Stability analysis of spectrometric standard curve for conventional nonmetallic compounds in area of occupational health
-
+ English摘要:目的 通过汇总分析常见非金属化合物光谱检测法的标准曲线截距和斜率的稳定性,为实验室质量控制提供新的解决方案。方法 收集整理了2009—2021年8种职业卫生领域常见非金属化合物的标准曲线,使用SPSS软件对标准曲线的斜率和截距进行统计分析,对离群值进行原因分析并合理剔除。结果 以上几种标准曲线的斜率在同批次固体试剂下相对稳定,即使使用不同批次的水,对斜率的影响在95%置信区间内,仍可接受,但截距变化较大。当试剂重新配制后,同批次固体试剂的影响可忽略,所做的标准曲线具有良好的稳定性;当更换不同批次的固体试剂后,部分标准曲线的斜率会有变化。以氨为例拟合一条经验标准曲线,检验其相对标准偏差(RSD)为0.83% ~ 3.57%,回收率为94.7% ~ 98.6%,具有良好的准确度和回收率。结论 相同批次固体试剂下,8种常见非金属化合物光谱检测法的标准曲线均具有较高稳定性。这一特点可以作为在工作中质量控制的手段。
-
分光光度法的基本定律是朗伯比尔定律(Lambert-Beer law),是通过测定被测物质在特定波长或一定波长范围内光的吸光度或发光强度,对该物质进行定性和定量分析的方法。吸光系数只与入射光的波长以及待测物的浓度有关。理论上固定入射光波长后,同一浓度的待测物,其吸光系数应该相同。基于该原理推断,不同时间段配制的相同浓度的标准系列,其吸光度以及在吸光度和浓度梯度上建立的标准曲线应该保持稳定。
本文以氨为目标化合物,收集整理既往检测数据,通过统计分析,评估不同时间段配制的标准系列及其曲线的稳定性,为日常工作中质量控制和曲线稳定性分析提供参考依据。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 材料
1.1.1 仪器
岛津UV2550紫外可见分光光度计;1 cm比色皿;10 mL具塞比色管。
1.1.2 试剂
2019年5月之前,实验用水为蒸馏水,之后为超纯水,试剂为分析纯。20℃下1.84 g/mL的硫酸(国药集团化学试剂有限公司);吸收液:硫酸溶液(0.005 mol/L);纳氏试剂(天津基准化学试剂有限公司);标准溶液:国家认可的标准溶液(中国计量科学研究院),1.0 mg/mL,临用前用吸收液稀释成20.0 μg/mL的氨标准溶液。
1.2 方法
1.2.1 数据来源
收集从2009—2020年的不同批次水配制的试剂所绘制的氨标准曲线数据和2021年使用相同批次水配制的试剂所绘制的氨标准曲线数据。标准曲线依据GBZ/T 160.29—2004《工作场所空气有毒物质测定无机含氮化合物》 [1]和GBZ/T 300.43—2017《工作场所空气有毒物质测定第43部分:叠氮酸和叠氮化钠》 [2]绘制。
1.2.2 统计学分析
使用SPSS 23.0统计软件进行分析。采用箱图离群值[3]筛选方法对标准曲线的斜率和截距的离群值(95%置信区间)进行原因分析并合理剔除。使用Kolmogorov-Smirnov检验、Shapiro-Wilk检验对样本进行正态性判断[4-5]。根据既往标准曲线的斜率和截距,得到在95%置信区间内的经验标准曲线,再通过检验其相对标准偏差和回收率,判断曲线的稳定性和准确度[6-7]。P < 0.05为差异有统计学意义。
2. 结果
2.1 批间氨标准曲线稳定性分析
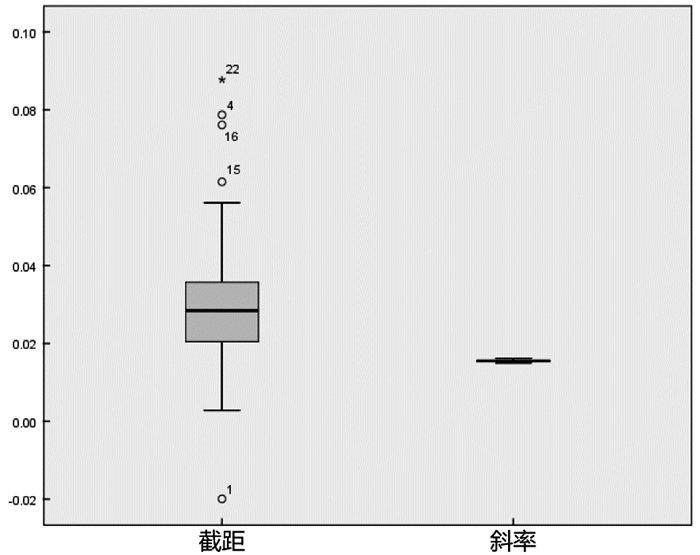
共收集2009—2020年58条不同时段氨标准曲线。斜率的最大值0.016 15,最小值0.014 97,平均值0.015 53 ± 0.000 29。截距的最大值0.056 13,最小值0.002 80,平均值0.027 28 ± 0.011 35。58条氨标准曲线斜率的相对标准偏差RSD为1.87%,斜率稳定,精密度高。截距的相对标准偏差RSD为41.60%,截距稳定性差,变化频繁,分析原因可能为试验当时所使用的水或者比色管等器皿受污染导致。
2.2 离群值判断
图 1中的空心圆点代表离群点,即观察值距离箱体底部距离超过箱体高度的1.5倍视为离群点,图中的星号代表极端值,即观察值距离箱体底部超过箱体高度的3倍视为极端值,图 1中的数字分别表示离群点和极端值所在数据库中的id编号。由图 1可以看出截距存在5个离群值,其中有1个极端值,说明截距变化较大,主要原因是早些年使用的水纯度不够,有较大差异,或者被污染,导致空白值偏高,需剔除离群值后进行正态性检验。
2.3 剔除离群值后正态性检验
剔除离群值后,可以看出斜率和截距的两种正态性检验方法P值均 > 0.05,服从正态分布。见表 1。
表 1 剔除离群值后正态性检验结果项目 Kolmogorov-Smirnov检验 Shapiro-Wilk检验 统计量 自由度 P值 统计量 自由度 P值 截距 0.088 53 0.200 0.982 53 0.617 斜率 0.089 58 0.200 0.967 58 0.121 2.4 回收率试验和精密度试验
由于早期做标准曲线所用的水为外购的一次水,水质较差,导致标准曲线的截距变化较大。针对水质,后期改用超纯水机制水,进而对改用超纯水后最近的6次标准曲线截距值进行分析,截距的RSD = 7.48%,截距平均值0.013 98 ± 0.001 05,相对稳定。得到经验标准曲线为y = 0.015 53 x + 0.013 98。对不同浓度样品进行加标回收,重复测定6次,利用经验标准曲线计算样品平均加标回收率为94.7% ~ 98.6%,相对标准偏差为0.83% ~ 3.57%,具有稳定的准确度和精密度。见表 2。
表 2 回收率和精密度试验结果编号 样品含量/μg 加标量/μg 测定值/μg 回收率/% RSD/% 1 4.0 2.0 5.89 94.7 3.57 2 8.0 4.0 11.95 98.6 1.71 3 12.0 6.0 17.83 97.1 0.83 2.5 批内氨标准曲线稳定性分析
收集了2021年2月22日—2021年6月4日10条不同时间的氨标准曲线,采用了同批次实验用水。斜率的相对标准偏差RSD为0.79%,截距的相对标准偏差RSD为16.07%,与批间标准曲线相比,相同批次水所做标准曲线斜率和截距变异系数均变小,说明不同批次的水对实验结果有影响。见表 3。
表 3 氨(相同批次水)标准曲线斜率和截距编号 日期 斜率 截距 1 2021/2/22 0.015 50 0.024 60 2 2021/2/23 0.015 18 0.022 81 3 2021/2/25 0.015 39 0.024 87 4 2021/3/1 0.015 57 0.013 99 5 2021/3/4 0.015 37 0.024 42 6 2021/3/19 0.015 46 0.021 26 7 2021/3/29 0.015 46 0.020 66 8 2021/4/25 0.015 62 0.022 22 9 2021/5/10 0.015 38 0.021 38 10 2021/6/4 0.015 36 0.017 33 平均值 0.015 43 0.021 35 标准差 0.000 12 0.003 43 变异系数/% 0.79 16.07 2.6 酚、臭氧、二氧化氮、盐酸、二氧化硫、甲醛的标准曲线稳定性分析
2.6.1 批间稳定性
以同样的方法总结了酚、臭氧、二氧化氮、盐酸、二氧化硫、甲醛的标准曲线,发现都具有同样的稳定性,其中二氧化硫由于其间更换了固体试剂,导致斜率在试剂更换前后有明显变化,这可能是由于不同批次固体试剂的纯度存在差异导致。
各项标准曲线的截距变异系数普遍较大,分析原因为各批次水不同,以及所用玻璃器皿洁净程度不同。酚标准曲线斜率的变异系数较大,这与4-氨基安替比林溶液配制时间有关,4-氨基安替比林溶液随时间的放置逐渐稳定,进而影响曲线斜率的大小,导致变异系数偏大,但斜率整体符合正态分布,在95%置信区间内。二氧化硫在2016年1月更换了氨基磺酸,导致斜率前后变化明显,因此对其斜率分别进行了统计,更换之前的斜率远大于更换之后的斜率,见表 4。
表 4 批间标准曲线斜率和截距汇总日期 项目 标准曲线条数 类型 平均值 标准差 变异系数% 2009.12—2019.3 酚 34 斜率 0.022 27 0.001 78 7.99 截距 2009.12—2020.12 臭氧 49 斜率 0.073 19 0.003 12 4.26 截距 0.057 81 0.011 35 19.63 2009.9—2020.12 二氧化氮 55 斜率 0.185 29 0.003 50 1.89 截距 0.014 00 0.005 30 37.86 2009.11—2018.12 盐酸 46 斜率 0.005 55 0.000 21 3.78 截距 2009.10—2020.12 甲醛 53 斜率 0.368 72 0.010 21 2.77 截距 0.032 53 0.013 31 40.92 2009.9—2015.12 二氧化硫 32 斜率 0.050 60 0.001 33 2.63 截距 0.038 84 0.007 78 20.03 2016.1—2020.4 二氧化硫 15 斜率 0.034 73 0.000 96 2.76 截距 0.032 00 0.007 91 24.72 注:空白处表示不呈正态分布,未做统计。 2.6.2 批内稳定性
对没有明确使用有效期的试剂,以使用同一批试剂的周期内标准曲线进行分析。分析发现批内酚、臭氧、二氧化氮、盐酸的标准曲线斜率相对稳定,表明试剂103 d内是相对稳定的。见表 5。
表 5 批内标准曲线斜率汇总项目 验证时间/d 标准曲线条数 类型 平均值 标准差 变异系数/% 酚 103 12 斜率 0.026 10 0.001 43 5.48 臭氧 103 16 斜率 0.075 19 0.001 67 2.22 二氧化氮 103 10 斜率 0.186 32 0.001 51 0.81 盐酸 103 11 斜率 0.005 78 0.000 11 1.90 3. 讨论
影响标准曲线截距的主要因素为实验用水的纯度[8-9],所用水的纯度不同造成试剂空白存在差异,进而影响截距的值。而截距相对斜率对结果的影响相对较小,同时斜率对结果的影响较为显著,因此,斜率为结果的主要影响因素。
通过统计分析可以得到以上几种标准曲线的斜率相对稳定,即使所使用水的纯度不够,对斜率的影响也在95%置信区间内,仍可接受。即使试剂重新配制,同批次固体试剂的影响也可忽略。当更换不同批次的固体试剂后,会对斜率产生一定的影响,比如二氧化硫,此时我们需要对曲线重新进行统计分析。
因此,实验室可以利用标准曲线稳定性这一性质,对实验进行质量控制,尤其是在没有质控样的情况下,判断标准曲线的准确性。比如氯标准曲线,使用甲基橙分光光度法,在购买不到质控样的前提下,在以往情况下是无法对测定结果做出准确判断的,而采用本研究的方法,则可以通过比较新做的标准曲线和经验标准曲线的斜率和截距,来初步判断实验的效果,达到实验室质量控制的目的。
综上所述,化学分析方法具有较高的稳定性,但是由于缺乏相关的研究数据,导致我们不敢长时间采用同一曲线进行样品分析。本次实验采用正态样本离群值的判断和处理,无论是批间对比,还是批内对比,都进一步佐证了化学分析方法具有较高稳定性。这一特点可以在工作中被作为质量控制的手段,类比经验标准曲线来判断实验的准确性,方便分析实验中出现的问题,进而提高实验室能力和工作效率。
作者声明 本文无实际或潜在的利益冲突 -
表 1 剔除离群值后正态性检验结果
项目 Kolmogorov-Smirnov检验 Shapiro-Wilk检验 统计量 自由度 P值 统计量 自由度 P值 截距 0.088 53 0.200 0.982 53 0.617 斜率 0.089 58 0.200 0.967 58 0.121 表 2 回收率和精密度试验结果
编号 样品含量/μg 加标量/μg 测定值/μg 回收率/% RSD/% 1 4.0 2.0 5.89 94.7 3.57 2 8.0 4.0 11.95 98.6 1.71 3 12.0 6.0 17.83 97.1 0.83 表 3 氨(相同批次水)标准曲线斜率和截距
编号 日期 斜率 截距 1 2021/2/22 0.015 50 0.024 60 2 2021/2/23 0.015 18 0.022 81 3 2021/2/25 0.015 39 0.024 87 4 2021/3/1 0.015 57 0.013 99 5 2021/3/4 0.015 37 0.024 42 6 2021/3/19 0.015 46 0.021 26 7 2021/3/29 0.015 46 0.020 66 8 2021/4/25 0.015 62 0.022 22 9 2021/5/10 0.015 38 0.021 38 10 2021/6/4 0.015 36 0.017 33 平均值 0.015 43 0.021 35 标准差 0.000 12 0.003 43 变异系数/% 0.79 16.07 表 4 批间标准曲线斜率和截距汇总
日期 项目 标准曲线条数 类型 平均值 标准差 变异系数% 2009.12—2019.3 酚 34 斜率 0.022 27 0.001 78 7.99 截距 2009.12—2020.12 臭氧 49 斜率 0.073 19 0.003 12 4.26 截距 0.057 81 0.011 35 19.63 2009.9—2020.12 二氧化氮 55 斜率 0.185 29 0.003 50 1.89 截距 0.014 00 0.005 30 37.86 2009.11—2018.12 盐酸 46 斜率 0.005 55 0.000 21 3.78 截距 2009.10—2020.12 甲醛 53 斜率 0.368 72 0.010 21 2.77 截距 0.032 53 0.013 31 40.92 2009.9—2015.12 二氧化硫 32 斜率 0.050 60 0.001 33 2.63 截距 0.038 84 0.007 78 20.03 2016.1—2020.4 二氧化硫 15 斜率 0.034 73 0.000 96 2.76 截距 0.032 00 0.007 91 24.72 注:空白处表示不呈正态分布,未做统计。 表 5 批内标准曲线斜率汇总
项目 验证时间/d 标准曲线条数 类型 平均值 标准差 变异系数/% 酚 103 12 斜率 0.026 10 0.001 43 5.48 臭氧 103 16 斜率 0.075 19 0.001 67 2.22 二氧化氮 103 10 斜率 0.186 32 0.001 51 0.81 盐酸 103 11 斜率 0.005 78 0.000 11 1.90 -
[1] 中华人民共和国卫生部. 工作场所空气有毒物质测定无机含氮化合物: GBZ/T 160.29—2004[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2004. [2] 中华人民共和国国家卫生和计划生育委员会. 工作场所空气有毒物质测定第43部分: 叠氮酸和叠氮化钠: GBZ/T 300.43—2017[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2017. [3] 中华人民共和国国家标准化管理委员会. 数据的统计处理和解释正态样本离群值的判断和处理: GB/T 4883—2008[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2009. [4] 谢成千. 概率论和数量统计[M]. 北京: 高等教育出版社, 2001. [5] 罗文海, 王玖, 韩春蕾, 等. 基于SPSS的正态性检验方法的选择[J]. 中国医院统计, 2015, 22(1): 48-51. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JTYY201501018.htm [6] 高坚, 付雪涛. 化学检测中线性回归标准曲线稳定性统计分析[J]. 信息技术与标准化, 2018(12): 427;430. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZBZ201812021.htm [7] 丁荔. 标准曲线斜率控制的应用[J]. 上海环境科学, 1991(12): 25-26. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GXKE201705021.htm [8] 张宵, 田桂艳, 王丹慧, 等. 水样亚硝酸盐标准曲线斜率质控图的应用分析[J]. 食品安全质量检测学报, 2018, 9(21): 222-226. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SPAJ201821047.htm [9] 张金萍, 肖军, 郑燕平. 标准曲线的斜率在环境监测分析质控中的作用[J]. 新乡师专学报(自然科学版), 1995, 9(2): 95-98. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XXSF199502028.htm -
期刊类型引用(0)
其他类型引用(1)





 下载:
下载:
