Protective effect of glycyrrhizic acid monosaccharide on acute lung injury caused by single-walled carbon nanotubes in mice
-
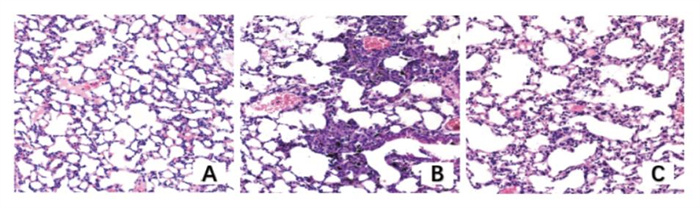
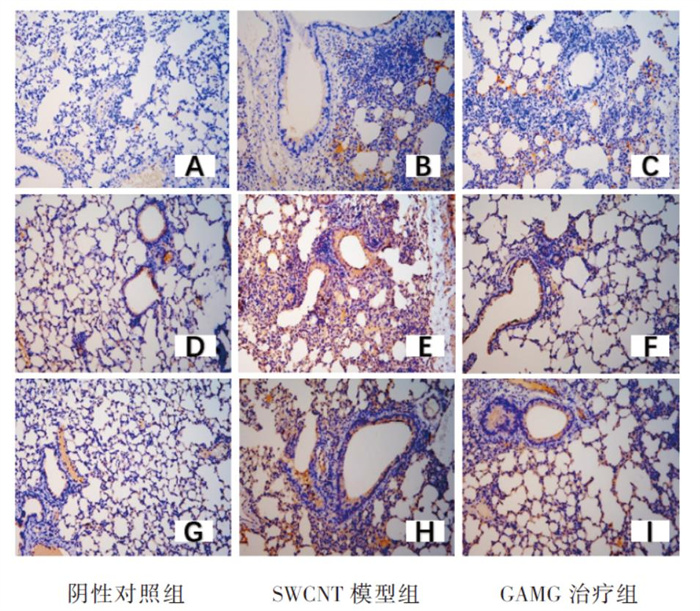
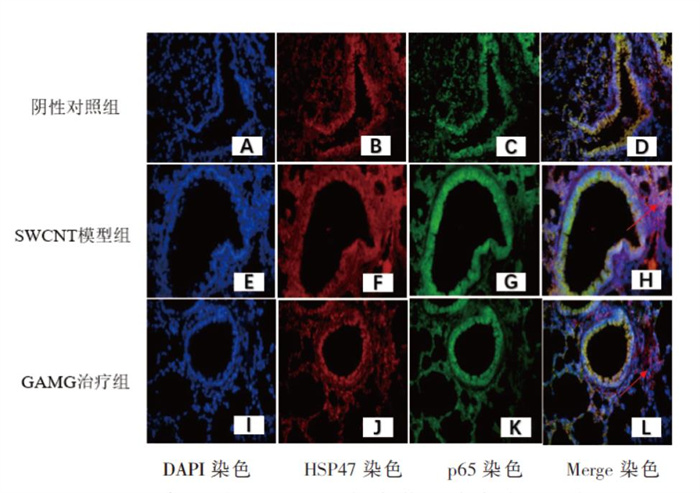
+ English摘要:目的 评估甘草酸单糖(glycyrrhizic acid monoglucuronide,GAMG)对单壁碳纳米管(single-walled carbon nanotubes,SWCNT)诱导的小鼠急性肺损伤的保护作用。方法 取7 ~ 8周龄雌性C57/BL小鼠30只,随机分为3组,每组10只,分别为阴性对照组(生理盐水40 μg/只,气管滴注)、SWCNT模型组(SWCNT 40 μg/只,气管滴注)、GAMG治疗组(SWCNT 40 μg/只,气管滴注+ GAMG 200 mg/kg),GAMG治疗组每天给予1次GAMG腹腔注射,连续3 d,其他组同时给予空白溶剂,在第3天对小鼠进行取材。观察各组小鼠肺组织HE染色病理改变和气管肺泡灌洗液中细胞因子白介素-6(IL-6)和单核细胞趋化蛋白1(MCP-1)的变化,采用免疫组化法检测TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB信号通路的蛋白表达水平,免疫荧光法检测NF-κB和HSP47的含量。结果 GAMG治疗组小鼠肺损伤程度明显减轻。与SWCNT组相比,GAMG治疗组BALF中MCP-1和IL-6水平降低(P < 0.01);TLR4和MyD88的表达减少,肺组织NF-κB p65和HSP47蛋白表达减少(P < 0.01)。结论 GAMG可显著改善SWCNT诱导的急性肺损伤,并抑制肺内TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB信号通路的激活。
-
世界卫生组织(WHO)认为“环境中对儿童威胁最大的是铅”,儿童铅中毒已成为一个全球性的公共安全问题,已引起了全世界广泛关注。儿童铅中毒47%来自食物,45%来自室内外尘土,6%来自饮水,其余来源于空气和其他[1-4]。铅中毒能够影响多个器官系统,导致许多机体功能变化,包括血液系统紊乱、神经系统紊乱以及肝肾功能受损[5-6]。近年来,随着我国工业化的快速发展,儿童铅污染问题日益突出,其中汽车尾气的排放、室内装修材料、工业铅对土壤和水资源的污染、含铅玩具及生活用品、食品等均能引起儿童铅污染,严重的可造成铅中毒[7]。因此,防治儿童铅中毒格外重要,而健康教育是防治儿童铅中毒的重要环节。目前湖南省从事儿童铅中毒治疗的医疗机构主要是湖南省儿童医院和湖南省职业病防治院。湖南省儿童医院以门诊口服药物治疗为主,针对的人群主要是高铅血症及轻度中毒患儿。湖南省职业病防治院(我院)职业病科除了门诊收治高铅血症及轻度中毒患儿,于2017年1月—2019年10月期间还将中度中毒患儿收治住院,在予以依地酸二钠钙(EDTA)静脉注射药物驱铅治疗的同时,加强多种形式的健康宣教,希望能做到将健康教育与临床治疗有机结合,以提高家长铅中毒知识的知晓率,改善患儿不良生活习惯或行为,减少患儿的铅吸收。现将我院对中度铅中毒儿童开展健康教育的干预效果报告如下。
1. 对象与方法
1.1 研究对象
2017年1月—2019年10月,在我院进行治疗的406例中度铅中毒患儿中进行筛选,在符合纳入标准的238例患儿中随机选取60例及其主要照顾人作为研究对象,其中大多数患儿伴有多动、食欲差、体重下降及注意力不集中等临床表现。铅中毒诊断标准:根据2006年国家卫生部印发的《儿童高铅血症和铅中毒预防指南》及《儿童高铅血症和铅中毒分级和处理原则(试行)》 [8],患儿2次静脉血铅检测水平均在250 ~ 449 μg/L为中度铅中毒。纳入标准:(1)初诊儿童;(2)静脉血铅水平为250 ~ 449 μg/L;(3)无佝偻病史、甲状腺功能紊乱史;(4)患儿监护人充分了解本次研究内容及目的后,书面同意并配合研究。排除标准:(1)复诊患儿;(2)有慢性肝胆、肠道疾病史、慢性肾脏病史;(3)近半年有骨折和慢性骨病史;(4)经评估为轻度或重度铅中毒。
1.2 研究方法
将60例患儿按照随机数字分组法分为试验组和对照组各30例,随机数字分组步骤具体为:首先,利用Excel将60例患儿姓名填入表中,利用RAND函数产生随机数,对产生的随机数字进行排序,公式= RANK.AVG(值,值区域);接着,将排序值除以2,提取余数代表对应的组号;求余数通用公式=[MOD(排序值,组数量)+1]&“组”,从而形成随机分组。
1.2.1 问卷调查
自行设计的调查问卷,主要了解患儿的一般情况、铅接触的途径以及生活习惯。在患儿入院当天,由主管医师在病房统一发放问卷,患儿主要照顾人按要求如实填写问卷内容,填写时间控制在30 min以内。主管医师全程监督问卷填写过程,在患儿主要照顾人填写完成后回收问卷。
1.2.2 健康教育
两组患儿住院期间均给予EDTA静脉注射药物驱铅治疗,并开展相关健康教育。其中,对照组进行常规健康教育,包括发放由本院自制的《儿童铅中毒防范手册》,并由课题组医师及护士进行口头宣教。
试验组在常规健康教育的基础上,还采用了多种形式的健康教育模式,具体如下:
(1)知识讲座:举行铅中毒相关知识的讲座,地点设置在院内3楼宣教室,每周举办1次,研究期间共举行45场,平均每场参加人员约为20人,累计922人次,要求试验组患儿及其家属参加该系列讲座。讲座内容包括:铅中毒的来源、途径、吸收、分布代谢、对人体的损害、检测方法、诊断标准、治疗(药物、饮食)、药物治疗中的注意事项、预后,并设置提问环节,现场解答患儿及患儿主要照顾人对于铅中毒的相关问题,并将问题归类收集。
(2)心理辅导:家长的不良情绪会影响患儿的行为,同时对于后续铅中毒的治疗及防范具有负面影响。通过专业心理医生对试验组伴有焦虑情绪的铅中毒患儿家长进行心理疏导,引导他们正确认识铅中毒,减轻焦虑及其他不良情绪,以更好地配合接下来的研究工作。地点位于心理咨询室,对象为有明显焦虑、抑郁或者其他不良情绪的患儿家长,在研究期间试验组共有9名家长接受了心理辅导,平均的心理辅导次数为5次,对于伴有焦虑、抑郁情绪的患儿家长给予音乐心理疗法、认知行为疗法及其他心理干预疗法。
(3)加强沟通:于2017年1月8日通过微信聊天软件,建立铅中毒防范群,发送有关铅中毒的专家讲座,并将讲座中家长提到的问题和处理方法归类成文档分享在群中。同时家长也可以在群中发送自己的问题,由课题组成员进行解答。设立铅中毒防治知识的公众号,定期发布有关铅中毒的防治知识,向试验组患儿家长进行重点推送,以方便家长及时获取最新研究及预防信息。研究期间,微信群中共有68人,其中试验组患儿父母共60人,医师3人,护理人员5人,发送防治铅中毒相关知识的帖子共98条,回答问题共302个。
1.3 观察指标
分别于干预前、出院时、出院后1个月、出院后2个月实施观察,观察指标如下。
1.3.1 患儿血铅水平
比较2组患儿干预前、出院时、出院后1个月、出院后2个月的血铅变化。血铅检测单位:湖南省职业病防治院,检测方法:石墨炉原子吸收光谱法(GFAAS),所用仪器:原子吸收光谱仪(仪器型号:ZEEnit 700,生产厂家:德国耶拿),标本采集和检测操作规范及依据:WS/T 20—1996《血中铅的石墨炉原子吸收光谱测定方法》和GBZ/T 316.1—2018《血中铅的测定第1部分:石墨炉原子吸收光谱法》,每个患儿检测次数为4次。
1.3.2 患儿生活习惯纠正情况
由患儿主要照顾人根据实际情况进行填写,生活习惯纠正及脱离铅污染源具体内容参照2006年原国家卫生部印发的《儿童高铅血症和铅中毒预防指南》及《儿童高铅血症和铅中毒分级和处理原则(试行)》 [8]。
1.3.3 患儿营养干预情况
分别在出院后1月、2月由患儿主要照顾人根据实际情况填写实施营养干预的情况。患儿营养素补充及微量元素(钙、铁、锌)摄入量参照2018年版《营养素补充剂使用科学共识》 [9],由患儿家长在医师指导下自行购买补充。评估标准:(1)营养改善程度:①改善:经过营养素补充后,各营养值均在正常范围内;②未改善:经营养素补充后,各营养值未完全恢复至正常范围。(2)出院后补充营养素情况:①间断服用:未按时规律服用钙铁锌营养素制剂;②持续服用:每日按时规律服用钙、铁、锌营养素制剂。(3)脱离铅污染源情况:①已脱离:出院后未接触相关铅污染源;②间断接触:出院后偶有接触相关铅污染源;③未脱离:出院后仍持续接触相关铅污染源。
1.3.4 患儿主要照顾人对铅中毒知识的知晓情况
由患儿主要照顾人根据实际情况进行填写,共20个问题,包括铅中毒及高铅血症的危害,铅中毒神经、消化及血液系统表现,工业性及生活铅污染,铅进入机体的途径,如何避免及预防铅中毒等。答对1题计1分,共20分。
1.4 统计学分析
由课题组成员将调查问卷中研究数据录入EpiData软件(V3.1),采用SPSS 22.0软件进行数据分析。符合正态性的计量资料以均数±标准差(x ± s)表示,组间比较采用独立样本t检验,组内前后比较采用配对t检验;计数资料以频数、率或构成比表示,二分类资料对比使用独立样本χ2检验,单向有序资料对比使用Mann-Whitney U检验。P < 0.05为差异有统计学意义。
2. 结果
2.1 两组一般资料
调查试验组和对照组各30例患儿的性别及年龄、主要照顾人性别、年龄及学历、平素补充剂添加情况(添加剂包括补充锌剂、钙剂、鱼肝油/维生素AD、其他维生素类)、患儿神经系统情况(症状包括多动、注意力不集中、脾气暴躁、攻击性行为、头痛、头晕等)、贫血情况以及血铅水平等的组间差异均无统计学意义(P > 0.05),具体见表 1。
表 1 两组患儿及其主要照顾人的一般资料项目 试验组(n = 30) 对照组(n = 30) χ2、t或Z值 P值 患儿性别 0.071 0.791 男 19 18 女 11 12 患儿年龄/岁 4.90 ± 2.49 4.70 ± 2.25 0.332 0.741 主要照顾人性别 0.417 0.519 男 5 7 女 25 23 主要照顾人年龄/岁 44.20 ± 11.62 41.40 ± 13.04 0.878 0.384 主要照顾人学历 0.275 0.872 高中以下 9 8 大专或大学本科 15 17 研究生及以上 6 5 平素是否给予患儿补充剂 0.300 0.584 是 9 11 否 21 19 患儿是否有神经系统症状 0.287 0.592 是 12 10 否 18 20 患儿是否有贫血 0.271 0.602 是 16 18 否 14 12 患儿血铅水平/(μg/L) 264.10 ± 55.06 266.75 ± 51.93 - 0.192 0.836 2.2 两组治疗前后血铅水平对比
两组患儿治疗后的3个时期的血铅水平同治疗前相比均显著下降。出院时试验组患儿血铅水平与对照组相比,差异无统计学意义(P > 0.05);但出院后1个月、2个月时试验组血铅水平均低于对照组,差异有统计学意义(P < 0.05)。见表 2。
表 2 两组治疗后血铅水平对比(μg/L) 组别 例数 干预前 出院时 出院后1个月 出院后2个月 试验组 30 264.10 ± 55.06 163.83 ± 30.46 152.93 ± 22.06 154.50 ± 24.72 对照组 30 266.75 ± 51.93 163.00 ± 37.92 171.60 ± 38.02 178.70 ± 39.72 t值 - 0.192 0.094 - 2.326 - 2.834 P值 0.836 0.117 0.005 0.026 2.3 两组患儿生活习惯纠正情况
在入院干预前,两组患儿的生活习惯差异无统计学意义(均P > 0.05)。出院后1个月,试验组有24例患儿养成勤洗手习惯,纠正情况优于对照组(P < 0.01),其他生活习惯的纠正情况与对照组相比差异无统计学意义(P > 0.05)。出院后2个月,除了食用爆米花和爱用油画棒、蜡笔画画这两种生活习惯外,其余生活习惯的纠正情况,试验组患儿均优于对照组,差异有统计学意义(P < 0.05)。见表 3。
表 3 两组患儿干预前后生活习惯比较(n = 30)(例) 患儿生活习惯 干预前 出院后1个月 出院后2个月 试验组 对照组 χ2值 P值 试验组 对照组 χ2值 P值 试验组 对照组 χ2值 P值 无勤洗手 21 24 0.800 0.371 6 16 7.177 0.007 8 20 9.643 0.002 啃咬手指、玩具 14 17 0.601 0.438 6 12 2.857 0.091 5 14 6.239 0.012 啃咬、玩弄钥匙或金属拉链 15 15 < 0.001 >0.999 5 8 0.884 0.347 3 10 4.812 0.028 食用爆米花 12 10 0.287 0.592 2 4 0.741 0.389 1 4 1.964 0.161 食用膨化食品或含铅的食物 14 12 0.271 0.602 10 13 0.635 0.426 8 16 4.444 0.035 食用东西前洗手 16 9 3.360 0.067 25 19 3.068 0.080 27 17 8.523 0.004 爱用油画棒、蜡笔画画 13 15 0.268 0.605 6 8 0.373 0.542 4 10 3.354 0.067 2.4 两组患儿营养干预情况
分别比较出院后1个月、2个月两组患儿营养改善程度、补充营养素(钙、铁、锌)及脱离铅污染源等情况,经Mann-Whitney U检验、χ2检验,试验组均优于对照组,差异均有统计学意义(P < 0.05)。见表 4。
表 4 两组患儿出院后1个月、2个月时营养干预情况(n = 30)(例) 项目 出院后1个月 出院后2个月 试验组 对照组 χ2或Z值 P值 试验组 对照组 χ2或Z值 P值 营养改善程度 5.455 0.020 4.356 0.037 改善 28 21 26 19 未改善 2 9 4 11 是否补充钙、铁、锌 - 2.221 0.026 - 2.389 0.017 未服用 5 9 5 11 间断服用 9 14 12 14 持续服用 16 7 13 5 脱离铅污染源 - 2.175 0.030 - 2.061 0.039 已脱离 27 20 28 22 间断接触 3 10 2 8 未脱离 0 0 0 0 2.5 两组患儿主要照顾人对铅中毒知识的知晓得分情况
在干预前,两组患儿主要照顾人对铅中毒知识的知晓得分差异无统计学意义(P < 0.05);干预后,同组内出院时、出院后1个月、出院后2个月的知晓得分均较干预前提高,差异有统计学意义(P < 0.05);干预后,试验组在出院时、出院后1个月、出院后2个月的知晓得分均高于对照组,差异有统计学意义(P < 0.05)。见表 5。
表 5 两组患儿主要照顾人对铅中毒知识知晓得分比较(x ± s,分) 组别 例数 干预前 出院时 出院后1个月 出院后2个月 试验组 30 10.93 ± 2.18 17.30 ± 2.32① 17.00 ± 1.78① 16.77 ± 2.30① 对照组 30 10.70 ± 2.82 15.27 ± 2.92① 13.43 ± 2.01① 12.03 ± 1.73① t值 0.359 2.983 7.271 9.006 P值 0.721 0.004 < 0.001 < 0.001 注:①组内与干预前对比,P < 0.05。 干预前,两组患儿主要照顾人对铅中毒知识的知晓率差异无统计学意义(P > 0.05);干预后,试验组有6道题目的知晓率优于对照组,差异有统计学意义(P < 0.05)。具体见表 6。
表 6 干预前后两组患儿主要照顾人对铅中毒知识答对人数对比[知晓人数(知晓率/%)] 项目 干预前 干预后(出院时) 试验组 对照组 χ2值 P值 试验组 对照组 χ2值 P值 铅中毒或高铅血症对儿童的危害 23(76.67) 22(73.33) 0.089 0.766 26(86.67) 27(90.00) 0.162 0.688 血铅超标量 23(76.67) 22(73.33) 0.089 0.766 26(86.67) 25(83.88) 0.131 0.718 铅中毒或高铅血症的神经系统表现 15(50.00) 16(53.33) 0.067 0.796 26(86.67) 18(60.00) 5.455 0.020 铅中毒或高铅血症的消化系统表现 18(60.00) 17(56.67) 0.069 0.793 23(76.67) 22(73.33) 0.089 0.766 铅中毒或高铅血症的血液系统表现 15(50.00) 14(46.67) 0.067 0.796 27(90.00) 20(66.67) 4.812 0.028 工业性铅污染有哪些 14(46.67) 12(40.00) 0.271 0.602 28(93.33) 21(70.00) 5.455 0.020 生活中铅污染有哪些 13(43.33) 14(46.67) 0.067 0.795 25(83.88) 24(80.00) 0.111 0.739 红丹粉的作用及危害 11(36.67) 10(33.33) 0.073 0.787 26(86.67) 19(63.33) 4.356 0.037 铅进入儿童体内的途径 10(33.33) 11(36.67) 0.073 0.787 28(93.33) 18(60.00) 9.317 0.002 儿童容易发生铅中毒的原因 19(63.33) 20(66.67) 0.073 0.787 26(86.67) 26(86.67) < 0.001 1.000 如何避免工业性铅污染 22(73.33) 19(63.33) 0.693 0.405 26(86.67) 25(83.88) 0.131 0.718 如何避免生活性铅污染 15(50.00) 16(53.33) 0.067 0.796 27(90.00) 20(66.67) 4.812 0.028 正确的洗手方法 24(80.00) 25(83.88) 0.111 0.739 28(93.33) 27(90.00) 0.218 0.640 铅中毒的预防方法 15(50.00) 16(53.33) 0.067 0.796 27(90.00) 24(80.00) 1.176 0.278 获取儿童铅中毒及预防知识的途径 14(46.67) 13(43.33) 0.067 0.795 24(80.00) 22(73.33) 0.373 0.542 哪些获取途径帮助最大 13(43.33) 15(50.00) 0.268 0.605 24(80.00) 22(73.33) 0.373 0.542 对儿童铅中毒或高铅血症的认识 13(43.33) 11(36.67) 0.278 0.598 26(86.67) 24(80.00) 0.480 0.488 如果周围孩子血铅超标(> 100 μg/L),您会带孩子测血铅吗 17(56.67) 16(53.33) 0.067 0.795 24(80.00) 24(80.00) < 0.001 1.000 如果孩子血铅超标的处理方式 16(53.33) 14(46.67) 0.267 0.606 26(86.67) 24(80.00) 0.480 0.488 驱铅治疗是否需多饮水 20(66.67) 18(60.00) 0.287 0.592 26(86.67) 26(86.67) < 0.001 1.000 3. 讨论
铅中毒是一种环境疾病,具有累积性和不可逆转的健康影响[10]。幼儿特别容易接触到铅,这是因为幼儿需要通过手对嘴和物体对嘴的行为来探索他们的环境,而这些行为恰恰增加了铅的摄取量。儿童的生理特点导致铅在婴儿和幼儿的胃肠道吸收远远高于成人,此外,在铁和钙等微量元素缺乏的情况下,儿童对铅的吸收增加,且比成人更常见。与成人相比,儿童对铅中毒更加敏感,主要表现在发育阶段儿童中枢神经系统对铅的毒性最为敏感,铅对成年人神经系统的影响在停止接触后倾向于逆转,但儿童的影响往往持续存在。过去的十年里,在逐步淘汰含铅汽油后,儿童铅中毒的数量虽然有所减少,但铅中毒仍然是危害儿童健康的主要原因。在美国,6岁以下的铅中毒儿童多达50万,而与铅中毒相关的认知障碍每年造成美国经济生产力损失约509亿美元[11]。在非洲,儿童铅中毒的主要来源包括铅矿开采和冶炼、油漆和电池回收[12]。如在尼日利亚发生的儿童铅中毒并造成400多名儿童死亡的重大事件,主要是由金矿开采和加工造成的[13]。
Tirima等[14]发现,大部分膳食铅暴露与在收获后加工和家庭准备过程中的主食谷物和豆类受污染有关,采摘后和加工谷物含铅量分为0.32 mg/kg和0.85 mg/kg,同时铅的摄入和吸收加剧很可能与尘土飞扬的环境、两餐之间禁食时间长和营养缺乏。所以在本研究中,对患儿及家长的健康教育除了告知远离工业区、靠近大马路的居住环境外,同时还要尽量避免尘土较多的环境,每日三餐按时规律食用,避免过饱或过饥,少吃加工食品。
美国疾控中心和美国儿科学会(AAP)强调,终结儿童期铅中毒的最佳方法是预防、控制和消除铅暴露。重点从照顾有症状的儿童转向针对高危社区的初级预防方法,是保护儿童免受铅中毒的最可靠和最经济有效的策略[15]。开展铅中毒相关的健康教育就是重要的预防措施及方法[16],近年来我国对健康教育预防儿童铅中毒的相关研究也逐渐增多,如裴一洁等[17]通过健康行为教育加强了家长和老师对儿童铅中毒防治的认识(知晓率由57.99%增至90.40%),随之儿童生活的不良卫生习惯、行为以及血铅水平均较前得到改善,证实了健康教育的必要性。本研究发现,试验组患儿家长在经过多种形式的健康教育后,其防治铅中毒知识得分提高(P < 0.05),说明经过针对儿童铅中毒防治的健康教育,能够提高患儿家长对于铅中毒防治相关知识的了解。吴晓燕等[18]对35名儿童家长进行铅中毒健康教育后,有82.86%的家长认为“预防是关键”,随访1年时所有儿童的血铅水平也较干预前有所下降,验证了健康教育对预防儿童铅中毒的积极作用。在本研究中,经过多形式的健康教育,试验组患儿家长在出院时、出院后1个月及2个月,对铅中毒相关知识知晓率明显优于对照组(P < 0.05),表明通过多形式的健康教育方式能让家长深刻意识到铅中毒的危害。试验组患儿出院后日常生活中的不良行为及卫生习惯的纠正情况优于对照组(P < 0.05),提示多种形式的健康教育在改善铅中毒患儿不良的生活习惯上有明显的积极影响,同时也从侧面说明在纠正患儿不良行为上需要一定的改变时间,家长要有耐心。
在营养干预方面,试验组患儿在出院后随访时间内改善程度均优于对照组(P < 0.05),两组所有患儿基本脱离了铅的污染源,但在偶然接触铅污染源的对比上,试验组患儿人数明显少于对照组,可能与对照组家长对铅的污染源及铅进入儿童体内的途径了解不够有关。随着患儿逐渐脱离铅污染源以及不良行为的改善,试验组患儿出院后血铅水平也在逐渐下降,而对照组患儿血铅水平在出院后反呈上升趋势,高于试验组(P < 0.05),说明患儿家长对铅的污染源及铅进入儿童体内的途径认识不够,提示通过多种形式的健康教育能够提高家长对铅中毒危害的认识,减少中度铅中毒患儿铅的摄入量,同郭宏丹等[19]的研究结果基本一致。本次研究中,经过课题组成员面对面进行铅中毒相关知识的宣讲,能够加深患儿及其家长的印象,充分了解避免铅中毒的重要性,加上讲座形式可以让患儿及其家长更加系统全面地熟悉防治铅中毒的相关内容,建立微信群能够加强医护及患者、患者家属之间的沟通及联系,第一时间掌握家长在防治铅中毒过程中的相关动态,有助于提高家长的积极性及配合度。同时,经过专业心理医师的心理治疗,部分伴有不良心理情绪的家长也能够及时得到干预,这同样有助于患儿康复。
随着工业化发展,我国家庭中含铅用品的使用正在增加,特别是色彩鲜艳(红色、黄色和橙色)的水性涂料等。世界卫生组织和环境署等国际组织呼吁采取行动,应对可预防的铅接触风险。在预防铅中毒上,健康教育形式是一项重要措施。本研究通过多种形式的健康教育,有效地提高中度铅中毒患儿家长对铅中毒防治知识的了解及掌握,患儿不良行为和生活习惯得到改善,血铅水平下降明显。今后的调查将进一步扩大样本量,并增加对轻度及重度铅中毒患儿的研究。
作者声明 本文无实际或潜在的利益冲突 -
表 1 各组小鼠肺组织的IL-6和MCP-1含量比较
(n = 6,pg/mL) 组别 IL-6 MCP-1 阴性对照组 56.84 ± 6.34 72.67 ± 2.52 SWCNT模型组 159.25 ± 9.03① 190.00 ± 10.00① GAMG治疗组 95.31 ± 4.88② 125.00 ± 5.00② F值 165.435 236.816 P值 < 0.001 < 0.001 注:①与阴性对照组相比,P < 0.01;②与SWCNT模型组相比较,P < 0.01。 表 2 各组小鼠肺组织的TLR4、MyD88、NF-κB含量比较
(n = 3) 组别 TLR4 MyD88 p65 阴性对照组 5.32 ± 1.04 9.25 ± 1.18 5.23 ± 0.61 SWCNT模型组 43.26 ± 2.49① 88.68 ± 7.49① 68.56 ± 7.51① GAMG治疗组 18.15 ± 2.50② 18.36 ± 2.86② 27.52 ± 2.11② F值 247.186 258.833 151.526 P值 < 0.001 < 0.001 < 0.001 注:①与阴性对照组相比,P < 0.01;②与SWCNT模型组相比,P < 0.01。 -
[1] ROCO M C. The long view of nanotechnology development: the National Nanotechnology Initiative at 10 years[J]. Nanopart Res, 2011, 13: 427-445. doi: 10.1007/s11051-010-0192-z
[2] DE VOLDER M F, TAWFICK S H, BAUGHMAN R H, et al. Carbon nanotubes: present and future commercial applications[J]. Science, 2013, 339(6119): 535-539. doi: 10.1126/science.1222453
[3] 周金鹏, 张方方, 黄红英, 等. 多壁碳纳米管职业接触致工人氧化损伤及炎症反应水平研究[J]. 职业卫生与应急救援, 2019, 37(3): 213-217. doi: 10.16369/j.oher.issn.1007-1326.2019.03.002 [4] DONG J, MA Q. Myofibroblasts and lung fibrosis induced by carbon nanotube exposure[J]. Fibre Toxicol, 2016, 13: 60-66. doi: 10.1186/s12989-016-0172-2
[5] 索田栋, 张军良, 郭燕文, 等. 甘草酸及其衍生物的研究进展[J]. 精细与专用化学品, 2006(17): 13-16. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JXHX200617002.htm [6] TANG Z H, LI T, TONG Y G, et al. Systematic review of the anticancer properties of compounds isolated from Licorice(Gancao)[J]. Planta Med, 2015, 81(18): 1670-1687. doi: 10.1055/s-0035-1558227
[7] LI B, YANG Y, CHEN L, et al. 18α-Glycyrrhetinic acid monoglucuronide as an anti-inflammatory agent through suppression of the NF-κB and MAPK signaling pathway[J]. Medchemcomm, 2017, 8(7): 1498-1504. doi: 10.1039/C7MD00210F
[8] DONG J, MA Q. Osteopontin enhances multi-walled carbon nanotube-triggered lung fibrosis by promoting TGF-β1 activation and myofibroblast differentiation[J]. Part Fibre Toxicol, 2017, 14(1): 18-28. doi: 10.1186/s12989-017-0198-0
[9] ZHANG X L, LI B, ZHANG X, et al. 18β-Glycyrrhetinic acid monoglucuronide (GAMG) alleviates single-walled carbon nanotubes (SWCNT)-induced lung inflammation and fibrosis in mice through PI3K/AKT/NF-κB signaling pathway[J]. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf, 2022, 242: 113858. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2022.113858
[10] KHALIULLIN T O, KISIN E R, MURRAY A R, et al. Mediation of the single-walled carbon nanotubes induced pulmonary fibrogenic response by osteopontin and TGF-β1[J]. Exp Lung Res, 2017, 43(8): 311-326. doi: 10.1080/01902148.2017.1377783
[11] 周金鹏, 张方方, 黄红英, 等. 广东省某新材料生产企业工人的肺部和心血管系统损伤研究[J]. 职业与健康, 2019, 35(8): 1027-1030. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZYJK201908005.htm [12] GROMMES J, SOEHNLEIN O. Contribution of neutrophils to acute lung injury[J]. Mol Med, 2011, 17(3-4): 293-307. doi: 10.2119/molmed.2010.00138
[13] 陈阳晔. 甘草酸对LPS诱导的急性肺损伤模型血管内皮功能的影响[D]. 长沙: 湖南师范大学, 2019. [14] BAILLY C, VERGOTEN G. Glycyrrhizin: an alternative drug for the treatment of COVID-19 infection and the associated respiratory syndrome[J]. Pharmacol Ther, 2020, 214: 107618. doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2020.107618
[15] OLONA A, HATELEY C, MURALIDHARAN S, et al. Sphingolipid metabolism during Toll-like receptor 4(TLR4)-mediated macrophage activation[J]. Br J Pharmacol, 2021, 178(23): 4575-4587. doi: 10.1111/bph.15642
[16] GAO H, XIAO D Q, GAO L B, et al. MicroRNA-93 contributes to the suppression of lung inflammatory responses in LPS-induced acute lung injury in mice via the TLR4/MyD88/NfK B signaling pathway[J]. Int J Mol Med, 2022, 46(2): 561-570.
[17] 赵朝华, 廖和和, 王甲林, 等. 阿奇霉素对慢阻肺大鼠肺脏病理损伤、氧化应激及TLR4/NF-κB信号通路的调节作用[J]. 西部医学, 2019, 31(12): 1831-1836. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XIBU201912008.htm [18] DONG J, MA Q. Myofibroblasts and lung fibrosis induced by carbon nanotube exposure[J]. Part Fibre Toxicol, 2016, 13(1): 60.
-
期刊类型引用(1)
1. 王燕,林海,符大天,莫文纹,韩锐. 儿童铅中毒特性及临床诊治研究进展. 临床军医杂志. 2023(08): 874-877 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(0)





 下载:
下载: