Research on emergency response to acute occupational poisoning accidents based on interpretative structural modeling and cross-impact matrix multiplication applied to classification
-
+ English摘要:目的 通过分析急性职业中毒事故应急处置的影响因素,为相关部门加强急性职业中毒事故应急处置能力提供依据。方法 基于危机管理4 R理论,从应急预备、预案、响应和恢复四个方面,提取急性职业中毒事故应急处置的影响因素,运用解释结构建模(interpretative structural modeling,ISM)确定影响因素的多层递阶层次结构,再通过交叉影响矩阵相乘法(cross-impact matrix multiplication applied to classification,MICMAC)计算出每个影响因素的驱动力和依赖性,进而提出有针对性的应急处置策略。结果 确定出急性职业中毒事故应急处置的12个影响因素。其中应急预案、应急演练、应急培训、组织调度既是影响急性职业中毒事故应急处置最根本的深层因素,也是驱动力最强的因素;控制毒物、危险区隔离是急性职业中毒事故应急处置中最关键的直接因素。结论 在事故发生后的应急处置中应优先进行毒物控制和危险区的隔离;同时,应加强应急预案、应急演练、应急培训和组织调度等方面的建设。
-
矽肺是由于长期吸入生产性游离二氧化硅(SiO2)粉尘而导致的肺部纤维化性疾病。在我国患有尘肺病的全部病例中,有接近一半是矽肺病人,矽肺在尘肺病中危害最大、影响面最广[1]。2013年,尘肺病造成全球260 000人死亡[2]。近年来,我国矽肺的发病例数呈上升趋势。有研究显示,氧化应激在游离SiO2致病过程中起着重要作用。最近新发现一种过氧化物还原酶(peroxiredoxin,PRDX)能够有效使体内的过氧化氢含量降低,从而起到保护细胞的作用[3]。目前在哺乳动物内已发现6种PRDX蛋白[4],其中过氧化物还原酶6(peroxiredoxin 6,PRDX6)同时具有谷胱甘肽过氧化物酶(glutathione peroxidase,GSH-Px)和磷脂酶A2(phospholipase A2,PL A2)活性[5]。有研究显示通过敲除小鼠PRDX6基因后发现,脂多糖诱导的急性肺损伤明显加重,证实急性肺损伤加重的部分原因是PRDX6基因敲除弱化了小鼠的抗氧化作用[6]。因此PRDX6受到研究者越来越多的关注和重视[7]。PRDX6通常出现在细胞质中,并且可以在多个器官脏器组织中检测到,在肺组织中表达最高[8]。越来越多的实验证明,它能够使机体的氧化还原状态保持平衡,修复由氧化应激引起的膜损伤,调节肺泡表面活性物质的新陈代谢,减轻肺泡上皮细胞凋亡程度[9]。
蛋白质在人类的生命活动过程中发挥着重要作用,目前很多疾病的发病机制仍不清楚,而蛋白质组学的研究在此类疾病的发病机制中具有重要地位。通过蛋白质组学研究可以发现疾病的生物标志,从而为疾病的治疗提供指导。本课题组前期通过蛋白质组学发现PRDX6蛋白在不同期别矽肺患者的肺灌洗液中的表达具有差异,因此使用蛋白免疫印迹(Western blot)技术对存在于不同期别矽肺患者肺灌洗液中的PRDX6的表达情况进行验证。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 材料
1.1.1 对象
选择在2017年7月—2018年10月于中国煤矿工人北戴河疗养院尘肺科就诊的男性工人作为研究对象。纳入标准:根据我国GBZ 70—2015《职业性尘肺病的诊断》[10]诊断为矽肺,未脱尘或脱尘未满5年,既往未接受过全肺大容量灌洗治疗,现欲进行全肺大容量灌洗治疗的从事矿山开采的工人。选取华北理工大学附属医院入院的与矽肺患者年龄相近(± 5岁)的非矽肺男性患者为对照,该组患者灌洗液样本是在做支气管肺泡灌洗检查时获取的,为支气管镜检查正常肺段的灌洗液。排除标准:患有乙型肝炎或其他肺部纤维化疾病的患者。本次研究共纳入对照组5例、壹期矽肺19例、贰期矽肺5例、叁期矽肺14例。向43例研究对象说明此次试验的目的和过程,请研究对象自愿签署知情同意书。本项研究通过华北理工大学医学伦理委员会论证。
1.1.2 仪器与试剂
Versa Max型连续光谱酶标仪(美国Molecular Devices公司)、TE77X半干电泳仪(美国Hoefer公司)、Mini-PROTEAN型垂直电泳槽(美国Bio-Rad公司)、Fluor Chem HD2型凝胶成像系统(美国Alpha公司)、低温高速离心机(德国Eppendorf公司)。BCA试剂盒(北京索莱宝科技有限公司)、脱脂奶粉(美国BD公司)、十二烷基硫酸钠(大连美仑生物技术有限公司)、兔抗PRDX6抗体(Affinity公司)、兔抗IgG多克隆抗体(北京北方公司)、三羟甲基氨基甲烷(北京博奥拓科技有限公司)。
1.2 方法
1.2.1 肺灌洗液的收集与处理
肺灌洗回收液中,因为第1瓶有很多黏液和细菌,过滤很困难,而第2瓶少了这些弊端,且仍有很多支气管肺泡中的有效成分,因此本研究采集研究对象的第2瓶肺灌洗回收液约500 mL;经四层纱布过滤去除黏液和不溶性粉尘颗粒,低温离心后取上清液,编号,于超低温冰箱内保存。为减少个体差异及节约检测成本,将对照组5例、壹期矽肺19例、贰期矽肺5例、叁期矽肺14例分别构建1个、3个、1个、3个共8个蛋白池。每个蛋白池均检测3次。
1.2.2 BCA法测定蛋白浓度
(1)根据样品数量,按50体积BCA试剂A加1体积BCA试剂B(50:1)配制适量BCA标准品,充分混匀;(2)取适量5 mg/mL蛋白标准品,用磷酸盐缓冲液(phosphate buffered saline,PBS)稀释成终浓度为0.5 mg/mL的蛋白标准;(3)将标准品按0、1、2、4、8、12、16、20 μL的量加入96孔板的标准品孔中,用PBS补足到20 μL;(4)加入2 μL的蛋白样品到96孔板的样品孔中,加标准品稀释到20 μL;(5)每孔中均加入200 μL BCA工作液,于37 ℃放置30 min;(6)用酶标仪测定波长562 nm时的吸光度值,根据标准品作出标准曲线,根据标准曲线计算样品的蛋白浓度。
1.2.3 免疫印迹法检测各组样品中的PRDX6蛋白表达
根据各蛋白池蛋白浓度和体积计算各组样品用量,按照计算好的体积将蛋白样品上样,在55 V电压下进行20 min电泳;在110 V电压下进行80 min电泳,把半干转印电泳仪的电压设置为20 V,将使用半干转溶液浸泡过的海绵、含有目标条带的胶和PVDF膜放置在半干转印电泳仪上,转膜15 min,用质量分数为5%的脱脂奶粉室温封闭120 min后,将含有目标条带的PVDF膜浸泡于PRDX6蛋白(体积比1:750)的抗体中,4 ℃摇床过夜。第2天用PBS洗膜后,将含有目标条带的PVDF膜浸泡于HRP标记的山羊抗兔IgG(体积比1:4 000),室温孵育120 min以可见光化学发光凝胶成像系统采集图像,以各自的β-actin作为内参,用Fluorchem HD2软件分析图像。采用目的蛋白条带的灰度值(PRDX6)与相应内参β-actin条带的灰度值的比值作为目的蛋白的相对表达水平。每个蛋白池检测3次。
1.2.4 统计学分析
建立数据库,使用SPSS 22.0对研究对象的基本数据和实验结果进行分析。计量资料采用均数±标准差(x ± s)表示,多组间差异比较采用单因素方差分析,使用LSD法对均数进行两两比较。计数资料采用χ2检验,理论频数不符合χ2检验要求的采用Fisher确切概率法进行检验。P < 0.05为差异有统计学意义。
2. 结果
2.1 研究对象吸烟情况
对照组5例患者全部吸烟,壹期矽肺、贰期矽肺、叁期矽肺吸烟患者分别为18、3、12例,各占94.7%、60.0%、85.7%。经Fisher确切概率法检验,各组吸烟占比差异无统计学意义(P = 0.171)。
2.2 BCA法测定蛋白浓度
利用BCA法测定各个混样蛋白池中总蛋白的浓度。首先绘制标准曲线(见图 1),吸光度值(y)与样品浓度(x)具有很好的线性相关(y = 0.000 5 x + 0.166 4,R2 = 0.998)。该方程可以用于计算样品中总蛋白的浓度。各组蛋白池蛋白质量浓度见表 1。
表 1 各组样品蛋白质量浓度蛋白池样品 蛋白池蛋白浓度/(μg/μL) 样品体积/μL 蛋白总量/μg 对照组 1.00 100 100 一(壹期) 1.65 100 165 二(壹期) 1.06 100 106 三(壹期) 1.02 100 102 四(贰期) 0.87 100 87 五(叁期) 1.26 100 126 六(叁期) 1.58 100 158 七(叁期) 1.38 100 138 2.3 不同期别矽肺患者肺灌洗液中PRDX6的表达情况
根据各个蛋白池总蛋白的浓度,计算10 μg上样量所需每个样品的体积,确保每一条泳道上都有同样质量的总蛋白。PRDX6蛋白在不同期别矽肺患者肺灌洗液中均有表达(见图 2)。对照组、壹期矽肺、贰期矽肺、叁期矽肺各组灰度值分别为0.536 7 ± 0.066 6、0.567 8 ± 0.072 8、0.713 3 ± 0.080 8、0.785 6 ± 0.097 6。PRDX6蛋白在不同期别矽肺患者间的表达水平差异有统计学意义(F = 5.048,P < 0.05);进一步的两两比较结果显示,壹期矽肺患者肺灌洗液中PRDX6蛋白表达水平与对照组相比,差异无统计学意义(P > 0.05);贰期矽肺、叁期矽肺患者肺灌洗液中PRDX6蛋白表达水平均高于对照组和壹期矽肺患者,差异有统计学意义(P < 0.05);叁期矽肺患者肺灌洗液中PRDX6蛋白表达水平高于贰期矽肺,差异有统计学意义(P < 0.05)。见图 3。
3. 讨论
矽肺是一种严重威胁劳动者健康的职业病,主要病理改变是肺组织弥漫性纤维化。矽肺纤维化的发生发展首先是弥漫性肺泡炎,然后成纤维细胞呈现病理性增生,细胞外基质胶原增多,最后导致正常肺组织结构被取代[11]。尽管矽肺的发病机制已被广泛报道[12],但与SiO2诱导的肺部炎症和纤维化形成有关的关键细胞和分子机制仍不清楚。PRDX蛋白是近年来发现的一种在清除体内活性氧方面起重要作用的过氧化物酶,它能够保护细胞不受氧化应激的损伤,也可能参与信号转导、肺肿瘤进展和应激抵抗[13]。PRDX6是唯一一种同时具有诱导GSH-Px和PLA2活性的过氧化还原蛋白,它能够使机体的氧化还原状态保持平衡,减轻肺泡上皮细胞凋亡。本次实验结果显示:PRDX6蛋白在各个时期的矽肺患者肺灌洗液中均有表达,而且随着纤维化程度增加,PRDX6蛋白的表达量也增加。这可能是因为,随着接尘时间的延长和病情的进展,粉尘刺激导致的活性氧(reactive oxygen species,ROS)量逐渐增加,需要更多的过氧化物酶与之对抗,出现负反馈的结果。Liu等[14]通过大鼠气管内注射50 mg/mL SiO2建立大鼠矽肺模型,Western blot和免疫组化结果显示,随暴露时间的延长,肺组织PRDX6蛋白表达逐渐增加,并在暴露后28 d达到最高水平。这可能是因为,随着染尘剂量的增加和时间的延长,粉尘刺激导致的ROS量逐渐增加,需要更多的过氧化物酶与之对抗,所以才出现了这样实验的结果。Vuong等[15]细胞实验发现,随着颗粒物浓度升高(0、60、140、200 μg/cm2),人肺上皮A549细胞系中PRDX6蛋白表达量升高,与本次实验的结果一致,说明PRDX6蛋白可能在矽肺发生发展过程中发挥重要的作用,对于防治矽肺具有重要意义,但详细的生物学机制尚需进一步的论证和探讨。
作者声明 本文无实际或潜在的利益冲突 -
表 1 急性职业中毒事故应急处置影响因素及专家评分
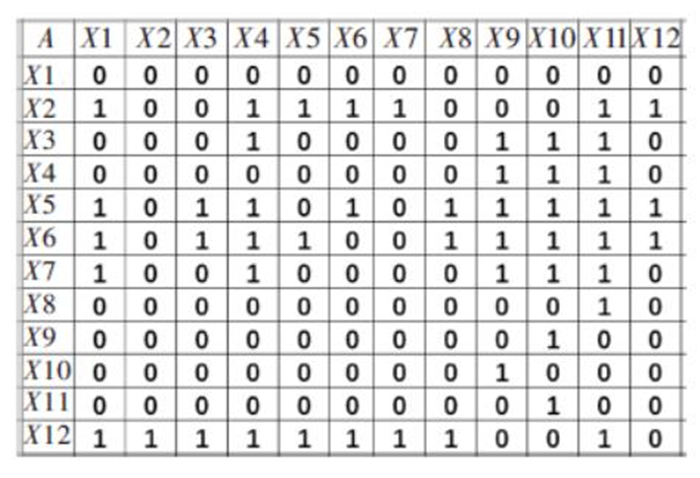
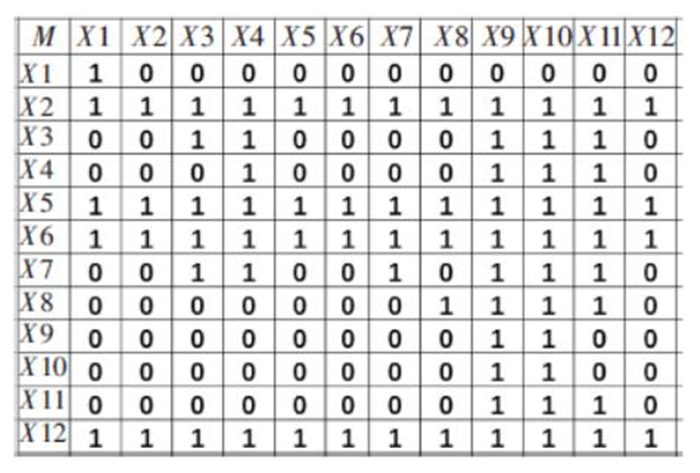
一级指标 二级指标 编号 具体解释 专家平均评分 缩减力 识别危险源 X1 是否在事故还未发生前对危险源头进行发现与识别 4.70 预备力 应急预案 X2 是否制定相应的应急预案开展突发化学中毒事件救援行动 4.40 应急队伍 X3 应急队伍的建设是否完善 4.25 应急物资 X4 应急救援与防护物资储备是否完善 4.60 应急演练 X5 是否定期进行应急演练活动 4.60 应急培训 X6 是否组织专业应急培训活动 4.60 反应力 专家咨询评估 X7 在应急响应过程中,是否咨询相关专家并进行有关评估 4.05 风险沟通交流 X8 救援人员之间以及与受害人群是否进行有效沟通 4.10 毒物控制 X9 是否对作业场所的毒物进行有效控制隔绝与洗消 4.25 危险区隔离 X10 是否对危险区进行隔离 4.55 应急救援技术 X11 事故发生后采取的应急救援技术是否合理有效 4.80 人员组织调度 X12 应急人员是否能够迅速进行组织调度 4.70 表 2 可达集合与先行集合及其交集表
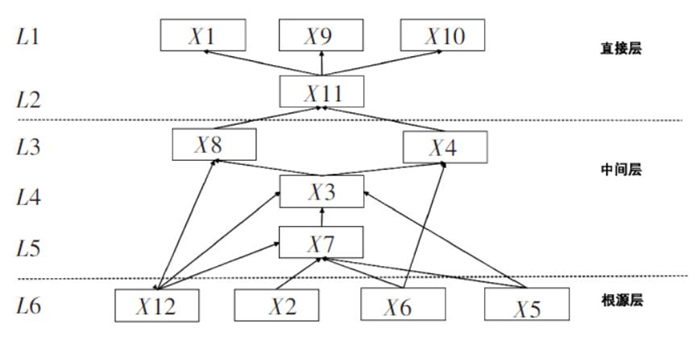
指标 可达集合R 先行集合Q 共同集T=R∩Q X1 1 1,2,5,6,7,12 1 X2 1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10,11,12 2,5,6,12 2,5,6,12 X3 3,4,9,10,11 2,3,5,6,12 3 X4 4,9,10,11 2,3,4,5,6,7,12 4 X5 1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10,11,12 2,5,6,12 2,5,6,12 X6 1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10,11,12 2,5,6,12 2,5,6,12 X7 1,4,7,9,10,11 2,5,6,7,12 7 X8 8,9,10,11 2,5,6,8,12 8 X9 9,10 2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10,11,12 9,10 X10 9,10 2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10,11,12 9,10 X11 9,10,11 2,3,4,5,6,7,8,11,12 11 X12 1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10,11,12 2,5,6,12 2,5,6,12 表 3 急性职业中毒应急处置影响因素层级分布
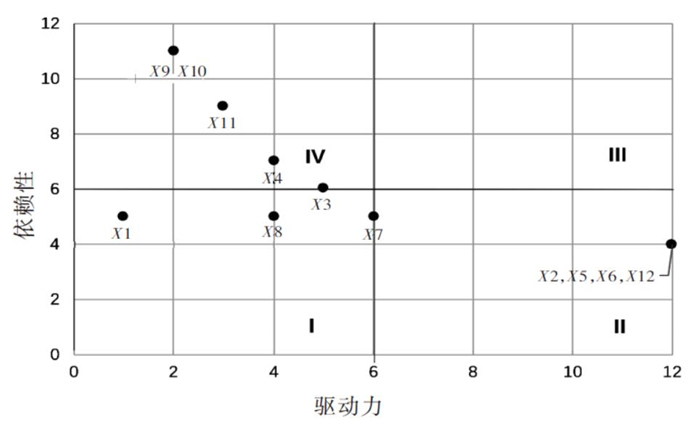
层级 影响因素 第1层(顶层) X1,X9,X10 第2层 X11 第3层 X4,X8 第4层 X3 第5层 X7 第6层(底层) X12,X2,X5,X6 表 4 急性职业中毒应急处置影响因素驱动力和依赖性
因素 驱动力 依赖性 因素 驱动力 依赖性 X1 1 5 X7 6 5 X2 12 4 X8 4 5 X3 5 6 X9 2 11 X4 4 7 X10 2 11 X5 12 4 X11 3 9 X6 12 4 X12 12 4 -
[1] 薛澜, 钟开斌. 突发公共事件分类、分级与分期: 应急体制的管理基础[J]. 中国行政管理, 2005 (2): 102-107. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZXGL200502032.htm [2] 邢娟娟, 姜秀慧, 胡福静, 等. 重大突发职业中毒事故应急研究[J]. 中国安全生产科学技术, 2009, 5(1): 65-70. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LDBK200901019.htm [3] WHO. Early warning, alert and response system in emergencies: a field experience of a novel WHO project in north-east Nigeria[J]. Wkly Epidemiol Rec, 2017, 92(5): 45-50.
[4] 胡菲菲, 解志韬, 凌宏发. 公共危机管理视角下的高校智库应急服务研究[J]. 智库理论与实践, 2021, 6(1): 65-70. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZKSL202101014.htm [5] 罗伯特·希斯. 危机管理[M]. 王成, 宋炳辉, 金瑛, 译. 北京: 中信出版社, 2001: 272-282. [6] 崔庆宏, 王森. 基于ISM-MICMAC的建筑工人不安全行为影响因素[J]. 沈阳大学学报(自然科学版), 2021, 33(3): 272-278. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYDA202103013.htm [7] 陈婉霞. 2019年佛山市突发化学中毒事件应急处置能力调查[J]. 职业卫生与病伤, 2022, 37(2): 115-119. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZYWB202202010.htm [8] 徐佳南, 朱宝立, 杨丹丹, 等. 江苏省疾控机构中毒事件卫生应急处置能力调查[J]. 职业卫生与应急救援, 2018, 36(1): 37-41. doi: 10.16369/j.oher.issn.1007-1326.2018.01.010 [9] 徐王权, 秦侠, 江启成, 等. 突发急性职业中毒事件应急处置浅析[J]. 环境与职业医学, 2013, 30(9): 714-716. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LDYX201309020.htm [10] 周静, 张美辨. 我国突发中毒事件卫生应急处置体系和能力建设[J]. 职业卫生与应急救援, 2023, 41(1): 4-9. doi: 10.16369/j.oher.issn.1007-1326.2023.01.002 [11] 赵祥宇, 王兴旺, 王汉斌. 突发群体性化学中毒应急处置模式探讨[J]. 职业卫生与应急救援, 2016, 34(1): 70-71;75. doi: 10.16369/j.oher.issn.1007-1326.2016.01.024 [12] 李晶, 李颖, 彭晓易. 基于矩阵自乘的一种解释结构建模改进方法[J]. 系统科学与数学, 2021, 41(7): 2046-2062. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-STYS202107019.htm [13] 岳茂兴, 李奇林. 混合气体中毒卫生应急处置与临床救治专家共识(2016)[J]. 中华卫生应急电子杂志, 2016, 2(6): 325-332. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YJWS201606002.htm [14] 姜秀慧. 企业突发职业中毒事故应急物资准备研究[J]. 中国安全生产科学技术, 2010, 6(3): 225-227. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LDBK201003051.htm [15] 赵盛, 李凤, 孙迪, 等. 建设石化企业急性职业中毒应急药品储备系统构想[J]. 安全、健康和环境, 2014, 14(7): 28-29. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SAFE201407010.htm [16] 张小燕, 王斌斌. 公立医院突发公共卫生事件应急医疗队伍建设与管理探究[J]. 中国医药导报, 2022, 19(25): 146-149;157. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YYCY202225031.htm [17] 郭庆华, 李敏嫣, 黄德寅. 化工园区职业卫生应急管理现状及问题思考[J]. 职业卫生与应急救援, 2022, 40(3): 347-352. doi: 10.16369/j.oher.issn.1007-1326.2022.03.018 [18] 陈小霞, 苏首勋, 李举跃. 应急救援预案在一起职业中毒事故中的应用[J]. 中国城乡企业卫生, 2010, 25(2): 86. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZCXW201002054.htm






 下载:
下载: