影响NMDA受体的功能,进而影响PC12细胞膜对Ca2+的通透性[15]。PC12细胞内Ca2+浓度的变化对谷氨酸信号通路的激活具有重要的调控作用,与谷氨酸的兴奋毒性密切相关。研究还发现,NR1/NR2A和NR1/NR2B是NMDA受体的主要组合形式,而含有NR2B亚基的NMDA受体与神经元兴奋毒性的关系更为密切[16],因此本实验决定检测谷氨酸、NR1/NR2B亚基来探究CORM-2处理对PC12细胞谷氨酸信号通路的影响。本研究结果显示,与对照组比较,浓度为250和300 μmol/L的CORM-2刺激,均可引起PC12细胞释放谷氨酸的含量和NR2B的蛋白的表达上调(P < 0.05);且250和300 μmol/L两个剂量组间,谷氨酸含量和NR2B表达情况的差异也具有统计学意义(P < 0.05),提示CORM-2处理激活了PC12细胞的谷氨酸信号通路。
Ca2+是细胞内一种重要的第二信使,细胞内的钙稳态对维持细胞的正常活性和生理功能具有重要意义。大量动物研究表明,CO中毒可引起谷氨酸的过度释放,过量的谷氨酸使突触后膜上的NMDA受体过度激活,进而引发Ca2+大量内流而使细胞钙超载。CO中毒时,缺氧导致神经组织无氧代谢增加,使得乳酸产生增多,而细胞内H+浓度增加也会破坏钙稳态[17]。研究发现,神经组织在缺血缺氧时,细胞钙超载与神经细胞死亡联系密切[18];神经退行性疾病与神经组织细胞内长期内质网应激(ERS)启动凋亡通路而引发的细胞死亡密切相关。目前多认为外界干扰所引起的细胞钙超载是引发细胞凋亡的始动因素,细胞内Ca2+水平异常升高会引发一系列的级联反应,最终导致细胞坏死或凋亡[19]。本研究发现,与对照组和低剂量组相比,中、高剂量(250 μmol/L、300 μmol/L)染毒12 h后,细胞内Ca2+浓度随着染毒剂量的增加而增加,细胞凋亡率逐渐增加,细胞内Ca2+水平的变化与谷氨酸及其受体含量的变化同向,且Ca2+水平变化与细胞活性的变化反向。
综上所述,本研究结果显示外源性CORM-2暴露可引起PC12细胞谷氨酸释放增加,NMDA受体表达上调,从而引起细胞内Ca2+浓度增加,干扰了细胞内钙稳态环境,进而导致细胞凋亡。以上结果为揭示一氧化碳中毒迟发性脑病的机制提供了实验参考依据。
作者声明 本文无实际或潜在的利益冲突 -
表 1 各组PC12中NR1和NR2B蛋白相对表达水平比较
(x ± s) 组别 重复次数 NR1 NR2B 对照组 4 1.41 ± 0.18 0.99 ± 0.21 200 μmol/L 4 1.37 ± 0.23 1.14 ± 0.18 250 μmol/L 4 1.29 ± 0.20 1.24 ± 0.13① 300 μmol/L 4 1.28 ± 0.13 1.61 ± 0.18①②③ F值 0.46 13.63 P值 > 0.05 < 0.01 注:①与对照组比较,P < 0.05;②与200 μmol/L剂量组比较,P < 0.05;③与250 μmol/L剂量组比较,P < 0.05。 -
[1] 李健. 丁苯酞对一氧化碳中毒迟发性脑病的临床疗效及磁共振脑白质病变的影响[D]. 呼和浩特: 内蒙古医科大学, 2020. [2] SERT E T, KOKULU K, MUTLU H. Clinical predictors of delayed neurological sequelae in charcoal-burning carbon monoxide poisoning[J]. Am J Emerg Med, 2021, 48: 12-17. doi: 10.1016/j.ajem.2021.04.001
[3] 吴薇. 四川省部分地区一氧化碳中毒迟发性脑病相关因素研究[D]. 泸州: 西南医科大学, 2020. [4] COSKUN A, EREN F A, EREN S H, et al. Predicting of neuropsychosis in carbon monoxide poisoning according to the plasma troponin, COHb, RDW and MPV levels: neuropsychoses in carbon monoxide poisoning[J]. Am J Emerg Med, 2019, 37(7): 1254-1259. doi: 10.1016/j.ajem.2018.09.017
[5] 厉永强, 王萌, 王来, 等. 永久缺血缺氧对PC12细胞自噬的影响[J]. 解剖学报, 2017, 48(3): 242-253. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JPXB201703002.htm [6] 李兴义, 杨帆, 满劲进, 等. 急性一氧化碳中毒迟发性脑病早期预测研究进展[J]. 神经损伤与功能重建, 2021, 16(4): 219-221. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GWKF202104010.htm [7] 高生伟, 王秉卿, 温超, 等. 鼠神经生长因子联合高压氧治疗一氧化碳中毒迟发性脑病的临床研究[J]. 世界最新医学信息文摘, 2019, 19(92): 201-202. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-WMIA201992119.htm [8] HAN S T, BHOPALE V M, THOM S R. Xanthine oxidoreductase and neurological sequelae of carbon monoxide poisoning[J]. Toxico Lett, 2007, 170(2): 111-115. doi: 10.1016/j.toxlet.2007.02.006
[9] JEON S B, SOHN C H, SEO D W, et al. Acute brain lesions on magnetic resonance imaging and delayed neurological sequelae in carbon monoxide poisoning[J]. JAMA Neurol, 2018, 75(4): 436-443. doi: 10.1001/jamaneurol.2017.4618
[10] 朱红灿, 高萌, 张新凯. 急性一氧化碳中毒迟发性脑病发病机制的研究进展[J]. 内科理论与实践, 2018, 13(5): 264-268. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-NKLL201805002.htm [11] TAPIERO H, MATHé G, COUVREUR P, et al. Ⅱ. Glutamine and glutamate[J]. Biomed Pharmacother, 2002, 56(9): 446-457. doi: 10.1016/S0753-3322(02)00285-8
[12] LAU A, TYMIANSKI M. Glutamate receptors, neurotoxicity and neurodegeneration[J]. Pflugers Arch, 2010, 460(2): 525-542. doi: 10.1007/s00424-010-0809-1
[13] 马利锋. 血红素氧合酶-1/一氧化碳系统(HO-1/CO)在新生鼠缺氧缺血性脑损伤中的变化和作用的研究[D]. 天津: 天津医科大学, 2009. [14] STRONG K L, JING Y, PROSSER A R, et al. NMDA receptor modulators: an updated patent review(2013—2014)[J]. Expert Opin Ther Pat, 2014, 24(12): 1349-1366. doi: 10.1517/13543776.2014.972938
[15] LANG E, MALLIEN A S, VASILESCU A N, et al. Molecular and cellular dissection of NMDA receptor subtypes as antidepressant targets[J]. Neurosci Biobehav Rev, 2018, 84(6): 352-358.
[16] 焦明非. NMDA受体介导神经元兴奋毒性的机制研究[D]. 杭州: 浙江大学, 2018. [17] NEDERGAARD M. Intracellular Ca2+ transients evoked by lactic acid in cultured mammalian neurons[J]. Am J Physiol, 1995, 268(2): 506-513.
[18] CAO W, FENG S J, KAN M C. Naringin targets NFKB1 to alleviate oxygen-glucose deprivation/reoxygenation-induced injury in PC12 cells via modulating HIF-1α/AKT/mTOR-signaling pathway[J]. J Mol Neurosci, 2021, 71(1): 101-111. doi: 10.1007/s12031-020-01630-8
[19] YANG X, WANG Y, LUO J, et al. Protective effects of YC-1 against glutamate induced PC12 cell apoptosis[J]. Cell Mol Neurobiol, 2011, 31(2): 303-311. doi: 10.1007/s10571-010-9622-9
-
期刊类型引用(1)
1. 张师勉,曾宪容. 急性一氧化碳中毒迟发性脑病危险因素研究进展. 实用临床医药杂志. 2023(22): 138-142+148 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(1)





 下载:
下载: