Prognosis prediction of paraquat poisoning with lasso-logistic regression
-
+ English摘要:目的 确定临床中常用且简单的检测指标,预测百草枯中毒患者的预后,以便对患者采取及时有效的救治方案,提高患者生存率。方法 以广州市第十二人民医院2010—2019年收治的199例百草枯中毒患者为研究对象。收集患者基本资料以及入院24 h内的血气分析指标、凝血指标、血常规指标和血生化指标。使用SPSS 26和R 4.0.3软件对数据进行整理和统计学分析。采用lasso回归筛选出影响百草枯中毒患者预后的影响因素,然后使用R软件构建lasso-logistic临床预测模型对其进行验证。结果 199名患者中死亡率为62.31%(124/199)。lasso回归筛选出口服百草枯剂量、碳酸氢根离子(HCO3-)浓度、凝血酶时间(TT)、白细胞(WBC)计数、血糖(GLU)、尿素氮(BUN)和血肌酐(SCr)是百草枯中毒患者预后的潜在影响因素,进一步的logistic回归分析结果显示:口服剂量、WBC、SCr数值增加是百草枯中毒患者死亡的危险因素(OR>1,P<0.05),HCO3-浓度增加是百草枯中毒患者死亡的保护因素(OR = 0.811,P < 0.05)。百草枯中毒预测列线图模型的C值> 0.9,Calibration校准曲线中理想曲线与校准曲线高度重合。决策曲线分析表明,在整个阈值范围内预测模型都具有临床有效性。结论 百草枯中毒患者的死亡率高,基于lasso-logistic回归制作的百草枯中毒死亡风险列线图预测模型具有一定的准确性和可操作性。
-
百草枯(paraquat)是一种廉价、高效且非选择性的吡啶类除草剂[1],其化学名为“1,1-二甲基4,4- 二联吡啶二氯化物”。成人百草枯致死剂量为20 ~ 40 mg/kg,约相当于服用质量分数为20%的5 ~ 15 mL的百草枯水溶液[2]。早在2004年已有报道指出,中美洲等地区每年因百草枯农药导致中毒的病例达40万例[3]。我国每年也有上万人中毒。已有研究表明,百草枯中毒会引发肝、肾、肺、心、脑等脏器或神经系统的损伤[4]。晚期患者死亡原因主要是肺纤维化,肺部逐渐失去呼吸能力而窒息死亡。百草枯中毒已成为我国重要的医学及社会问题[5]。近年来,有关百草枯中毒患者预后预测系统的研究日益增多,如百草枯中毒严重指数(SIPP)[6]、急性生理学与慢性健康状况评分(APACHE)系统[7-8]、序贯器官衰竭(SOFA)评分[9-11]等。此类系统预测指标繁多,预测难度大,难以在基层医疗机构实现。如何在基层医疗机构对患者的抢救过程中,探索一种简单、易用、快速的死亡风险预测系统,对评估百草枯中毒的严重程度、提高患者生存率都具有重要的实用价值。
1. 对象与方法
1.1 对象
收集广州市第十二人民医院2010—2019年职业病科收治的340例百草枯中毒患者的临床资料和实验室检测结果进行回顾性研究。患者的诊断标准符合GBZ 246—2013 《职业性急性百草枯中毒的诊断》[12]。纳入标准:为了筛选出普适人群的预测模型,要求患者年龄≥ 12岁;中毒方式为口服百草枯溶液;中毒后24 h内送入本院就诊。排除标准:混合口服其他类型农药(丁草胺、甲胺磷、甲维盐或甲基异柳磷等)的中毒患者;曾有过肺、肝或肾等脏器损伤或手术史;患有高血压、糖尿病、冠心病等慢性心血管疾病。依据上述标准,本研究最终纳入199例百草枯中毒患者作为研究对象。
1.2 方法
1.2.1 资料收集和指标检测
查阅病案资料,收集患者临床资料和实验室检测结果,主要包括五大类:入院基线资料(性别、年龄、口服剂量等)、血气分析指标[动脉血酸碱度(pH值)、动脉氧分压(PaO2)、动脉二氧化碳分压(PaCO2)、碳酸氢根离子(HCO3-)浓度、剩余碱(BE)]、凝血指标[凝血酶原时间(PT)、活化部分凝血酶原时间(APTT)、凝血酶时间(TT)、纤维蛋白原(Fbg)]、血常规指标[白细胞(WBC)计数、中性粒细胞数(NUT)、血红蛋白(HGB)、血小板(PLT)计数] 和血生化指标[丙氨酸氨基转移酶(ALT)、天门冬氨酸氨基转移酶(AST)、总胆红素(TBIL)、直接胆红素(DBIL)、血糖(GLU)、尿素氮(BUN)和血肌酐(SCr)等]。上述所有检测指标均为患者中毒24 h内的检测结果。依据相关参考文献[13-22],以上指标均可作为百草枯中毒预后的潜在预测因素。
1.2.2 统计学分析
应用SPSS 26和R 4.0.3软件对数据进行统计学分析。首先对各计量资料进行正态性检验,其中符合正态分布的以均数±标准差(x ± s)来表示,两组间差异采用两独立样本t检验进行比较;不符合正态分布的以中位数(四分位数间距),即M(P25,P75)来表示,采用Wilcoxon秩和检验进行组间比较;计数资料组间比较采用χ2检验。
为避免本研究中各变量在数据分析中存在共线性,采用lasso回归筛选特征变量;然后使用R软件构建lasso -logistic临床预测模型并对其进行验证。使用R Studio将随机种子数设为123,将数据集按照3 ∶1的比例划分为训练集和验证集。通过glmnet包对训练集进行lasso回归,根据交叉验证法计算lambda值,以误差最小的lambda值为标准,筛选出特征变量。基于筛选出的特征变量进行多因素logistic回归(向前:LR,预测变量引入标准为P<0.05)建立临床预测模型,并使用Nomogram包绘制列线图对模型进行可视化分析。最后通过绘制ROC曲线、Calibration校准曲线和DCA决策曲线对模型进行内部验证。P<0.05为差异有统计学意义。
2. 结果
2.1 患者一般情况
199例入组患者中,存活75例,死亡124例。比较两组百草枯中毒患者的一般情况,结果显示,存活组和死亡组间的年龄、性别、动脉氧分压(PaO2)、动脉二氧化碳分压(PaCO2)、凝血酶原时间(PT)、活化部分凝血酶原时间(APTT)、纤维蛋白原(Fbg)、血红蛋白(HGB)和血小板(PLT)计数差异无统计学意义(P>0.05)。百草枯中毒患者的口服百草枯剂量、动脉血酸碱度(pH值)、碳酸氢根离子(HCO3-)浓度、剩余碱(BE)、凝血酶时间(TT)、白细胞(WBC)计数、丙氨酸氨基转移酶(ALT)、天门冬氨酸氨基转移酶(AST)、总胆红素(TBIL)、直接胆红素(DBIL)、血糖(GLU)、尿素氮(BUN)和血肌酐(SCr)等指标差异具有统计学意义(P<0.05)。见表 1。
表 1 百草枯中毒患者基本特征变量 检验存活组(n = 75) 死亡组(n = 124) t、χ2或W值 P值 年龄/岁 29.173 ± 12.181 31.790 ± 14.033 - 1.338 0.182 性别 男(n = 103) 37 66 0.284 0.594 女(n = 96) 38 58 口服剂量 15.00(10.00,30.00) 50.00(20.00,100.00) - 6.847 <0.001 血气分析指标 pH值 7.408 ± 0.042 7.381 ± 0.100 2.621 0.010 PaO2/mmHg 12.333 ± 2.230 12.918 ± 9.200 - 0.532 0.602 PaCO2/mmHg 4.391 ± 0.644 3.880 ± 2.752 1.528 0.128 HCO3-(/ mmol/L) 20.70(2.60) 16.55(4.31) 8.466 <0.001 BE(/ mmol/L) - 3.990 ± 2.620 - 8.811 ± 5.523 8.049 <0.001 凝血指标 PT/s 12.458 ± 3.744 13.286 ± 3.348 - 1.526 0.129 APTT/s 28.20(23.25,32.25) 27.05(23.63,33.13) - 0.217 0.828 TT/s 17.30(16.25,18.35) 18.00(16.60,19.75) - 2.150 0.032 Fbg(/ g/L) 2.35(1.96,2.68) 2.40(1.89,3.14) - 3.313 0.754 血常规指标 WBC(/ 109/L) 11.800 ± 4.042 22.237 ± 10.851 - 9.377 <0.001 NUT(/ 109/L) 8.97(6.81,11.91) 18.59(12.99,24.33) - 1.824 0.070 HGB(/ g/L) 138.014 ± 18.273 142.719 ± 19.445 - 1.652 0.111 PLT(/ 109/L) 241.041 ± 77.679 248.658 ± 90.865 - 0.591 0.555 血生化指标 ALT(/ U/L) 15.30(10.93,20.83) 25.45(17.50,54.18) - 5.842 <0.001 AST(/ U/L) 21.40(16.23,25.80) 43.60(28.33,117.25) - 8.635 <0.001 TBIL(/ umol/L) 15.55(11.80,20.38) 17.65(13.23,33.78) - 2.375 0.018 DBIL(/ umol/L) 2.70(2.03,3.60) 3.90(2.30,8.68) - 3.430 0.001 GLU(/ mmol/L) 6.43(5.77,7.43) 7.59(6.43,9.55) - 4.304 <0.001 BUN(/ mmol/L) 4.177 ± 1.661 7.457 ± 3.929 - 7.986 <0.001 SCr(/ umol/L) 79.284 ± 33.221 190.309 ± 115.695 -9.771 <0.001 注:性别间的例数分布差异采用χ2检验。 2.2 lasso回归预测模型的因子
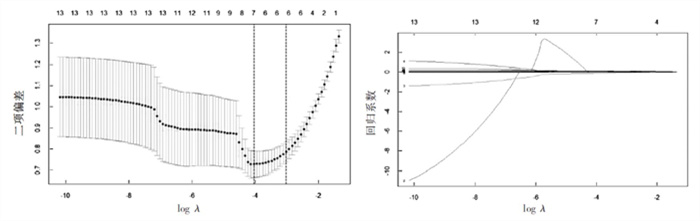
结合临床信息,对上述13个指标进行lasso回归,筛选出模型的预测因子。通过R软件中glmnet进行lasso回归,初始设置的lambda迭代为100次。结果见图 1,在结果代码cv.glmnet显示其最小lambda值和对应筛选的特征变量。图 1左图显示,左右两条虚线分别对应lambda.min和lambda.1se,在[lambda.1se,lambda.min]区间内模型预测偏差变动幅度较小。误差最小时最终迭代次数为97次,lambda值(左边虚线)为0.018,所对应的影响因素数目为7个。结合有关百草枯中毒影响因素的参考文献[16-18, 23-25],最终选择这7个指标为预测因子,分别为:口服百草枯剂量、碳酸氢根离子(HCO3-)浓度、凝血酶时间(TT)、白细胞(WBC)计数、血糖(GLU)、尿素氮(BUN)和血肌酐(SCr),以上均为数值变量。
2.3 预测模型的建立
根据筛选出的7个预测因子,以百草枯中毒患者存活或死亡结局(死亡= 1,存活= 0)为响应变量进行logistic回归分析。结果显示:口服剂量、白细胞(WBC)计数、血肌酐(SCr)的量或者浓度增加(OR>1,P<0.05)是百草枯中毒患者死亡的危险因素,碳酸氢根离子浓度(HCO3-)浓度增加(OR<1,P<0.05)是百草枯中毒患者死亡的保护因素。见表 2。
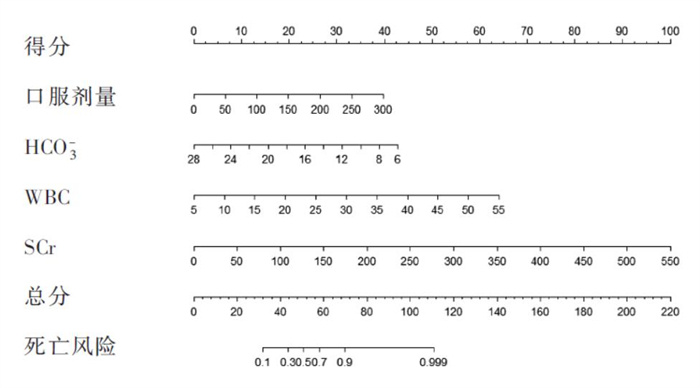
表 2 百草枯中毒死亡风险预测因子的logistic回归分析影响因素 回归系数 标准误 Wald χ2值 P值 OR(95%CI) 截距 - 1.830 2.301 0.632 0.427 0.160(0.002 ~ 13.251) SCr(/ umol/L) 0.017 0.007 5.267 0.022 1.017(1.004 ~ 1.034) 口服剂量/mL 0.016 0.008 3.909 0.048 1.016(1.001 ~ 1.033) HCO3-(/ mmol/L) - 0.209 0.094 4.893 0.027 0.811(0.667 ~ 0.969) TT/s 0.009 0.009 1.151 0.283 1.010(0.992 ~ 1.028) WBC(/ ×109/L) 0.132 0.059 5.040 0.025 1.141(1.023 ~ 1.292) GLU(/ mmol/L) 0.149 0.119 1.626 0.209 1.161(0.945 ~ 1.513) BUN(/ mmol/L) 0.088 0.168 0.315 0.599 1.092(0.788 ~ 1.531) 通过多因素logistic回归构建预测模型。最终的预测模型方程式为:lnP(/ 1 - P)= - 1.830 + 0.016X1 - 0.209X2 + 0.132X3 + 0.017X4,其中:X1为口服剂量;X2为HCO3-浓度;X3为WBC计数;X4为SCr浓度;P为阳性结果发生的概率。根据构建的预测模型,绘制Nomogram列线图对各指标进行评分,从而预测百草枯中毒患者的死亡风险,以便对患者的病情严重程度或结局进行辅助性预判。见图 2。
例如在百草枯中毒患者就医时,根据患者的百草枯口服剂量(ingestion)、HCO3-、WBC、SCr的检测数值,分别将这4个变量的数据按照列线图垂直对准最上面的分值线,就能得到变量的1个赋值,假设这4个变量值分别赋值后为P1、P2、P3、P4,那么其总分就等于P1 + P2 + P3 + P4,其向下垂直对准死亡风险刻度线的值,就是该患者的死亡风险。
2.4 模型的评估(R软件)
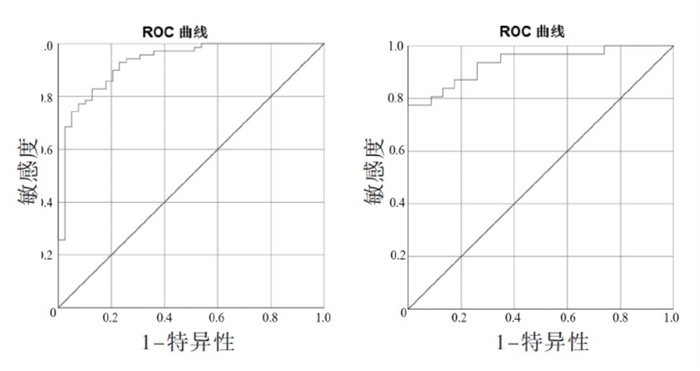
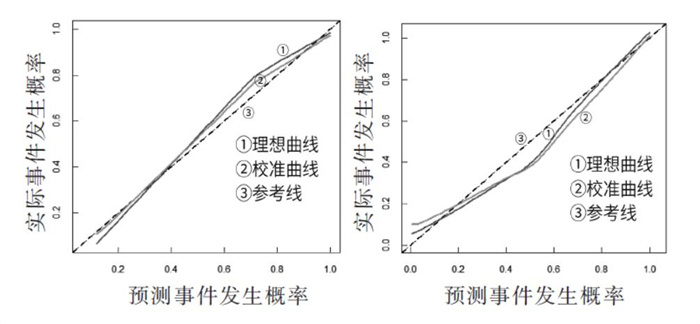
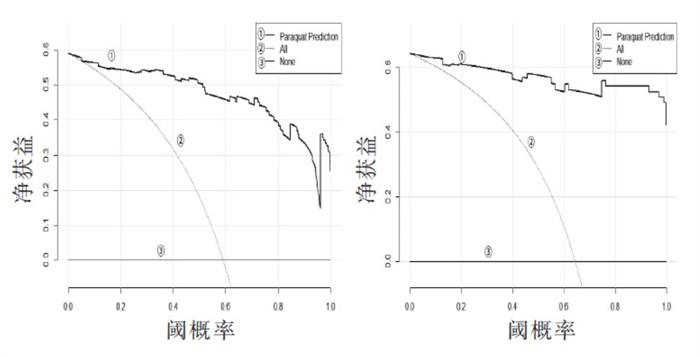
根据3∶1的比例将数据集随机划分为训练集(n = 152)和验证集(n = 47)。预测模型的区分度评估指标为C值和AUC值。结果显示,训练集中,C值为0.927,AUC及其95% 可信区间为0.928(0.878 ~ 0.979);验证集中,C值为0.932,AUC及其95%可信区间为0.935(0.873 ~ 0.998)。训练集和验证集中C指数均大于0.9,提示该预测模型的区分度高。见图 3。预测模型的校准度评估指标为Hosmer - Lemeshow检验[20]和Calibration曲线。训练集HosmerLemeshow检验结果显示χ2 = 6.950(P = 0.542>0.05);验证集中Hosmer Lemeshow检验结果显示χ2 = 4.553(P = 0.804>0.05)。提示训练集和验证集中实际观测值和模型预测值之间差异无统计学意义。图 4显示,训练集和验证集中的理想曲线和校准曲线重合度高,说明预测概率和观测概率近似相等,提示该模型的校准度高。预测模型的临床有效性评估指标为DCA临床决策曲线。如图 5所示,训练集和验证集中预测模型曲线走向基本一致,且该临床预测模型在近似全阈值内具有临床有效性。
3. 讨论
百草枯中毒患者的临床严重程度与多个初始检测指标相关,其常见的预后影响因素有白细胞计数、口服百草枯剂量、血肌酐、肺部损伤、肝肾功能指标等。本研究通过lasso回归筛选特征变量,lasso回归的一个重要优势是变量间的共线性对其筛选结果无影响,有效地克服了变量间的多重共线性[27],最终筛选得到百草枯中毒严重程度的预测因子共4个:口服剂量、HCO3-浓度、WBC计数和SCr。
中毒剂量与百草枯中毒患者的死亡相关密切[23-25]。汪镜静等[28]meta研究结果显示,中毒剂量是百草枯中毒患者死亡的预测因子(OR = 1.2,95%CI:1.11 ~ 1.29)。本研究通过lasso回归筛选出口服剂量为百草枯中毒的特征变量,符合常理和一般研究结果。本次研究所得的口服剂量依据病人或其家属回忆和临床医生的工作经验,做如下估算:男性口服一小口约为20 mL,女性一小口约为10 ~ 15 mL;男性中等口服量约为40 mL,女性约为30 mL;男性一大口约为60 mL,女性约为50 mL[29]。以上数据能相对准确地反映出患者的实际口服剂量情况。
本次logistic回归分析结果显示,死亡组患者白细胞计数高于存活组(P<0.05),对急性百草枯中毒患者的预后具有早期预测价值[25, 30]。Zhou等[31] 的研究发现,WBC可能是有效预测百草枯中毒患者30 d死亡率的预测因子。李奕冰等[32]通过meta分析,对纳入的8篇文献(980例患者)进行系统评价,结果显示WBC是预测早期百草枯中毒结局的危险因素(OR = 18.63,P<0.001)。侯运辉等[33]的研究同样表明24 h内白细胞计数是入院百草枯中毒患者预后的影响因素。
logistic回归分析结果显示血肌酐与百草枯中毒患者预后有相关性(P<0.05),患者血肌酐值越高,病死率也高,与田冬梅[14]、朱文捷[34]的研究一致。相似地,Wan等[35]通过氨基酸代谢组学分析发现血肌酐水平与百草枯死亡结局密切相关(r = 0.84,P = 0.01)。本研究还发现HCO3-浓度与百草枯中毒患者死亡风险相关。这可能是由于百草枯进入血液后,在实质性器官中蓄积,对肺部呼吸[20]和肾脏[16, 34]造成损伤所致。
本研究也存在一些不足之处:研究资料来自单一机构,代表性可能不够强。回顾性研究中存在一定的信息缺失,可能遗漏某些有价值的指标。今后的研究将增加外部数据进行同步验证并做调整,以提高预测模型的可信度。
作者声明 本文无实际或潜在的利益冲突 -
表 1 百草枯中毒患者基本特征
变量 检验存活组(n = 75) 死亡组(n = 124) t、χ2或W值 P值 年龄/岁 29.173 ± 12.181 31.790 ± 14.033 - 1.338 0.182 性别 男(n = 103) 37 66 0.284 0.594 女(n = 96) 38 58 口服剂量 15.00(10.00,30.00) 50.00(20.00,100.00) - 6.847 <0.001 血气分析指标 pH值 7.408 ± 0.042 7.381 ± 0.100 2.621 0.010 PaO2/mmHg 12.333 ± 2.230 12.918 ± 9.200 - 0.532 0.602 PaCO2/mmHg 4.391 ± 0.644 3.880 ± 2.752 1.528 0.128 HCO3-(/ mmol/L) 20.70(2.60) 16.55(4.31) 8.466 <0.001 BE(/ mmol/L) - 3.990 ± 2.620 - 8.811 ± 5.523 8.049 <0.001 凝血指标 PT/s 12.458 ± 3.744 13.286 ± 3.348 - 1.526 0.129 APTT/s 28.20(23.25,32.25) 27.05(23.63,33.13) - 0.217 0.828 TT/s 17.30(16.25,18.35) 18.00(16.60,19.75) - 2.150 0.032 Fbg(/ g/L) 2.35(1.96,2.68) 2.40(1.89,3.14) - 3.313 0.754 血常规指标 WBC(/ 109/L) 11.800 ± 4.042 22.237 ± 10.851 - 9.377 <0.001 NUT(/ 109/L) 8.97(6.81,11.91) 18.59(12.99,24.33) - 1.824 0.070 HGB(/ g/L) 138.014 ± 18.273 142.719 ± 19.445 - 1.652 0.111 PLT(/ 109/L) 241.041 ± 77.679 248.658 ± 90.865 - 0.591 0.555 血生化指标 ALT(/ U/L) 15.30(10.93,20.83) 25.45(17.50,54.18) - 5.842 <0.001 AST(/ U/L) 21.40(16.23,25.80) 43.60(28.33,117.25) - 8.635 <0.001 TBIL(/ umol/L) 15.55(11.80,20.38) 17.65(13.23,33.78) - 2.375 0.018 DBIL(/ umol/L) 2.70(2.03,3.60) 3.90(2.30,8.68) - 3.430 0.001 GLU(/ mmol/L) 6.43(5.77,7.43) 7.59(6.43,9.55) - 4.304 <0.001 BUN(/ mmol/L) 4.177 ± 1.661 7.457 ± 3.929 - 7.986 <0.001 SCr(/ umol/L) 79.284 ± 33.221 190.309 ± 115.695 -9.771 <0.001 注:性别间的例数分布差异采用χ2检验。 表 2 百草枯中毒死亡风险预测因子的logistic回归分析
影响因素 回归系数 标准误 Wald χ2值 P值 OR(95%CI) 截距 - 1.830 2.301 0.632 0.427 0.160(0.002 ~ 13.251) SCr(/ umol/L) 0.017 0.007 5.267 0.022 1.017(1.004 ~ 1.034) 口服剂量/mL 0.016 0.008 3.909 0.048 1.016(1.001 ~ 1.033) HCO3-(/ mmol/L) - 0.209 0.094 4.893 0.027 0.811(0.667 ~ 0.969) TT/s 0.009 0.009 1.151 0.283 1.010(0.992 ~ 1.028) WBC(/ ×109/L) 0.132 0.059 5.040 0.025 1.141(1.023 ~ 1.292) GLU(/ mmol/L) 0.149 0.119 1.626 0.209 1.161(0.945 ~ 1.513) BUN(/ mmol/L) 0.088 0.168 0.315 0.599 1.092(0.788 ~ 1.531) -
[1] CUI J W, XU Y, WANG Y, et al. Efficacy of initial haemopurification strategy for acute paraquat poisoning in adults: study protocol for a randomised controlled trial (HeSAPP)[J]. BMJ Open, 2018, 8(6): e021964. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2018-021964
[2] WANG Y, CHEN Y, MAO L, et al. Effects of hemoperfusion and continuous renal replacement therapy on patient survival following paraquat poisoning[J]. PLoS One, 2017, 12(7): e0181207. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0181207
[3] 李玉新. 百草枯面临强大的压力[J]. 新农药, 2004(3): 27. [4] SHADNIA S, EBADOLLAHI -NATANZI A, AHMADZADEH S, et al. Delayed death following paraquat poisoning: three case reports and a literature review[J]. Toxicol Res(Camb), 2018, 7 (5): 745-753. doi: 10.1039/c8tx00120k
[5] 张宝兰, 姚朗, 欧艺. 1991—2008年我国百草枯中毒文献分析[J]. 中国急救医学, 2010, 30(2): 139-141. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-1949.2010.02.013 [6] SAWADA Y, YAMAMOTO I, HIROKANE T, et al. Severity index of paraquat poisoning [J]. Lancet, 1988, 1(8598): 1333.
[7] 郭伟, 陈翠, 王银凤, 等. APACHEⅡ评分及口服剂量评估百草枯中毒预后的应用价值[J]. 中国急救复苏与灾害医学杂志, 2020, 15(5): 587-590. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-6966.2020.05.024 [8] 杨梦莹, 刘振宁. APACHEⅢ评分在评估急性百草枯中毒患者预后中的临床价值[J]. 中国急救复苏与灾害医学杂志, 2021, 16(9): 988-991;1007. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-6966.2021.09.007 [9] 温宇, 张彩霞, 张海英, 等. 早期血糖水平和序贯器官衰竭评分对急性百草枯中毒患者的预后评估[J]. 中国医科大学学报, 2013, 42(1): 73-76. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-4646.2013.01.020 [10] 肖国辉. 百草枯中毒患者早期血糖和SOFA评分与预后的关系[J]. 西南国防医药, 2016, 26(9): 1008-1010. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-0188.2016.09.018 [11] WENG C H, HU C C, LIN J L, et al. Sequential organ failure assessment score can predict mortality in patients with paraquat intoxication[J]. PLoS One, 2012, 7(12): e51743. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0051743
[12] 中华人民共和国卫生部. 职业性急性百草枯中毒的诊断: GBZ 246—2013[S]. 北京: 人民卫生出版社, 2013. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LDBK201704027.htm [13] 刘景艳. 急性百草枯中毒预后相关因素[J]. 中国工业医学杂志, 2021, 34(1): 48-50;54. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SOLE202101017.htm [14] 田冬梅. 急性百草枯中毒预后影响因素的研究[J]. 现代诊断与治疗, 2015, 26(23): 5281-5283. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XDZD201523003.htm [15] 徐志高, 黄丽, 张晶晶, 等. 早期白细胞计数及中性粒细胞比率变化对急性百草枯中毒的预后分析[J]. 中国实用医刊, 2017, 44(7): 20. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1674-4756.2017.07.007 [16] 谭花蕊. 百草枯中毒患者出现急性肾损伤的危险因素分析[J]. 现代诊断与治疗, 2021, 32(3): 412-413. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XDZD202103038.htm [17] 王金柱, 兰超, 李莉, 等. 176例急性百草枯中毒患者预后危险因素分析[J]. 中国中西医结合急救杂志, 2013, 20(4): 240- 243. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-9691.2013.04.019 [18] HU X, GUO R, CHEN X, et al. Increased plasma prothrombin time is associated with poor prognosis in patients with paraquat poisoning[J]. J Clin Lab Anal, 2018, 32(9): e22597.
[19] ZHOU D C, ZHANG H, LUO Z M, et al. Prognostic value of hematological parameters in patients with paraquat poisoning[J]. Sci Rep, 2016(6): 36235.
[20] 刘景艳, 李兰荣, 金慧燕, 等. 急性百草枯口服中毒患者预后的影响因素[J]. 中华劳动卫生职业病杂志, 2012, 30(9): 686-687. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1001-9391.2012.09.013 [21] 焦峰军, 祝文, 王涛宁, 等. 急性百草枯中毒患者预后危险因素分析[J]. 中华危重病急救医学, 2015, 27(11): 906-910. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.2095-4352.2015.11.008 [22] 黄昌保, 孙兆瑞, 杨志洲, 等. 肝脏酶谱变化对急性百草枯中毒患者的预后作用的研究[J]. 临床急诊杂志, 2016, 17(11): 823-828. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZZLC201611002.htm [23] 柯道, 姚为学, 周宁, 等. 影响百草枯中毒患者预后的相关风险因素分析[J]. 中国当代医药, 2017, 24(12): 29-31;46. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-4721.2017.12.009 [24] 张琳刚, 姚世红, 杜运宏, 等. 百草枯中毒患者预后影响因素分析[J]. 山西医科大学学报, 2014, 45(6): 497-499. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SXYX201406017.htm [25] 孟兆华, 苏小云, 宫玉, 等. 272例急性百草枯中毒患者早期预后影响因素分析[J]. 中国急救医学, 2017, 37(4): 352-358. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-1949.2017.04.015 [26] HOSMER D W, HOSMER T, LE CESSIE S, et al. A comparison of goodness -of -fit tests for the logistic regression model [J]. Stat Med, 1997, 16(9): 965-980. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1097-0258(19970515)16:9<965::AID-SIM509>3.0.CO;2-O
[27] 曹芳, 朱永忠. 基于多重共线性的lasso方法[J]. 江南大学学报(自然科学版), 2012, 11(1): 87-90. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-7147.2012.01.017 [28] 汪镜静, 娄真帅, 张敏, 等. 急性百草枯中毒患者预后因素的meta分析[J]. 沈阳医学院学报, 2020, 22(1): 30-37. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYX202001020.htm [29] 徐维明, 刘卫国, 王伟, 等. 急性百草枯中毒292例临床研究[J]. 武警医学, 2011, 22(3): 189-191. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-3594.2011.03.002 [30] 才权, 刘志. 急性百草枯中毒早期死亡相关因素分析[J]. 中华危重病急救医学, 2014, 26(6): 379-382. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.2095-4352.2014.06.003 [31] ZHOU D C, ZHANG H, LUO Z M, et al. Prognostic value of hematological parameters in patients with paraquat poisoning[J]. Sci Rep, 2016(6): 36235.
[32] 李奕冰, 张红华, 张国秀. 早期白细胞计数评估急性百草枯中毒患者预后的meta分析[J]. 中华危重病急救医学, 2019, 31 (8): 1013-1017. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.2095-4352.2019.08.020 [33] 侯运辉, 苏建玲, 田英平, 等. 入院24小时内急性百草枯中毒患者预后的影响因素[J]. 医学临床研究, 2017, 34(6): 1051- 1053;1057. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-7171.2017.06.003 [34] 朱文捷. 急性百草枯中毒患者百草枯含量、肾及肺功能指标对其预后影响[J]. 中国伤残医学, 2014, 22(9): 61-62. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XCYZ201409042.htm [35] WAN X, ZHOU C, KANG X, et al. Metabolic profiling of amino acids associated with mortality in patients with acute paraquat poisoning[J]. Med Sci Monit, 2018(24): 1397-1407.
-
期刊类型引用(2)
1. 李娜,徐晨雪,韩然然,孙玉倩,焦桂梅. 基于随机森林模型的乳腺癌病人心理资本现况及影响因素. 护理研究. 2023(08): 1325-1331 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 王军,王奕宁. 基于CiteSpace的百草枯中毒的热点与前沿趋势分析. 现代医院. 2023(09): 1457-1463 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(1)





 下载:
下载: