Characteristics of acute occupational poisoning in Baoshan District of Shanghai from 2000 to 2021
-
+ English摘要:目的 了解上海市宝山区急性职业中毒事故发生情况及特征。方法 收集整理2000-2021年上海市宝山区急性职业中毒事件资料, 采用描述性流行病学方法分析其流行特征。结果 宝山区2000-2021年共发生急性职业中毒事件63起, 急性职业中毒病例171例, 死亡36例(病死率21.05%), 事件发生的起数总体呈下降趋势。事件涉及14种行业, 7类26种化学物质, 其中发病前三位的行业分别为化学原料和化学制品制造业(11起, 占17.46%), 金属制品、机械和设备修理业(10起, 占15.87%), 装卸搬运和仓储业(7起, 占11.11%); 导致急性中毒死亡人数居前三的化学物质依次为氨(18例, 占50.00%)、硫化氢(6例, 占16.67%)、一氧化碳(3例, 占8.33%)。未正确使用个人防护用品和未配备有效的个人防护设备为引起中毒事件的主要原因。有限空间作业中毒病例病死率(36.96%), 明显高于非有限空间作业(15.20%)(P < 0.05)。结论 近年来宝山区急性职业中毒情况有所好转, 但仍存在中毒风险, 一氧化碳和硫化氢为该区预防急性职业中毒的重点。相关部门应继续做好急性职业中毒预防工作, 应重点监管用人单位个人防护设备的配备和佩戴情况, 重视有限空间的职业中毒风险, 切实保护劳动者的生命健康和安全。
-
职业中毒是严重危害劳动者健康的职业病之一,2020年全国共报告各类职业病17 064例,其中职业性化学中毒486例[1]。相较于慢性职业中毒,急性中毒在单次或短时间接触高浓度毒物后即可引起健康损害效应,其发病急骤,症状严重,病情变化快,常危及中毒者生命。上海市宝山区辖区内企业众多,产业结构复杂,存在发生急性职业中毒的风险。为了解上海市宝山区急性职业中毒事故发生特征及动态趋势,制定科学有效的预防措施,本研究对宝山区2000—2021年急性职业中毒资料进行了回顾性分析,现将结果报告如下。
1. 资料与方法
1.1 资料来源
收集国家“突发公共卫生事件报告管理信息系统”中2000—2021年间发生在上海市宝山区用人单位的各类急性职业中毒事件,核对有职业中毒诊断资质单位填写的“职业中毒和职业病报告卡”,以及上海市宝山区疾病预防控制中心赴现场进行调查后填写的“急性职业中毒现场劳动卫生学调查表”和“急性职业中毒流行病学调查报告”。接到职业中毒和职业病更正报告的病例以更正报告为准。
1.2 方法
整理调查资料中急性职业中毒事故发生的时间、中毒人数、中毒者个人信息、职业病诊断结果和程度、事故发生单位的行业、毒物类型、事故原因等信息。采用Excel 2016建立数据库,SPSS 22.0软件进行统计学分析。计数资料采用频数、构成比进行统计描述,组间差异采用χ2检验,其等级资料组间差异采用Mann-Whitney U秩和检验,P < 0.05为差异有统计学意义。
2. 结果
2.1 基本情况
2000—2021年宝山区共报告急性职业中毒事件63起,涉及急性职业中毒病例171例,其中死亡36例,病死率21.05%。按照职业病诊断分级,中毒病例轻度中毒99例,中度14例,重度58例;男性139例(占81.29%),女性32例(占18.71%);年龄集中在18 ~ 58岁,平均(36.74 ± 9.54)岁,平均死亡年龄(35.30 ± 9.30)岁;工龄分布在1个月~ 33年9个月,其中 < 1年33例(占19.30%),1 ~ 4年49例(占28.65%),5 ~ 9年27例(占15.79%),≥ 10年62例(占36.26%)。中毒病例涉及14个行业、26种化学物质。
2.2 时间分布
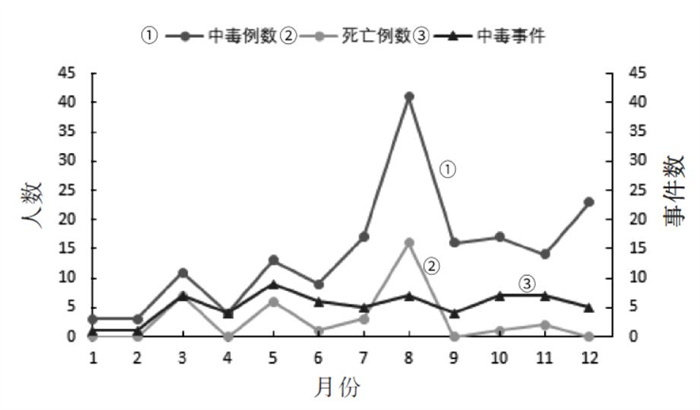
2000—2021年宝山区急性职业中毒事件发生数略有波动,总体呈下降趋势。除个别年度外,中毒人数也呈逐年下降趋势。急性职业中毒中,各月份发生事件数呈小幅度波动,7—12月份中毒人数升高,3、5、8月份死亡人数呈现小高峰,其中8月份中毒人数(41例,占23.98%)及死亡人数(16例,占44.44%)均最高。见表 1、图 1。
表 1 2000—2021年宝山区急性职业中毒发生及死亡情况年份 中毒事件数 中毒例数 死亡例数 年份 中毒事件数 中毒例数 死亡例数 2000 3 4 0 2012 1 1 1 2001 4 9 0 2013 4 34 16 2002 8 22 0 2014 1 2 1 2003 3 8 0 2015 1 2 0 2004 4 8 1 2016 3 5 1 2005 5 14 2 2017 1 3 0 2006 3 5 4 2018 2 3 2 2007 3 7 3 2019 2 2 0 2008 5 8 2 2020 1 1 0 2009 4 13 3 2021 2 3 0 2010 1 14 0 合计 63 171 36 2011 2 3 0 2.3 行业分布
急性职业中毒共涉及14个行业,中毒事件数居前三的行业分别为化学原料和化学制品制造业(11起,占17.46%),金属制品、机械和设备修理业(10起,占15.87%),装卸搬运和仓储业(7起,占11.11%);中毒人数居前三的行业分别为装卸搬运和仓储业(52例,占30.41%),黑色金属冶炼和压延加工业(24例,占14.04%),金属制品、机械和设备修理业(17例,占9.94%);死亡例数居前三的行业分别为装卸搬运和仓储业(20例,占55.56%),黑色金属冶炼和压延加工业(4例,占11.11%),金属制品、机械和设备修理业(4例,占11.11%)。其中装卸搬运和仓储业(低温仓储)引起的急性职业中毒以氨中毒为主,黑色金属冶炼和压延加工业以甲醛和一氧化碳中毒为主,金属制品、机械和设备修理业以一氧化碳中毒为主,化学原料和化学制品制造业中引起急性职业中毒的化学毒物种类较多(10种)。见表 2。
表 2 2000—2021年宝山区不同行业急性职业中毒发生及死亡情况行业 中毒事件数 中毒例数 死亡例数 建筑业 6 16 1 多式联运和运输代理业 4 12 0 装卸搬运和仓储业 7 52 20 化学原料和化学制品制造业 11 14 2 金属制品、机械和设备修理业 10 17 4 皮革、毛皮、羽毛及其制品和制鞋业 2 10 1 黑色金属冶炼和压延加工业 5 24 4 非金属矿物制品业 2 2 1 医药制造业 2 3 0 金属制品业 1 1 0 食品加工制造业 5 12 2 通用设备制造业 1 1 0 仪器仪表制造业 1 1 0 劳务派遣服务业 6 6 1 合计 63 171 36 2.4 毒物种类分布
按化学毒物种类分型,引起的急性职业中毒的化学毒物共计7类,包括有机溶剂、苯的氨基和硝基化合物、氨基甲酸酯类农药、有机磷农药、刺激性气体、单纯窒息性气体、化学窒息性气体。各类型化学毒物引起的急性职业中毒的程度占比各不相同,其中刺激性气体引起的急性中毒人数最多;单纯窒息性气体引起的急性重度职业中毒占比最大,刺激性气体的占比次之。引起急性职业中毒的化学物质有26种,其中事件发生数居前三位的依次为一氧化碳(16起,占26.40%)、硫化氢(7起,占11.11%)、4-硝基苯胺(5起,占4.94%),共计28起,占总中毒事件数的44.44%;中毒人数居前三的依次为一氧化碳(31例,占18.13%)、氨(31例,占18.13%)、4-硝基苯胺(17例,占9.94%),共计79例,占总中毒人数的46.20%;死亡人数居前三的依次为氨(18例,占50.00%)、硫化氢(6例,占16.67%)、一氧化碳(3例,占8.33%),共计27例,占总死亡例数的75.00%。单纯窒息性气体引起的急性职业中毒病死率最高,为60.00%;苯的氨基和硝基化合物、氨基甲酸酯类农药、有机磷农药引起的急性职业中毒无死亡病例。报告的急性职业中毒病例中,有限空间作业共46例,占总中毒人数26.90%。引起有限空间作业中毒的化学物质均为工业性毒物,包括有机溶剂、刺激性气体、窒息性气体,其中单纯窒息性气体10例,化学窒息性气体17例,有机溶剂11例,刺激性气体8例。见表 3。
表 3 2000—2021年宝山区不同毒物急性职业中毒发生及死亡情况化学物质 中毒事件数 中毒例数 中毒程度例数 有限空间作业例数 死亡例数 中毒病死率/% 轻 中 重 是 否 有机溶剂 11 26 17 0 9 11 15 2 7.69 苯的氨基硝基化合物 8 20 15 4 1 0 20 0 0 氨基甲酸酯类 4 15 15 0 0 0 15 0 0 有机磷农药 1 1 1 0 0 0 1 0 0 刺激性气体 9 51 22 4 26 8 44 18 35.29 单纯窒息性气体 5 10 4 0 6 10 0 6 60.00 化学窒息性气体 25 48 25 6 16 17 30 10 20.83 合计 63 171 99 14 58 46 125 36 21.05 2.5 中毒主要原因分析
63起急性职业中毒事件中,未正确使用个人防护用品引起的事件数最多,为24起(占38.10%),未配备有效的个人防护设备次之(20起,占31.75%);171例急性职业中毒病例中,未配备有效个人防护设备引起的中毒病例数最多(占40.00%),设备跑冒滴漏或意外事故次之(占26.90%);设备跑冒滴漏或意外事故引起职业中毒事件中平均每起病例数及死亡人数最多,约每起7例,共死亡20例;引起有限空间作业中毒病例中,盲目施救引起的中毒人数最多(占39.13%)。见表 4。
表 4 2000—2021年宝山区急性职业中毒病例中毒主要原因病例中毒主要原因 中毒事件数 中毒例数 有限空间作业例数 死亡例数 否 是 违反操作规程 12 13 3 10 8 设备跑冒滴漏或意外事故 7 46 44 2 20 未配备有效个人防护设备 20 53 50 3 2 未正确使用个人防护设备 24 41 28 13 0 盲目施救 0 18 0 18 6 合计 63 171 125 46 36 2.6 有限空间作业急性职业中毒存活情况
急性职业中毒病例中,有限空间作业46例,占26.90%,其中死亡17例,病死率36.96%;非有限空间作业125例,占73.10%,其中死亡19例,病死率15.20%。发生急性职业中毒病例中有限空间作业者病死率高于非有限空间作业者,差异有统计学意义(χ2 = 9.576,P < 0.05)。
2.7 有限空间作业急性职业中毒程度分布情况
有限空间作业者中轻度急性中毒14例、中度2例、重度30例,非有限空间作业者中轻度85例、中度12例、重度28例。有限空间作业者发生急性中毒以重度为主(占65.22%),非有限空间作业者发生急性中毒以轻度为主(占68.00%)。经MannWhitney U检验可得,发生急性职业中毒者中是否为有限空间作业的中毒程度不同(Z = - 4.902,P < 0.05),重度中毒病例在有限空间内占比更多。见表 5。
表 5 有限空间作业急性职业中毒程度分布情况[例(占比/%)] 中毒程度 有限空间作业 是 否 轻度 14(30.43) 85(68.00) 中度 2(4.35) 12(9.60) 重度 30(65.22) 28(22.40) 合计 46(100) 125(100) 3. 讨论
急性职业中毒多发病急骤,呈群体性,病情发展迅速,病死率较高,严重威胁劳动者生命健康。本次分析结果显示,2000—2021年上海市宝山区共报告急性职业中毒事件63起,涉及病例171例,轻度99例,中度14例,重度58例,其中死亡36例。由于宝山区地处郊区,工业企业数目众多,同期急性职业中毒事件的发生数远高于处于市区的普陀区[2],与同处郊区的浦东新区[3]、青浦区[4]大致相似。急性职业中毒病例男性远多于女性,与从事职业病危害因素作业中男性工人为主有关。中毒病例平均(36.74 ± 9.54)岁,此年龄段劳动者是接触职业病危害因素岗位中的主力,应作为开展职业卫生的重点宣传培训对象。
无论从事件发生数还是中毒人数来看,近年来急性职业中毒均呈下降趋势,可能与企业产业结构改变、劳动用工制度改善、相关部门及企业对职业病认识程度提升等有关。1、2月份宝山区急性职业中毒事件发生率最低,之后呈上升趋势,5月份达到最高,之后又缓慢下降,与2006—2015年江苏省急性职业中毒发病趋势[5]相似,可能是因为1、2月份企业有较长的假期,3月份复工复产,而后随着气温升高,毒物更易挥发,导致二、三季度急性职业中毒高发。
宝山区化学原料与化学制品制造业、金属制品业、机械和设备修理业、装卸搬运和仓储业发生中毒事件数居前三位,其中金属制品业、机械和设备修理业用人单位主要为宝山区内冶金行业提供仪器设备的检修服务,中毒事件现场多发生在冶金行业工作场所。装卸搬运和仓储业涉及产品主要以化工原料、成品为主。装卸搬运和仓储业、金属制品、机械和设备修理业、黑色金属冶炼中毒人数及病死率均居前三位。宝山区急性职业中毒多发生在化工、冶金等行业,与全国急性职业中毒报道[6]相近,应加强对以上重点行业的急性职业中毒预防教育和常态化监管工作。
从毒物种类看,窒息性气体引起的急性职业中毒事件数最多,窒息性气体中又以一氧化碳与硫化氢中毒发生率较高。一氧化碳、硫化氢等化学性窒息性气体进入机体后,导致血液运输氧或组织利用氧的能力产生障碍,导致组织缺氧,引起“细胞内窒息”[7]。全国职业中毒现状分析也表明一氧化碳和硫化氢是引起急性职业中毒的主要化学品,主要发生于化工、冶金、有色金属、轻工和煤炭等行业[6]。由此可见,宝山区应把一氧化碳和硫化氢作为急性职业中毒的预防重点。
急性职业中毒事件的发生,往往是由多种原因造成。研究发现未正确使用有效个人防护用品引起的急性职业中毒事件数最多,未配备有效个人防护设备次之,与上海市浦东新区[3]的情况一致。因此用人单位应根据工作场所可能存在的危害因素配备有效的个人防护用品,加强劳动者培训,敦促其正确使用和更换个人防护用品。工作场所的跑、冒、滴、漏存在偶然性和不确定性,加之用人单位和劳动者对危害因素风险认识不足,往往导致严重后果。这类事件造成的后果较为严重,平均每起事件中毒人数及死亡人数较多,用人单位及劳动者均应提高警惕,定期对工作场所管道进行排查,及时发现、排除安全隐患。研究还发现盲目施救是引起该区有限空间作业急性职业中毒的主要原因,与全国有限空间中毒特征[8]一致。施救人员缺乏正确的应急救援知识,盲目救援导致二次事故的发生,扩大人员伤亡[9]。用人单位应提高作业人员的自我保护意识,为劳动者提供专业的应急救援培训,切实提高劳动者的自救互救能力。
从中毒环境看,宝山区非有限空间作业发生的急性职业中毒病例占多数,但有限空间作业发生的急性职业中毒病死率、严重程度高于非有限空间作业。在有限空间内作业,易造成有毒有害、易燃易爆物质积聚或者氧含量不足。有限空间作业过程中一旦防护不当或操作不当,极易引起群死群伤安全事故,历来是事故防范的重中之重[10]。用人单位应制定有限空间作业职业病危害防护控制计划、准入程序和安全作业规范,作业人员应提前知晓计划、程序和规程;作业人员应受到专业的职业安全卫生培训,作业前应对有限空间内存在的职业病危害因素进行识别、评估,严格落实准入制度;明确有限空间作业负责人、准入者和监护者三者职责,在有限空间外设置警示标志,作业人员应被告知有限空间的位置和所存在的危害;作业人员应配备有效的个人防护设备,并配备有专业的应急救援保障。
作者声明 本文无实际或潜在的利益冲突 -
表 1 2000—2021年宝山区急性职业中毒发生及死亡情况
年份 中毒事件数 中毒例数 死亡例数 年份 中毒事件数 中毒例数 死亡例数 2000 3 4 0 2012 1 1 1 2001 4 9 0 2013 4 34 16 2002 8 22 0 2014 1 2 1 2003 3 8 0 2015 1 2 0 2004 4 8 1 2016 3 5 1 2005 5 14 2 2017 1 3 0 2006 3 5 4 2018 2 3 2 2007 3 7 3 2019 2 2 0 2008 5 8 2 2020 1 1 0 2009 4 13 3 2021 2 3 0 2010 1 14 0 合计 63 171 36 2011 2 3 0 表 2 2000—2021年宝山区不同行业急性职业中毒发生及死亡情况
行业 中毒事件数 中毒例数 死亡例数 建筑业 6 16 1 多式联运和运输代理业 4 12 0 装卸搬运和仓储业 7 52 20 化学原料和化学制品制造业 11 14 2 金属制品、机械和设备修理业 10 17 4 皮革、毛皮、羽毛及其制品和制鞋业 2 10 1 黑色金属冶炼和压延加工业 5 24 4 非金属矿物制品业 2 2 1 医药制造业 2 3 0 金属制品业 1 1 0 食品加工制造业 5 12 2 通用设备制造业 1 1 0 仪器仪表制造业 1 1 0 劳务派遣服务业 6 6 1 合计 63 171 36 表 3 2000—2021年宝山区不同毒物急性职业中毒发生及死亡情况
化学物质 中毒事件数 中毒例数 中毒程度例数 有限空间作业例数 死亡例数 中毒病死率/% 轻 中 重 是 否 有机溶剂 11 26 17 0 9 11 15 2 7.69 苯的氨基硝基化合物 8 20 15 4 1 0 20 0 0 氨基甲酸酯类 4 15 15 0 0 0 15 0 0 有机磷农药 1 1 1 0 0 0 1 0 0 刺激性气体 9 51 22 4 26 8 44 18 35.29 单纯窒息性气体 5 10 4 0 6 10 0 6 60.00 化学窒息性气体 25 48 25 6 16 17 30 10 20.83 合计 63 171 99 14 58 46 125 36 21.05 表 4 2000—2021年宝山区急性职业中毒病例中毒主要原因
病例中毒主要原因 中毒事件数 中毒例数 有限空间作业例数 死亡例数 否 是 违反操作规程 12 13 3 10 8 设备跑冒滴漏或意外事故 7 46 44 2 20 未配备有效个人防护设备 20 53 50 3 2 未正确使用个人防护设备 24 41 28 13 0 盲目施救 0 18 0 18 6 合计 63 171 125 46 36 表 5 有限空间作业急性职业中毒程度分布情况
[例(占比/%)] 中毒程度 有限空间作业 是 否 轻度 14(30.43) 85(68.00) 中度 2(4.35) 12(9.60) 重度 30(65.22) 28(22.40) 合计 46(100) 125(100) -
[1] 国家卫生健康委员会. 2020年我国卫生健康事业发展统计公报[J]. 中国病毒病杂志, 2021, 11(5): 321-329. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZRYX202105001.htm [2] 胡芳, 彭臻, 张焕生. 2004-2019年上海市普陀区突发公共卫生事件流行特征与处置情况分析[J]. 上海预防医学, 2021, 33(12): 1187-1190;1200. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SHYI202112017.htm [3] 杨黎明, 黄云彪, 王宇, 等. 80起急性职业中毒事件流行病学分析[J]. 环境与职业医学, 2012, 29(3): 171-172. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LDYX201203013.htm [4] 刘晓晓, 潘引君, 叶开友, 等. 上海市某区近5年急性职业中毒事故深度分析[J]. 职业卫生与应急救援, 2020, 38(2): 187-190. doi: 10.16369/j.oher.issn.1007-1326.2020.02.024 [5] 顾呈华, 丁帮梅, 韩磊, 等. 2006-2015年江苏省急性职业中毒发病情况分析[J]. 中国工业医学杂志, 2018, 31(2): 130-132. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SOLE201802023.htm [6] 孙国翔, 周川, 杨小兵, 等. 1993-2016年我国职业中毒现状分析及防治对策[J]. 中国安全生产科学技术, 2018, 14(10): 187-192. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LDBK201810030.htm [7] 孙贵范. 职业卫生与职业医学[M]. 7版. 北京: 人民卫生出版社, 2012: 103-121. [8] 王媛媛. 职业中毒事故行为原因分析及预防对策[D]. 吉林: 吉林建筑大学, 2020. [9] 王致, 张晋蔚, 邓冠华, 等. 窒息性气体急性职业中毒事故原因分析及对策[J]. 职业卫生与应急救援, 2015, 33(6): 453-455. doi: 10.16369/j.oher.issn.1007-1326.2015.06.022 [10] 孙伟锋. 有限空间作业安全事故预防对策[J]. 现代职业安全, 2021(12): 54-57. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-4156.2021.12.024





 下载:
下载: