Study on protective ability of typical respiratory protective equipment against different airborne metal particles in workplaces
-
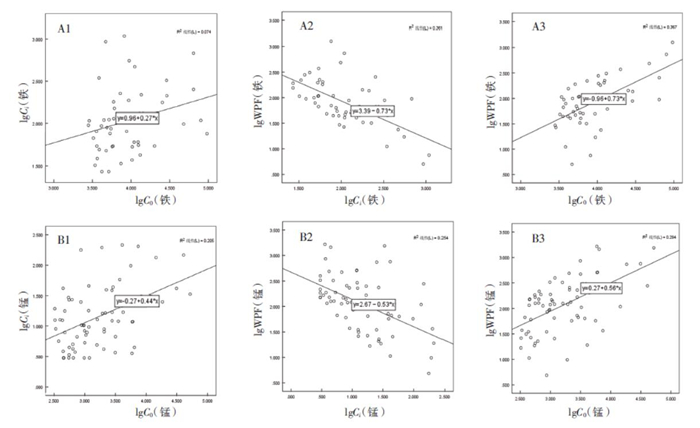
+ English摘要:目的 通过测定焊接工人佩戴的不同呼吸防护用品(respiratory protection equipment,RPE)对不同金属的工作场所防护因数(workplace protection factor,WPF),比较不同类型RPE对不同金属颗粒物的防护能力。方法 选择上海某船厂焊接岗位工人18人(17名男性和1名女性)为研究对象,根据工人日常工作实际佩戴的RPE类型,确定相应的RPE测试,其中5人佩戴过滤式半面罩(RPE1),13人佩戴三折折叠式防颗粒物口罩(RPE2),采用改良的美国WPF测试方法分别测试RPE内、外的金属颗粒物浓度,计算WPF值并进行对数转换,组间相关性采用Pearson相关分析,组间比较采用两因素非参数Scheirer-Ray-Hare检验。结果 锰颗粒和铁颗粒的WPF值符合对数正态分布,呼吸防护用品对锰颗粒和铁颗粒的WPF第5百分位数(WPF5%)分别为15.01和13.60,几何均数(GM)分别为114.76和82.37,RPE1和RPE2的WPF5%分别为11.25和22.28,GM分别为86.49和123.01。两种RPE对空气中金属粉尘颗粒物的WPF数值差异无统计学意义(P > 0.05),而铁和锰两种金属的WPF数值差异亦无统计学意义(P > 0.05),且RPE类型和不同金属颗粒物之间对防护效果不存在交互作用(P > 0.05)。结论 改良的WPF测试方法能有效测试RPE的WPF值,本次测试的2种RPE对不同金属颗粒物均能起到防护作用,防护效果接近。
-
氟元素是人体所需的多种微量元素之一,是已知元素中化学性质最为活泼的非金属元素,以多种形式广泛存在于水、土壤、空气和有机体中。我国地方性氟中毒病区分布于28个省(市),受威胁人口达到1.52亿[1]。氟及其无机化合物在工业中用途广泛,化工行业用于制药、农药、冷冻剂、有机反应催化剂、氟塑料和氟橡胶等;轻工业用于制造玻璃、搪瓷、釉料、建筑材料以及玻璃蚀刻;冶金行业用于有色金属,如铝、镁、铍等的提炼,以及炼钢、生产特殊焊药等。氟是人体内一种必需的微量元素,但摄入过多会产生氟中毒。氟的工业性污染也能造成劳动者发生慢性氟中毒,由于同时叠加环境氟接触,使得氟骨症和氟斑牙患者在职业接触氟工人群体中发病人数较多[1]。除了引起骨代谢紊乱,氟对其他器官(如脑、肝、肾、心、甲状腺、睾丸、脊髓等)也可产生损害[2]。在氟中毒的诊断、治疗及流行病学调查等方面已有大量的研究和报道[3]。既往研究显示:氟性骨损伤受到年龄、性别、工龄、氟接触剂量等多种因素的影响,氟性骨损伤主要表现为骨硬化、骨疏松软化以及骨转换[4]。随着企业生产工艺和防护条件的改善,当前职业性无机氟接触主要表现为低剂量长期接触的特征,本次研究拟通过对华东某氟化工企业接触氟化氢工人的调查,了解车间工作环境氟接触水平、作业人员体格检查结果,探讨长期低剂量氟化氢接触对工人骨代谢的影响。
1. 对象与方法
1.1 对象
研究企业为我国华东某市工业开发区内氟化氢生产企业,近年来,该企业每年开展空气中氟化氢浓度检测,每年为氟化氢接触工人开展职业健康监护。选择该企业氟化氢生产车间接触氟化氢作业的工人302名为研究对象(接触组),其中男253人,女49人;年龄21 ~ 58岁,平均(38.1 ± 8.4)岁;平均接触氟化氢工龄(12.6 ± 8.3)年;操作工225人,分析工38人,检修工1人。
选取华东某电子厂85名工人为对照组,该组工人工作中无氟化氢接触,且工厂生活条件,工人生活习惯、社会经济状况和对照组基本相同。其中男63人,女22人;年龄22 ~ 59岁,平均(36.1 ± 9.4)岁;装配工76人,管理岗位9人。两组研究对象年龄、性别差异均无统计学意义(t年龄 = 1.902,χ性别2 = 3.51,P>0.05)。
两组入选研究对象均已排除糖尿病、甲状腺炎症等内分泌疾病;骨骼检测时排除骨肿瘤、骨畸形等疾病。本课题经过上海市化工职业病防治院医学伦理审查,伦理审查编号:上海市化工职业病防治院医学伦理委员会批准通知书2021-0001。
1.2 方法
1.2.1 问卷调查
本研究组成员经统一培训后参加本次调查。问卷内容包括一般情况、有害因素接触史、生活方式、疾病史等项目,由当地医院人员在体格检查时询问并录入体检系统,课题组成员对调查内容进行核对、校验。
1.2.2 尿氟值检测
用清洁聚乙烯塑料瓶收集班前尿样20 ~ 30 mL,低温运输至实验室,-20℃保存,根据中华人民共和国卫生行业标准中的离子选择电极法测定尿氟[5],并采用加标方法进行质量控制。
1.2.3 骨密度测定
使用EXA-PRESTO骨密度仪测量骨密度,测量时人体取坐位,测量部位为右手桡骨,由桡骨茎突至尺骨鹰嘴伸面的长度,取中、下三分之一交界点位测量点。仪器测量均由同一技术员操作,开机前经标准模块校正标定,重复测定误差在2%之内。每个个体的骨密度均作Z评分[6]。Z评分<-2.4时定义为骨质疏松,Z评分<-1.0时为骨量减少,同时将Z评分绝对值>2.4作为骨代谢异常的依据。
1.2.4 骨骼影像诊断
放射科体检骨盆正位片、尺桡骨正侧位片、胫腓骨正侧位片影像异常,或出现骨岛、骨质密度不均匀、高密度影像等诊断定为骨骼影像诊断异常。
1.2.5 氟化氢作业工人外剂量测定
(1)工作场所空气中氟化氢浓度的测定:采样点布置在工人操作岗位(呼吸带高度),采用浸渍滤膜采样,以5 L/min流量采集样品15 min,滤膜采用盐酸溶解后,以离子选择电极法测定。工作场所氟化氢浓度按不同岗位进行测定,并按照各车间不同工段采集样品中氟化氢浓度(每个采样点分别在同一个工作日的上午、中午、下午三个时段采样并加权平均,得到该检测点的氟化氢空气浓度),若低于检测限则一律取检测限值的半值计算。每小时有效通气量=(潮气量-解剖无效腔)×呼吸频率。(潮气量-解剖无效腔)按照500 mL估算,每分钟呼吸频率按照16次计算,每小时通气量按照480 L进行估算,女性按照男性的呼气量的75%进行估算。
(2)氟化氢摄入外剂量估算:工作场所氟化氢摄入量=工作场所氟化氢浓度(mg/m3)×每小时有效通气量(m3/h)×每年工作时间(40 h/周× 50周/年)×工龄×吸收系数(0.03)[7]。
1.2.6 统计学分析
以Excel建立数据库,并用SPSS 19.0软件进行统计学分析。计量资料采用均数±标准差(x ± s)表示,两组间差异比较采用独立样本t检验,三组及以上组间差异采用单因素方差分析;不符合正态分布的,采用中位数和第25、75百分位数[M(P25,P75)]表示。计数资料以率表示,组间比较采用χ2检验,理论频数不符合χ2检验要求的采用Fisher确切概率法进行检验。计量资料之间的相关度采用Pearson相关分析。P<0.05为差异有统计学意义。
2. 结果
2.1 无机氟接触情况
2.1.1 车间环境氟化氢检测浓度
检测资料显示:2018年各车间30个检测点空气中氟化氢平均质量浓度为<0.017 ~ 0.64 mg/m3,中位数和第25、75百分位数[M(P25,P75)]为0.046(0.036,0.072)mg/m3;类似的,2019年车间30个检测点空气中氟化氢平均质量浓度为<0.017~1.867 mg/m3,[M(P25,P75)]为0.027(0.020,0.047)mg/m3;2020年车间空气中30个检测点氟化氢的平均质量浓度为<0.017 ~ 0.728 mg/m3,[M(P25,P75)]为0.008(0.008,0.026)mg/m3,均低于国家卫生标准最高容许浓度2.0 mg/m3[8-10]。
2.1.2 工人接触氟化氢外剂量情况
工人岗位较固定。应用2018、2019、2020年的车间空气氟化氢环境检测数据,测算302名氟化氢接触工人的外剂量摄入,工龄≤ 3年的工人,分别计算每年的摄入量再相加得到总摄入量;工龄>3年的工人接触的氟化氢浓度取3年车间各采样点空气氟化氢环境检测数据的均值(即三年中30个采样点,每个采样点取3年的均值)。结果显示氟化氢作业工人摄入外剂量最小值为0.24 mg,最大值为133.45 mg,中位数为21.3 mg。
将氟化氢接触工人按照年龄分为<30岁、30 ~ 40岁、>40岁组,外剂量分为0 ~ 2 mg、>2 ~ 5 mg、>5 ~ 10 mg、>10 ~ 20 mg以及>20 mg组。随着年龄增大,男性工人外剂量值有升高趋势(P<0.01);女性工人外剂量值也有升高趋势(P<0.05)。男性和女性工人之间氟化氢外剂量(以表 1中的合计值计)差异无统计学意义(χ2 = 8.22,P>0.05)。
表 1 不同年龄、性别氟化氢接触工人外剂量情况[人数(占比/%)] 性别 年龄/岁 氟化氢外剂量值/mg 趋势χ2值 P值 1(0 ~ 2) 3.5(>2 ~ 5) 7.5(>5 ~ 10) 15(>10 ~ 20) 25(>20) ≤ 30 13(18.8) 27(39.1) 16(23.2) 9(13.0) 4(5.8) 50.9 0.01 男 >30 ~ 40 4(5.6) 17(23.9) 16(22.5) 23(32.4) 11(15.5) >40 5(4.4) 19(16.8) 10(8.8) 40(35.4) 39(34.5) 合计 22(8.7) 63(24.9) 42(16.6) 72(28.5) 54(21.3) ≤ 30 1(33.3) 0(0) 1(33.3) 1(33.3) 0(0) 女 >30 ~ 40 0(0) 2(13.3) 4(26.7) 7(46.7) 2(13.3) 19.1 0.04 >40 1(3.2) 3(9.7) 4(12.9) 11(35.5) 12(38.7) 合计 2(4.1) 5(10.2) 9(18.4) 19(38.8) 14(28.6) 2.1.3 工人尿氟值情况
将两组研究对象分别按照年龄分组,观察班前研究对象尿氟值。不同性别、组别的研究对象的尿氟值在不同年龄间比较,差异均无统计学意义(P>0.05)。见表 2。可见本次研究中,年龄非尿氟值的影响因素。
表 2 不同年龄、性别氟化氢接触工人尿氟值组别 性别 年龄/岁 人数 尿氟值/(mg/L) F值 P值 接触组 男(n = 253) <30 69 1.05 ± 0.63 1.26 0.28 30 ~ 40 71 1.09 ± 0.71 >40 113 1.25 ± 1.13 女(n = 49) <30 3 1.73 ± 1.22 0.82 0.44 30 ~ 40 15 0.99 ± 0.43 >40 31 0.86 ± 0.77 对照组 男(n = 63) <30 25 0.44 ± 0.16 0.39 0.67 30 ~ 40 23 0.43 ± 0.11 >40 15 0.47 ± 0.13 女(n = 22) <30 1 0.31 1.36 0.21 30 ~ 40 16 0.42 ± 0.11 >40 5 0.52 ± 0.22 进一步分析,接触组中,男性工人尿氟质量浓度(1.15 ± 0.91)mg/L,女性(0.96 ± 0.71)mg/L,两组差异无统计学意义(t = 1.30,P = 0.19);对照组中,男性尿氟质量浓度(0.45 ± 0.14)mg/L,女性(0.44 ± 0.15)mg/L,两组差异无统计学意义(t = 0.21,P = 0.83)。可见本次研究中,性别也非尿氟值的影响因素。
接触组尿氟质量浓度(1.12 ± 0.95)mg/L,对照组(0.45 ± 0.14)mg/L,两组差异有统计学意义(t = 6.52,P<0.01)。接触组的尿氟值明显高于对照组。
2.1.4 不同工龄段、不同性别氟化氢接触工人尿氟值分布情况
美国工业卫生协会(ACGIH)将尿氟职业接触生物限值修订为班前2 mg/L[11],本次调查基于工人尿氟值的实际分布将其分为0 ~ 0.50 mg/L、>0.50 ~ 1.00 mg/L、>1.00 ~ 1.50 mg/L、>1.50 ~ 2.00 mg/L、>2.00 mg/L组。接触组中,不同工龄女性工人在不同尿氟组中分布差异无统计学意义(P>0.05),但是不同工龄男性工人在不同尿氟组中分布差异有统计学意义(P<0.05),工龄在10年以内的工人尿氟值在1.00 mg/L以上的占比要高于其他工龄段。见表 3。
表 3 不同工龄、性别氟化氢接触工人尿氟值分布[人数(占比/%)] 工龄/年 尿氟值(mg/L) χ2值 P值 0.25(0 ~ 0.50) 0.75(>0.50 ~ 1.00) 1.25(>1.00 ~ 1.50) 1.75(>1.50 ~ 2.00) 2.25(>2.00 ~ 8.10) 男 1 ~ 5 19(24.1) 26(32.9) 14(17.7) 12(15.2) 8(10.1) 25.66 <0.05 >5 ~ 10 6(10.9) 17(30.9) 14(25.5) 16(29.1) 2(3.6) >10 ~ 15 15(27.8) 16(29.6) 14(25.9) 6(11.1) 3(5.6) >15 ~ 20 4(22.2) 2(11.1) 4(22.2) 7(38.9) 1(5.6) >20 10(21.3) 17(36.2) 4(8.5) 9(19.1) 7(14.9) 合计 54(21.3) 78(30.8) 50(19.8) 50(19.8) 21(8.3) 女 1 ~ 10 6(50) 4(33.3) 0(0) 0(0) 2(16.7) 18.14 >0.05 >10 ~ 20 3(27.3) 5(45.5) 2(18.2) 1(9.1) 0(0) >20 12(46.2) 7(26.9) 2(7.7) 2(7.7) 3(11.5) 合计 21(42.9) 16(32.7) 4(8.2) 3(6.1) 5(10.2) 2.1.5 接触组氟化氢外剂量与尿氟之间的相关关系
取接触组工人的氟化氢外剂量值和尿氟值,对其进行Pearson相关分析,结果显示尿氟值与氟化氢外剂量具有相关性(r = 0.115,P<0.05)。
2.2 职业性氟化氢接触对骨代谢的影响
2.2.1 氟化氢接触与骨骼诊断异常的关系
将接触组氟化氢摄入的外剂量分为0 ~ 2 mg、>2 ~ 5 mg、>5 ~ 10 mg、>10 ~ 20 mg以及>20 mg组,结果显示:随着外剂量值的增加,不同外剂量组氟化氢接触工人未呈现骨量减少、骨质疏松、骨骼影像学诊断异常率升高或降低的趋势(趋势χ2 = 0.51、4.86、0.28,P>0.05)。见表 4。
表 4 外剂量接触与骨骼诊断异常的关系[异常例数(异常率/%)] 外剂量/mg 骨量减少 骨质疏松 骨骼影像诊断 0 ~ 2(n = 24) 11(45.8) 0(0) 1(4.1) >2 ~ 5(n = 68) 25(36.8) 2(2.9) 7(10.3) >5 ~ 10(n = 51) 19(37.3) 0(0) 5(9.8) >10 ~ 20(n = 91) 34(37.4) 3(3.3) 4(4.4) >20(n = 68) 28(41.2) 6(8.8) 5(7.4) 2.2.2 尿氟值与骨骼诊断异常的关系
不同尿氟组工人骨质疏松、骨骼影像学诊断异常率差异无统计学意义(χ2 = 0.46、3.27,P>0.05),但不同尿氟组工人骨量减少检出率差异有统计学意义(χ2 = 6.95,P<0.05),具体表现为:随着尿氟值增高,骨量减少的异常率升高,当尿氟值达到>1.0 ~ 1.5 mg/L时,骨量减少的异常率最高,随后当尿氟值继续增高时,骨量减少的异常率逐渐降低。见表 5。
表 5 尿氟值与骨骼诊断异常的关系[异常例数(异常率/%)] 尿氟值/(mg/L) 骨量减少 骨质疏松 骨骼影像诊断 0 ~ 0.5(n = 133) 28(21.1) 4(3.0) 6(4.5) >0.5 ~ 1.0(n = 120) 34(28.3) 3(2.5) 7(5.8) >1.0 ~ 1.5(n = 54) 27(50.0) 2(3.7) 3(5.6) >1.5 ~ 2.0(n = 53) 23(43.4) 1(1.9) 6(11.3) >2.0(n = 27) 6(22.2) 1(3.7) 3(11.1) 合计(n = 387) 118(30.4) 11(2.8) 25(6.5) 2.2.3 年龄与骨骼诊断异常的关系
接触组骨量减少的异常率为38.7%,对照组骨量减少的异常率为4.7%,差异有统计学意义(χ2 = 39.75,P<0.01)。接触组骨质疏松的异常率为3.6%,对照组骨质疏松的异常率为0,差异无统计学意义(χ2 = 0.46,P>0.05)。接触组骨骼影像诊断异常率7.3%,对照组骨骼影像诊断异常率4.5%,差异无统计学意义(χ2 = 3.21,P>0.05)。
将接触工人年龄分为<30、30 ~ 40、>40岁三个年龄段,各年龄组骨质疏松、骨骼影像学诊断异常率差异均无统计学意义(χ2 =1.18、0.15,P>0.05),但骨量减少检出率差异有统计学意义(χ2 = 12.01,P<0.01),<30岁年龄段工人中骨量减少检出率最高,其次是30 ~ 40岁年龄段,40岁以上年龄组骨量减少人数相对较少。见表 6。
表 6 年龄与骨骼诊断异常的关系[异常例数(异常率/%)] 年龄/岁 骨量减少 骨质疏松 骨骼影像诊断 <30(n = 72) 39(45.8) 2(2.8) 6(8.3) 30 ~ 40(n = 81) 35(40.7) 2(2.3) 6(7.0) >40(n = 144) 43(29.9) 7(6.1) 10(6.9) 合计(n = 302) 117(38.7) 11(3.6) 22(7.3) 2.2.4 工龄与骨骼诊断异常的关系
将接触工人工龄分为1 ~ 5、>5 ~ 10、>10 ~15、>15 ~ 20、>20年5个工龄段,各工龄组骨质疏松、骨骼影像学诊断异常率差异无统计学意义(χ2 = 4.86、1.34,P>0.05),但骨量减少检出率差异有统计学意义(χ2 = 8.50,P<0.01),1 ~ 5年工龄和>5 ~ 10年工龄段中骨量减少的比例最高,其次是>10 ~ 15年工龄段。见表 7。
表 7 工龄与骨骼诊断异常的关系[异常例数(异常率/%)] 工龄/年 骨量减少 骨质疏松 骨骼影像诊断 1 ~ 5(n = 83) 39(47.0) 4(4.8) 6(7.2) >5 ~ 10(n = 63) 29(46.0) 0(0) 5(7.9) >10 ~ 15(n = 60) 22(36.7) 3(5.0) 6(10) >15 ~ 20(n = 23) 6(26.1) 2(8.7) 1(4.3) >20(n = 73) 21(28.8) 2(2.7) 4(5.5) 合计(n = 302) 117(38.7) 11(3.6) 22(7.3) 3. 讨论
氟化氢主要通过呼吸道进入人体,并迅速进入血循环蓄积于骨、软组织中,导致全身大部分骨骼、软组织受累。氟在骨骼与牙齿的形成中有重要的作用,人体骨骼固体的60%为骨盐,而氟能与骨盐结晶表面的离子进行交换,形成氟磷灰石而成为骨盐的组成部分[12-13]。骨是氟中毒的主要靶器官之一,其Χ线改变主要为骨硬化(骨量增多)、骨疏松软化(骨量减少)以及骨硬化、疏松、软化的混合型(骨转换)等[4, 14]。对人氟骨症的研究已经证明,高氟摄入可引起氟中毒,并可加重骨质疏松[15]。骨吸收和骨硬化在氟骨症的发展过程中相互存在,处于动态平衡,而成骨细胞活动增强在氟化物的骨骼效应中起主导作用;在同一病例,四肢长管状骨更易表现出骨质疏松。高骨转换状态是氟骨症的重要特征,特别是密质骨松质化的改变与氟骨症的X线改变(如哈佛管扩大、骨质呈斑片状吸收、皮质界限不清、沿皮质长轴出现长短不等的细条状透亮线等)相吻合。中国营养学会(2007)推荐成年人的氟参考摄入量为1.5 mg/d,可耐受最高摄入量为3.0 mg/d,饮水含氟量为0.7 ~ 1.0 mg/L[1]。适量的氟(0.5~1.0 mg /L)能被牙釉质中的羟磷灰石吸附,形成坚硬致密的氟磷灰石表面保护层,有防龋作用,缺氟则影响氟磷灰石的形成,较易发生龋齿。摄入过多氟可影响体内氟、钙及磷的正常比例,形成较易沉积的氟化钙,引起氟骨症[1]。
人体内的氟约有75%是通过肾脏以尿氟的形式排出体外,因而尿氟值可直接反映体内氟负荷的情况。国内外研究[16-17]表明,尿氟值作为人群氟暴露的内剂量指标,可较好地反映一个地区人群近期氟负荷状况和环境水平,是评价人群氟暴露程度的一个良好指标。对于群体而言,尿氟排泄具有稳定性,可以反映人群的氟暴露水平和摄氟状况,评价人群的氟负荷状况和环境氟化物水平[18]。
本次研究调取的企业2018—2020年车间氟化氢浓度检测数据,分别对氟化氢装置预反应器、转炉炉尾、泵区、氟化反应器、罐区卸车处、焚烧炉、脱酸塔等30个岗位进行检测,发现车间氟化氢空气平均检测浓度均低于国家标准限值,说明该企业工人均为低浓度接触。根据工人的岗位分布推算出每人的外剂量接触值,因而工人的外剂量值与工龄和岗位氟化氢空气检测浓度高度相关。本次调查发现接触组工人外剂量随着年龄增大而增加(P<0.05),可能的原因为该企业工人流动性较低,年龄与工龄有一定的相关性。
调查发现接触组尿氟值远高于对照组(P<0.01),对照组的尿氟值(0.45 mg/L)反映环境和生活接触产生的无机氟本底值,与以前学者所得出的0.53 mg/L[19]基本类似。人体摄入的氟经胃肠道以被动转运方式吸收,一部分储留在体内,主要沉积于钙化组织中;另一部分则通过肾脏排出。尿氟是机体摄入氟量、吸收氟量、骨骼蓄积氟状况以及机体排泄氟能力综合作用的结果。以往学者发现年长者机体氟负荷较年轻者要高,氟从骨中排泄的速度也相应减慢,随着年龄的增加,摄氟时间变长,体内蓄积氟的量增大[20]。本次研究发现各性别、组别的尿氟值均不随工人的年龄而变化,这可能是年长者从事的岗位氟化氢浓度较低,同时该企业历年来监测氟化氢浓度均低于氟化氢限值,企业工人仅限于长期低浓度接触,且尿氟值的影响因素众多,是机体摄入与吸收氟、骨骼蓄积氟状况以及机体排泄氟能力的综合作用的表现。
接触组工龄在10年以内的男性工人尿氟值在1.00 ~ 1.50 mg/L以上的占比高于10年以上者,通过调查发现该段工龄的工人一般为企业一线工作人员,从事的岗位为反应器岗位、焚烧岗位,这些岗位氟化氢监测浓度较高(0.68 ~ 1.87 mg/m3)。女性由于接触人数较少,故尚未在统计学上发现有此趋势。
本次调查发现工人氟化氢外剂量与尿氟值之间仅存在弱相关,其一原因可能是,工人在企业工作时间较长,表现为长期低剂量接触;其二是本次研究选择某一天正常工况的测定值代表全年的检测浓度,以2018—2020年空气氟化氢检测加权平均数据推算部分人群总的外剂量,这可能给结果带来了一定的误差。但由于外剂量的测定是进行危害评估的首要步骤,今后的研究课题组要设法获取更全面、更精确的外剂量的数值;同时在后续的研究中我们也要更多地应用内剂量值来评估危害接触。
随着尿氟值增高,接触组工人骨量减少的异常率升高,当尿氟达到1.0~1.5 mg/L时,骨量减少的异常率最高,之后又逐渐降低,说明中低剂量氟化氢接触工人容易引起骨量减少,并且随着尿氟值的增加,异常率逐渐增高。这和以往学者[13, 21]的研究基本吻合,尿氟值在2.0 mg/g(以肌酐校正)以上发生骨质减少的发生率明显增高,说明接氟工人骨密度异常在某种程度上与尿氟值具有相关性,可与尿氟值一样作为判断职业性氟损伤的潜在指标。国外研究[22]也有同样的趋势,接触无机氟工人首先表现为骨密度降低,当尿氟值继续增加后达到210 μmol/L后将会观察到骨质增生。氟化物可以影响类骨组织的产生,少量的氟有刺激破骨细胞的作用,大量的氟可抑制破骨细胞而形成骨质增生[4, 23-24]。本次研究还发现15年工龄以内以及尿氟值在1.0 ~ 1.5 mg/L的工人的骨量减少检出率较高,可能原因有:(1)年龄较大(工龄也较长)的工人从事氟化氢浓度较低的岗位,如预反应器、中部反应器、泵区等;(2)尿氟值是反映无机氟代谢的指标,体内无机氟蓄积5 ~ 15年最易引起骨量减少;(3)存在健康工人效应。提示企业管理者更应关注40岁左右、工龄5 ~ 15年的接触氟化氢工人,对该对象进行重点干预。
由于骨量减少是最早出现的骨效应指标,早于骨质疏松和影像诊断异常等指标的出现,因此本次研究发现不同接触水平的工人的骨骼异常主要以骨量减少的检出率存在差异(P<0.05)为主。本次骨骼影像学诊断异常主要表现为股骨高密度影像及股骨、胫骨骨岛,有学者[22]研究匈牙利搪瓷厂氟接触工人指出班前尿氟值低于210 μmol/L骨质增生很难发生,本研究接触组工人尿氟均值为1.15 mg/L,最高值为8.1 mg/L,提示我们要对影像诊断异常对象做进一步跟踪随访。
作者声明 本文无实际或潜在的利益冲突 -
表 1 7种金属WPF检测情况
金属 样品数 C0(/mg/L) Ci(/mg/L) WPF值 锰 69 0.324 ~ 51.986 0.003 ~ 0.214 4.864 ~ 1 652.095 铁 49 0.806 ~ 96.099 0.027 ~ 1.085 5.035 ~ 1 267.090 镍① 83 0.015 0.015 ~ 0.427 锌① 83 0.018 ~ 0.165 0.018 ~ 5.919 镉① 83 0.002 0.002 铬① 83 0.003 ~ 0.010 0.003 ~ 0.131 铜① 83 0.005 ~ 0.011 0.005 ~ 1.771 注:①该金属颗粒物测得的浓度范围由未经筛选之前的全部样本得出,鉴于C0检测结果浓度较低,不符合C0最低可接受标准,未进行WPF值计算。 表 2 不同RPE对不同金属颗粒防护效果
类型 参数 WPF值 总计 锰 铁 RPE1 样品数 25 19 44 GM 93.62 77.94 86.49 GSD 3.85 3.03 3.46 WPF5% 13.27 12.55 11.25 RPE2 样品数 44 30 74 GM 128.84 85.31 123.01 GSD 3.22 3.01 2.83 WPF5% 18.82 13.91 22.28 合计 样品数 69 49 118 GM 114.76 82.37 107.87 GSD 3.44 2.99 3.08 WPF5% 15.01 13.60 16.93 表 3 两因素非参数Scheirer-Ray-Hare检验
项目 自由度 均方 H值 P值 RPE类型 1 1 287 1.099 52 0.294 37 金属类型 1 3 046 2.603 0 0.106 66 RPE和金属交互作用 1 618 0.528 32 0.467 31 残差 114 131 853 -
[1] American National Standards Institute (ANSI). American national standard for respiratory protection : ANSI-Z88.2[S]. New York: ANSI, 1998.
[2] Occupational Safety and Healthy Administration. The respiratory protection standard: 29 CFR1910.134[EB/OL]. [2022-07-08]. https://www.osha.gov/laws-regs/regulations/standardnumber/1910/1910.134.
[3] 中华人民共和国国家卫生和计划生育委员会. 工作场所空气有毒物质测定第17部分: 锰及其化合物: GBZ/T 300.17—2017[S]. 北京: 人民卫生出版社, 2017. [4] 中华人民共和国国家卫生和计划生育委员会. 工作场所空气有毒物质测定第31部分: 锌及其化合物: GBZ/T 300.31—2017[S]. 北京: 人民卫生出版社, 2017. [5] 中华人民共和国卫生部. 工作场所空气有毒物质测定第16部分: 镍及其化合物: GBZ/T 160.16—2004[S]. 北京: 人民卫生出版社, 2004. [6] 中华人民共和国国家卫生和计划生育委员会. 工作场所空气有毒物质测定第9部分: 铬及其化合物: GBZ/T 300.9—2017[S]. 北京: 人民卫生出版社, 2017. [7] 中华人民共和国国家卫生和计划生育委员会. 工作场所空气有毒物质测定第11部分: 铜及其化合物: GBZ/T 300.11—2017[S]. 北京: 人民卫生出版社, 2017. [8] 中华人民共和国国家卫生和计划生育委员会. 工作场所空气有毒物质测定第33部分: 金属及其化合物: GBZ/T 300.33—2017[S]. 北京: 人民卫生出版社, 2017. [9] 中华人民共和国国家卫生和计划生育委员会. 工作场所空气有毒物质测定第6部分: 镉及其化合物: GBZ/T 300.6—2017[S]. 北京: 人民卫生出版社, 2017. [10] DULING M G, LAWRENCE R B, SLAVEN J E, et al. Simulated workplace protection factors for half-facepiece respiratory protective devices[J]. J Occup Environ Hyg, 2007, 4(6): 420-431. doi: 10.1080/15459620701346925
[11] JANSSEN L L, NELSON T J, CUTA K T. Workplace protection factors for an N95 filtering facepiece respirator[J]. J Occup Environ Hyg, 2007, 4(9): 698-707. doi: 10.1080/15459620701517764
[12] MYERS W R, ZHUANG Z. Field performance measurements of half-facepiece respirators: steel mill operations[J]. Am Ind Hyg Assoc J, 1998, 59(11): 789-795. doi: 10.1080/15428119891010974
[13] WALLIS G, MENKE R, CHELTON C. Workplace field testing of a disposable negative pressure half-mask dust respirator (3M 8710)[J]. Am Ind Hyg Assoc J, 1993, 54(10): 576-583. doi: 10.1080/15298669391355080
[14] 吴光宗, 周其洪. 半封闭室内焊条电弧焊焊接粉尘的分析与预测[J]. 热加工工艺, 2021, 50(5): 133-137. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SJGY202105033.htm [15] JANSSEN L, MCCULLOUGH N V. Elastomeric, half-facepiece, air-purifying respirator performance in a lead battery plant[J]. J Occup Environ Hyg, 2009, 7(1): 46-53. doi: 10.1080/15459620903373537
[16] MYERS W R, ZHUANG Z, NELSON T. Field performance measurements of half-facepiece respirators: foundry operations[J]. Am Ind Hyg Assoc J, 1996, 57(2): 166-174. doi: 10.1080/15428119691015106
[17] ZHUANG Z, MYERS W R. Field Performance measurements of half-facepiece respirators: paint spraying operations[J]. Am Ind Hyg Assoc J, 1996, 57(1): 50-57. doi: 10.1080/15428119691015214
[18] BIDWELL J, JANSSEN L. The workplace performance of an N95 respirator in a concrete block manufacturing plant[C]. AIHce, 2004.
[19] HAN D. Correlations between Workplace protection factors and fit factors for filtering facepieces in the welding workplace[J]. Ind Health, 2002, 40(4): 328-334. doi: 10.2486/indhealth.40.328
[20] HINDS W C, BELLIN P. Performance of dust respirators with facial seal leaks: Ⅱ. Predictive model[J]. Am Ind Hyg Assoc J, 1987, 48(10): 842. doi: 10.1080/15298668791385688
-
期刊类型引用(6)
1. 董阳,邓红平,易成,胡凤霞,徐进,顾爱华. 晶硅太阳能电池制造业职业危害概述. 中华劳动卫生职业病杂志. 2024(08): 637-640 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 郑光,李凤仪,王翔,朱冬青,赵忠林,郭盈. 低剂量职业性氟化氢接触与骨代谢生化指标相关性分析及基准剂量研究. 中华劳动卫生职业病杂志. 2023(03): 198-203 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 何璐阳,张靖琦,李娟,李百春,孙宇涵,弓宇娟,路小婷,宋静,牛侨,王林平. 铝氟的交互作用对铝厂作业工人总体认知功能的影响. 环境与职业医学. 2023(06): 695-699 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 郑光,孙赟,赵忠林,金惜雯,陈香,郑幼桥,张雪涛. 氟化氢铵接触工人骨代谢生物标志研究. 职业卫生与应急救援. 2023(04): 403-408 .  本站查看
本站查看
5. 陈娜,张磊,杨亮,邓静,毛晓峰,万佳丽. 长寿区职业人群骨量减少与职业暴露相关性研究. 保健医学研究与实践. 2023(S2): 24-27 .  百度学术
百度学术
6. 芮小峰,陈博,张志龙. 氟接触工人sSema4D水平与骨损伤相关性分析. 中国地方病防治. 2022(03): 254-255 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(1)





 下载:
下载: